bladder trauma.ppt
•Download as PPT, PDF•
4 likes•961 views
1) Bladder trauma can occur from blunt or penetrating injuries and result in extraperitoneal or intraperitoneal ruptures. The most common causes are road traffic accidents, falls, assaults, or surgical complications. 2) Blunt trauma is more likely to cause extraperitoneal ruptures, especially if associated with pelvic fractures. Intraperitoneal ruptures usually result from a direct blow to a distended bladder. 3) Clinical manifestations include gross hematuria, suprapubic pain, and difficulty voiding. CT scans and cystography are used for diagnosis. Most extraperitoneal ruptures can be managed with catheter drainage but intraperitoneal ruptures often require surgical repair.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Bladder Trauma.pptx

Bladder injuries may result from blunt,Penetrating and Iatrogenic trauma.
Full bladder is more susceptible to injury than empty bladder.
Management varies from conservative to surgical aiming to directly repair the injury.
Urinary bladder trauma.pptx

The document provides tips for using a PowerPoint presentation (PPT) for active learning sessions on medical topics. It recommends:
1) Freely editing, modifying, and adding your name to the PPT.
2) Noting that half the slides are blank except for the title to elicit student responses.
3) Showing blank slides, asking students what they know, and then showing the content slide.
4) Repeating this process of blank slide + student response + content slide at the end for reinforcement.
5) This active learning approach can be repeated over three sessions for effective learning.
Renal trauma

This document provides an overview of renal trauma, including epidemiology, modes of injury, classification systems, diagnostic evaluation, disease management, and complications. It discusses the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma renal injury grading scale and recommendations for initial patient evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging modalities like CT, US, and IVP. Treatment options include conservative management with observation, angioembolization for bleeding injuries, and surgical exploration for hemodynamic instability or high-grade injuries. The goal is to control hemorrhage while salvaging the kidney through reconstruction when possible.
Bladder injuries

Bladder injuries can occur from trauma or medical procedures and range from extraperitoneal to intraperitoneal. Extraperitoneal injuries make up 70% of cases and are often associated with pelvic fractures, while intraperitoneal injuries expose the bladder more directly. Clinical signs include hematuria, pelvic pain, and inability to catheterize. Diagnosis involves cystography to detect contrast leakage. Treatment depends on the severity and location of the injury, with uncomplicated extraperitoneal injuries often managed conservatively with catheter drainage and complicated or intraperitoneal injuries typically requiring surgical repair.
renal abscess by waheed

This document discusses renal abscesses, including defining it as a collection of pus around the kidney caused by infection. It lists the etiology as bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli, and risk factors as diabetes, pregnancy, elderly age, and autoimmune diseases. Symptoms include fever, chills, loin pain, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis involves blood tests showing elevated white blood cells and hemoglobin changes, urine tests, ultrasound identifying enlarged kidney size or abscess, and CT/MRI distinguishing intra-renal from extra-renal abscesses. Treatment consists of antibiotics administered orally or intravenously, percutaneous drainage of large abscesses, and nephrectomy in some cases
Urinary tract injury (kidney injury)

Please find the power point on Urinary Tract Injury (Kidney Injury). I tried to present it on understandable way and all the contents are reviewed by experts and from very reliable references. Thank you
Genitourinary trauma

This document discusses genitourinary trauma. It begins by outlining the most common locations of GU trauma, with the kidney being the most frequently injured organ at 67%. It then provides detailed classifications and imaging findings for injuries to the kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra and external genitalia. CT is highlighted as the preferred imaging modality for evaluating renal trauma due to its ability to accurately assess the entire abdomen. Imaging findings are described for each grade of renal injury on CT and management guidelines emphasize initial conservative treatment for most blunt trauma injuries.
Acute and chronic urinary retention

This document discusses urinary retention, including its types, causes, clinical features, investigations, management, and prognosis. Urinary retention is defined as the inability to void despite bladder distention. It can be acute, chronic, or acute-on-chronic. Common causes in males include benign prostatic hyperplasia and urethral stricture. Clinical features depend on whether retention is acute or chronic. Initial management involves relieving the obstruction through catheterization. Long-term management depends on identifying and treating the underlying cause. Complications can include bladder and kidney damage if not properly treated.
Recommended
Bladder Trauma.pptx

Bladder injuries may result from blunt,Penetrating and Iatrogenic trauma.
Full bladder is more susceptible to injury than empty bladder.
Management varies from conservative to surgical aiming to directly repair the injury.
Urinary bladder trauma.pptx

The document provides tips for using a PowerPoint presentation (PPT) for active learning sessions on medical topics. It recommends:
1) Freely editing, modifying, and adding your name to the PPT.
2) Noting that half the slides are blank except for the title to elicit student responses.
3) Showing blank slides, asking students what they know, and then showing the content slide.
4) Repeating this process of blank slide + student response + content slide at the end for reinforcement.
5) This active learning approach can be repeated over three sessions for effective learning.
Renal trauma

This document provides an overview of renal trauma, including epidemiology, modes of injury, classification systems, diagnostic evaluation, disease management, and complications. It discusses the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma renal injury grading scale and recommendations for initial patient evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging modalities like CT, US, and IVP. Treatment options include conservative management with observation, angioembolization for bleeding injuries, and surgical exploration for hemodynamic instability or high-grade injuries. The goal is to control hemorrhage while salvaging the kidney through reconstruction when possible.
Bladder injuries

Bladder injuries can occur from trauma or medical procedures and range from extraperitoneal to intraperitoneal. Extraperitoneal injuries make up 70% of cases and are often associated with pelvic fractures, while intraperitoneal injuries expose the bladder more directly. Clinical signs include hematuria, pelvic pain, and inability to catheterize. Diagnosis involves cystography to detect contrast leakage. Treatment depends on the severity and location of the injury, with uncomplicated extraperitoneal injuries often managed conservatively with catheter drainage and complicated or intraperitoneal injuries typically requiring surgical repair.
renal abscess by waheed

This document discusses renal abscesses, including defining it as a collection of pus around the kidney caused by infection. It lists the etiology as bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli, and risk factors as diabetes, pregnancy, elderly age, and autoimmune diseases. Symptoms include fever, chills, loin pain, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis involves blood tests showing elevated white blood cells and hemoglobin changes, urine tests, ultrasound identifying enlarged kidney size or abscess, and CT/MRI distinguishing intra-renal from extra-renal abscesses. Treatment consists of antibiotics administered orally or intravenously, percutaneous drainage of large abscesses, and nephrectomy in some cases
Urinary tract injury (kidney injury)

Please find the power point on Urinary Tract Injury (Kidney Injury). I tried to present it on understandable way and all the contents are reviewed by experts and from very reliable references. Thank you
Genitourinary trauma

This document discusses genitourinary trauma. It begins by outlining the most common locations of GU trauma, with the kidney being the most frequently injured organ at 67%. It then provides detailed classifications and imaging findings for injuries to the kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra and external genitalia. CT is highlighted as the preferred imaging modality for evaluating renal trauma due to its ability to accurately assess the entire abdomen. Imaging findings are described for each grade of renal injury on CT and management guidelines emphasize initial conservative treatment for most blunt trauma injuries.
Acute and chronic urinary retention

This document discusses urinary retention, including its types, causes, clinical features, investigations, management, and prognosis. Urinary retention is defined as the inability to void despite bladder distention. It can be acute, chronic, or acute-on-chronic. Common causes in males include benign prostatic hyperplasia and urethral stricture. Clinical features depend on whether retention is acute or chronic. Initial management involves relieving the obstruction through catheterization. Long-term management depends on identifying and treating the underlying cause. Complications can include bladder and kidney damage if not properly treated.
Urethral stricture

A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra caused by scarring that can develop from infections, injuries, or other trauma. Men are more susceptible to urethral strictures since their urethras are longer. Common causes include sexually transmitted diseases, catheterization, or other instrumentation of the urethra. Symptoms include a slow or weak urine stream, pain while urinating, and blood in the urine. Diagnosis involves imaging tests of the urethra. Treatment options depend on the severity and location of the stricture, and may include gradual stretching through dilation, cutting the scar tissue, or surgical reconstruction of the urethra.
Urethral trauma

This document discusses urethral trauma, including classification, etiology, clinical manifestations, investigations, and principles of management. It separates discussions of posterior and anterior urethral injuries. For posterior injuries, immediate suprapubic cystostomy is standard, while delayed reconstruction is typically done via open posterior urethroplasty after 3 months. Anterior injuries may be treated with catheter diversion or primary realignment, while anastomotic urethroplasty is preferred for obliterated bulbar urethras after several weeks.
Management of bladder injuries dr aroju

The document discusses the management of bladder injuries, outlining their causes, clinical presentation, investigations including cystography, complications, and treatment approaches which may involve nonsurgical management for minor injuries or surgical repair for more severe injuries involving the bladder wall or neck. Grading systems are used to classify injury severity to determine the appropriate treatment.
Hydronephrosis

Hydronephrosis is the dilatation of the renal pelvis and calyces caused by obstruction of urine flow from the kidney. It can be caused by congenital abnormalities, such as ureteral atresia, or acquired issues like kidney stones. On imaging, the kidney appears enlarged with a distended pelvis and thinning of the renal parenchyma. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of obstruction, ranging from nephrostomy or pyeloplasty for mild hydronephrosis to nephrectomy if the kidney is non-functioning.
Urethral & bladder injury

Urethral and bladder injuries can occur from pelvic fractures or direct trauma. Posterior urethral injuries commonly occur from shearing forces in pelvic fractures and require initial suprapubic cystostomy with delayed repair to avoid complications. Anterior urethral injuries from straddle injuries may be contusions or lacerations, treated with catheterization or cystostomy depending on severity. Bladder injuries are often extraperitoneal from pelvic fractures and present as hematuria, diagnosed by cystography or CT cystography and treated with catheter drainage. Intraperitoneal bladder injuries require surgery.
Retention of urine 

Retention of urine occurs when one is unable to completely empty the bladder. It can be acute, occurring suddenly due to obstruction, or chronic, developing over time. Acute retention requires immediate catheterization to drain the bladder, while chronic retention involves identifying and treating the underlying cause of the partial obstruction. A thorough history, exam, and testing is needed to determine if the retention is due to issues in the bladder, prostate, urethra, or other causes and select the appropriate management.
Renal trauma

Renal trauma can be caused by either penetrating or blunt injuries. Blunt trauma accounts for 90-95% of renal injuries and is often caused by motor vehicle accidents or falls. The American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) classification system grades renal injuries from 1 to 5 based on CT or surgical findings, with higher grades indicating more severe parenchymal lacerations or vascular injuries. Computed tomography (CT) with contrast is the gold standard for evaluating stable patients with renal trauma as it can detect lacerations, extravasation, and vascular injuries.
Peritonitis ppt by ameer

Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It can result from a rupture or perforation in the abdomen or from other medical conditions. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, fever, and nausea. Treatment involves antibiotics and may require surgery to address the underlying cause. The prognosis depends on the number of organ systems affected, with higher organ failure associated with higher mortality rates.
Retention of urine

Urinary retention is defined as the inability to completely or partially empty the bladder. It can be caused by obstructions in the urinary tract like kidney stones or enlarged prostate, or by problems with the nerves that control urination. Symptoms include difficulty starting or fully emptying urine, abdominal pressure, and incontinence. Treatment depends on the cause but may involve catheterization to drain the bladder or surgery to remove obstructions. Chronic retention is when incomplete obstruction leads to large residual urine volumes and overflow incontinence.
Ureteral stricture

This document discusses urethral strictures, which are characterized by a narrowing of the urethral lumen causing obstruction. Common causes include ureteropelvic junction obstruction, pelvic radiation therapy, urinary diversion surgery, traumatic injuries, congenital anomalies, kidney stones, cancers, and infections. Symptoms include blood in urine or semen, painful urination, and decreased urine flow. Diagnosis involves examinations, urinalysis, imaging tests. Treatment options include balloon dilation, endoureterotomy, ureteral stents, transureteroureterostomy, and ureteroneocystostomy.
Peritonitis

Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum that can be caused by infection or non-infectious processes. It is typically caused by a perforation or leak in the gastrointestinal tract that allows bacteria to enter the abdominal cavity. The document outlines the types, causes, signs and symptoms, diagnostic workup, and treatment including antibiotics, surgery, and postoperative care for managing peritonitis.
Acute urinary retention mgt

Acute urinary retention is a urologic emergency most common in older men due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Common causes include BPH, medications, infections, and neurological disorders. Patients present with inability to pass urine and lower abdominal discomfort. Evaluation involves history, physical exam including bladder palpation, and rectal exam. Management is bladder decompression initially with Foley catheter, or emergency suprapubic puncture if catheterization fails. Patients require monitoring after decompression to watch for post-obstructive diuresis.
Prostatitis

Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland that is caused by infectious agents like bacteria or other conditions. There are four main types: acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome where the cause is unclear, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Prostatitis causes symptoms like perineal pain and difficulty urinating and is most common in men under 50. Treatment involves antibiotics, alpha-blockers, pain medication, and sitz baths. Chronic forms are difficult to treat due to poor antibiotic diffusion into prostatic fluid.
Hydronephrosis

definition of hydronephrosis,
causes and types of hydronephrosis
pathophysiology of hydronephrosis
clinical manifestation and diagnostic test for hydronephrosis
management
Peritonitis

Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity. It can be caused by infection, trauma, or perforation of gastrointestinal organs. Symptoms include abdominal pain and swelling, fever, nausea, and difficulty passing gas or stool. Diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging exams. Treatment requires antibiotics, intravenous fluids, pain medication, and sometimes surgery to drain abscesses or repair damaged organs. Nursing care focuses on monitoring for complications like shock, managing pain, and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.
Intestinal obstruction, BOWEL OBSTRUCTION

Intestinal obstruction occurs when the intestine is blocked, preventing normal movement of its contents. It can be caused by mechanical blockages such as tumors or hernias, or functional issues like neuromuscular problems. Symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, distension and constipation. Treatment involves fluid resuscitation, antibiotics, pain management, and sometimes surgery to remove the obstruction. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment are important to prevent complications like perforation and sepsis.
Intestinal perforation

A brief review of intestinal perforation, presented by Dr. Sara Khalid Memon, from LUMHS, Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan
Urine Retention

here give the knowledge that you should possess to manage acute and chronic urine retention. the lecture is more concerned about practical patient care and ward setting management. you should minimally be aware about following facts regarding urine retention. the multiple causes of retention will be discussed later in detailed manner. Direction of the lecture seems more toward BPH and acute retention management. beware there are many aspects of a patient present with an AUR. do no harm and always try to keep patient satisfaction. Let me know about your comments an Ideas. try to improve the quality. good luck.
Urology Trauma

Renal trauma is the most common genitourinary injury, accounting for 84% of cases. The kidneys are vulnerable to blunt trauma from motor vehicle accidents or falls. Computed tomography is the gold standard for evaluation and allows grading of injuries from Grade 1 to 5 based on the extent of laceration or devitalized tissue. Most Grade 1-3 injuries can be managed conservatively with bed rest, but higher grades or hemodynamic instability may require surgical exploration or nephrectomy. Ureteric injuries are less common, usually from penetrating trauma or surgery, and often diagnosed during laparotomy for other injuries.
Renal trauma kidney injury

The document discusses renal trauma, providing details on:
1) The anatomy, embryology, and blood supply of the kidneys.
2) Classification of renal injuries from Grade I to V based on severity.
3) Evaluation of renal trauma patients including history, exam, laboratory tests, ultrasound, IVU, CT, and angiography.
4) Management approaches including non-operative for lower grades and exploration for higher grades or hemodynamic instability.
IMAGING OF URETHRAL INJURY

Urethral injuries most commonly result from trauma and can be classified using the Goldman classification system into 5 types based on location and severity. Common causes include blunt trauma, penetrating injuries, and iatrogenic events. Clinical presentation may include blood at the urethral meatus, inability to void, and pain. Radiographic evaluation using retrograde urethrography can identify features like extravasation of contrast indicating partial or complete disruption. Treatment involves urinary diversion or urethral anastomosis, and long-term complications may include stricture formation.
Dx & Mx of urethral and bladder injuries

This document discusses injuries to the bladder and urethra, providing details on diagnosis and management. It notes that bladder injuries occur in 1.6% of blunt trauma victims and are usually associated with pelvic fractures. Gross hematuria is present in most bladder injury cases. Urethral injuries in males are divided into those affecting the posterior urethra associated with pelvic fractures, and anterior injuries from blunt or penetrating trauma. Diagnosis is via retrograde cystography or urethrography. Most extraperitoneal bladder ruptures are now managed non-operatively with catheter drainage, while intraperitoneal ruptures require surgical repair. Urethral injuries may be treated with immediate surgical closure, catheter drainage
More Related Content
What's hot
Urethral stricture

A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra caused by scarring that can develop from infections, injuries, or other trauma. Men are more susceptible to urethral strictures since their urethras are longer. Common causes include sexually transmitted diseases, catheterization, or other instrumentation of the urethra. Symptoms include a slow or weak urine stream, pain while urinating, and blood in the urine. Diagnosis involves imaging tests of the urethra. Treatment options depend on the severity and location of the stricture, and may include gradual stretching through dilation, cutting the scar tissue, or surgical reconstruction of the urethra.
Urethral trauma

This document discusses urethral trauma, including classification, etiology, clinical manifestations, investigations, and principles of management. It separates discussions of posterior and anterior urethral injuries. For posterior injuries, immediate suprapubic cystostomy is standard, while delayed reconstruction is typically done via open posterior urethroplasty after 3 months. Anterior injuries may be treated with catheter diversion or primary realignment, while anastomotic urethroplasty is preferred for obliterated bulbar urethras after several weeks.
Management of bladder injuries dr aroju

The document discusses the management of bladder injuries, outlining their causes, clinical presentation, investigations including cystography, complications, and treatment approaches which may involve nonsurgical management for minor injuries or surgical repair for more severe injuries involving the bladder wall or neck. Grading systems are used to classify injury severity to determine the appropriate treatment.
Hydronephrosis

Hydronephrosis is the dilatation of the renal pelvis and calyces caused by obstruction of urine flow from the kidney. It can be caused by congenital abnormalities, such as ureteral atresia, or acquired issues like kidney stones. On imaging, the kidney appears enlarged with a distended pelvis and thinning of the renal parenchyma. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of obstruction, ranging from nephrostomy or pyeloplasty for mild hydronephrosis to nephrectomy if the kidney is non-functioning.
Urethral & bladder injury

Urethral and bladder injuries can occur from pelvic fractures or direct trauma. Posterior urethral injuries commonly occur from shearing forces in pelvic fractures and require initial suprapubic cystostomy with delayed repair to avoid complications. Anterior urethral injuries from straddle injuries may be contusions or lacerations, treated with catheterization or cystostomy depending on severity. Bladder injuries are often extraperitoneal from pelvic fractures and present as hematuria, diagnosed by cystography or CT cystography and treated with catheter drainage. Intraperitoneal bladder injuries require surgery.
Retention of urine 

Retention of urine occurs when one is unable to completely empty the bladder. It can be acute, occurring suddenly due to obstruction, or chronic, developing over time. Acute retention requires immediate catheterization to drain the bladder, while chronic retention involves identifying and treating the underlying cause of the partial obstruction. A thorough history, exam, and testing is needed to determine if the retention is due to issues in the bladder, prostate, urethra, or other causes and select the appropriate management.
Renal trauma

Renal trauma can be caused by either penetrating or blunt injuries. Blunt trauma accounts for 90-95% of renal injuries and is often caused by motor vehicle accidents or falls. The American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) classification system grades renal injuries from 1 to 5 based on CT or surgical findings, with higher grades indicating more severe parenchymal lacerations or vascular injuries. Computed tomography (CT) with contrast is the gold standard for evaluating stable patients with renal trauma as it can detect lacerations, extravasation, and vascular injuries.
Peritonitis ppt by ameer

Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It can result from a rupture or perforation in the abdomen or from other medical conditions. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, fever, and nausea. Treatment involves antibiotics and may require surgery to address the underlying cause. The prognosis depends on the number of organ systems affected, with higher organ failure associated with higher mortality rates.
Retention of urine

Urinary retention is defined as the inability to completely or partially empty the bladder. It can be caused by obstructions in the urinary tract like kidney stones or enlarged prostate, or by problems with the nerves that control urination. Symptoms include difficulty starting or fully emptying urine, abdominal pressure, and incontinence. Treatment depends on the cause but may involve catheterization to drain the bladder or surgery to remove obstructions. Chronic retention is when incomplete obstruction leads to large residual urine volumes and overflow incontinence.
Ureteral stricture

This document discusses urethral strictures, which are characterized by a narrowing of the urethral lumen causing obstruction. Common causes include ureteropelvic junction obstruction, pelvic radiation therapy, urinary diversion surgery, traumatic injuries, congenital anomalies, kidney stones, cancers, and infections. Symptoms include blood in urine or semen, painful urination, and decreased urine flow. Diagnosis involves examinations, urinalysis, imaging tests. Treatment options include balloon dilation, endoureterotomy, ureteral stents, transureteroureterostomy, and ureteroneocystostomy.
Peritonitis

Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum that can be caused by infection or non-infectious processes. It is typically caused by a perforation or leak in the gastrointestinal tract that allows bacteria to enter the abdominal cavity. The document outlines the types, causes, signs and symptoms, diagnostic workup, and treatment including antibiotics, surgery, and postoperative care for managing peritonitis.
Acute urinary retention mgt

Acute urinary retention is a urologic emergency most common in older men due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Common causes include BPH, medications, infections, and neurological disorders. Patients present with inability to pass urine and lower abdominal discomfort. Evaluation involves history, physical exam including bladder palpation, and rectal exam. Management is bladder decompression initially with Foley catheter, or emergency suprapubic puncture if catheterization fails. Patients require monitoring after decompression to watch for post-obstructive diuresis.
Prostatitis

Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland that is caused by infectious agents like bacteria or other conditions. There are four main types: acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome where the cause is unclear, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Prostatitis causes symptoms like perineal pain and difficulty urinating and is most common in men under 50. Treatment involves antibiotics, alpha-blockers, pain medication, and sitz baths. Chronic forms are difficult to treat due to poor antibiotic diffusion into prostatic fluid.
Hydronephrosis

definition of hydronephrosis,
causes and types of hydronephrosis
pathophysiology of hydronephrosis
clinical manifestation and diagnostic test for hydronephrosis
management
Peritonitis

Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity. It can be caused by infection, trauma, or perforation of gastrointestinal organs. Symptoms include abdominal pain and swelling, fever, nausea, and difficulty passing gas or stool. Diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging exams. Treatment requires antibiotics, intravenous fluids, pain medication, and sometimes surgery to drain abscesses or repair damaged organs. Nursing care focuses on monitoring for complications like shock, managing pain, and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.
Intestinal obstruction, BOWEL OBSTRUCTION

Intestinal obstruction occurs when the intestine is blocked, preventing normal movement of its contents. It can be caused by mechanical blockages such as tumors or hernias, or functional issues like neuromuscular problems. Symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, distension and constipation. Treatment involves fluid resuscitation, antibiotics, pain management, and sometimes surgery to remove the obstruction. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment are important to prevent complications like perforation and sepsis.
Intestinal perforation

A brief review of intestinal perforation, presented by Dr. Sara Khalid Memon, from LUMHS, Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan
Urine Retention

here give the knowledge that you should possess to manage acute and chronic urine retention. the lecture is more concerned about practical patient care and ward setting management. you should minimally be aware about following facts regarding urine retention. the multiple causes of retention will be discussed later in detailed manner. Direction of the lecture seems more toward BPH and acute retention management. beware there are many aspects of a patient present with an AUR. do no harm and always try to keep patient satisfaction. Let me know about your comments an Ideas. try to improve the quality. good luck.
Urology Trauma

Renal trauma is the most common genitourinary injury, accounting for 84% of cases. The kidneys are vulnerable to blunt trauma from motor vehicle accidents or falls. Computed tomography is the gold standard for evaluation and allows grading of injuries from Grade 1 to 5 based on the extent of laceration or devitalized tissue. Most Grade 1-3 injuries can be managed conservatively with bed rest, but higher grades or hemodynamic instability may require surgical exploration or nephrectomy. Ureteric injuries are less common, usually from penetrating trauma or surgery, and often diagnosed during laparotomy for other injuries.
Renal trauma kidney injury

The document discusses renal trauma, providing details on:
1) The anatomy, embryology, and blood supply of the kidneys.
2) Classification of renal injuries from Grade I to V based on severity.
3) Evaluation of renal trauma patients including history, exam, laboratory tests, ultrasound, IVU, CT, and angiography.
4) Management approaches including non-operative for lower grades and exploration for higher grades or hemodynamic instability.
What's hot (20)
Similar to bladder trauma.ppt
IMAGING OF URETHRAL INJURY

Urethral injuries most commonly result from trauma and can be classified using the Goldman classification system into 5 types based on location and severity. Common causes include blunt trauma, penetrating injuries, and iatrogenic events. Clinical presentation may include blood at the urethral meatus, inability to void, and pain. Radiographic evaluation using retrograde urethrography can identify features like extravasation of contrast indicating partial or complete disruption. Treatment involves urinary diversion or urethral anastomosis, and long-term complications may include stricture formation.
Dx & Mx of urethral and bladder injuries

This document discusses injuries to the bladder and urethra, providing details on diagnosis and management. It notes that bladder injuries occur in 1.6% of blunt trauma victims and are usually associated with pelvic fractures. Gross hematuria is present in most bladder injury cases. Urethral injuries in males are divided into those affecting the posterior urethra associated with pelvic fractures, and anterior injuries from blunt or penetrating trauma. Diagnosis is via retrograde cystography or urethrography. Most extraperitoneal bladder ruptures are now managed non-operatively with catheter drainage, while intraperitoneal ruptures require surgical repair. Urethral injuries may be treated with immediate surgical closure, catheter drainage
Radiology Rounds 29 Year Old S

A 29 year old patient presented with fluid in the abdomen after a fall. A cystogram was performed to better define a possible bladder injury and showed intraperitoneal contrast from the cystogram, indicating a bladder rupture where urine had leaked into the abdominal cavity. The dome of the bladder is the least supported area and often the location of intraperitoneal bladder ruptures from a sudden increase in pressure in a full bladder.
Abdominal injury a forensic view

1) Abdominal trauma is the third most common type of trauma after head and chest injuries, with 25% of major trauma victims requiring abdominal exploration. Blunt trauma accounts for 75% of abdominal injuries, most often from road traffic accidents.
2) The spleen, liver, and small bowel are the organs most commonly injured in abdominal trauma. Solid organs like the liver and spleen are vulnerable to tearing at sites of ligament attachment from rapid deceleration.
3) Outcomes of abdominal trauma depend on the mechanism of injury. Blunt trauma can cause bruising, bleeding, organ rupture, and delayed complications. Penetrating injuries directly damage organs in the path of the object. Assessment of injury severity is crucial for
Abdominal trauma

This document discusses types of abdominal trauma, including penetrating and blunt trauma. It provides details on management of penetrating abdominal trauma, risk factors and commonly injured organs for different types of penetrating injuries. For blunt abdominal trauma, risk factors like MVCs and seatbelt injuries are outlined. The spleen and liver are most commonly injured in blunt trauma. Diagnostic strategies like physical exam, labs, radiology imaging and bedside procedures are summarized. Injuries in pediatric patients from blunt trauma are also addressed.
LECTURE NOTE ON URETHRAL STRICTURES AND STENOSIS.pdf

Urethral strictures are usually acquired due to trauma, inflammation, or medical instrumentation. The most common causes are trauma, iatrogenic factors, and inflammation. Strictures occur most often in the bulbar urethra and can be treated with internal urethrotomy or open repair techniques like resection and reanastomosis or graft urethroplasty. Endoscopic treatments have a low success rate so open repair is often recommended for recurrent strictures.
Injuries to bowel and mesentery. Lecture pptx

The document discusses traumatic injuries to the bowel and mesentery from blunt abdominal trauma. It notes that the bowel and mesentery are commonly injured structures after the liver and spleen. Delayed diagnosis of 8 hours or more of bowel and mesenteric injuries can result in severe complications like bleeding, peritonitis, and sepsis. CT scans are important for diagnosis as they can identify signs of intestinal perforation, bleeding, or vascular injuries that require immediate surgery. The most common sites of bowel injury are the small bowel, particularly the proximal jejunum and distal ileum. Colon injuries from blunt trauma are less common.
Urinary Bladder Injuries by Sayed Eleweedy

The bladder is vulnerable to injury in children due to its abdominal location. Blunt trauma from motor vehicle accidents or pelvic fractures can cause intraperitoneal or extraperitoneal ruptures. Intraperitoneal ruptures appear on cystogram as contrast in the abdomen, while extraperitoneal ruptures show leakage outside the bladder. Penetrating injuries require exploration to inspect for damage. Most bladder injuries require catheter drainage for 10 days. Intraperitoneal ruptures need surgical repair. Delayed diagnosis allows infection and complications.
Complications of TAPP

This document discusses potential complications of laparoscopic hernia repair surgery. It describes per-operative complications such as hemorrhage, nerve injuries, and visceral injuries. Early post-operative complications include pain, urinary retention, swelling, and infections. Late complications include chronic pain, mesh migration, port-site hernias, and recurrence. The document provides details on potential causes and approaches to prevention or management of several common complications.
Common urological emergencies 

This PPT is mainly for MBBS as well as Interns. They can easily differentiate Traumatic & Non-traumatic Injuries of Urogenital system in casualty.
Injuries to kidney

Kidneys are injured more often than any of the organs along the urinary tract from external trauma. If serious blunt or penetrating kidney injuries are not treated, complications, such as kidney failure or kidney loss, delayed bleeding, infection, and high blood pressure may result.
Management of urinary bladder injuries

Bladder injuries are rare. But when present in cases of polytrauma they pose both a diagnostic as well as surgical challenge to the attending surgeon. Understanding the mechanisms underlying bladder injuries is pivotal in developing a diagnostic algorithm in order to avoid missing of any urologic injury. Once the extent and site of damage is diagnosed then prompt surgical intervention is the mainstay of treatment. The pathophysiology and management of bladder injuries is discussed in this paper.
Bladder trauma ff.pptx

1. Bladder injuries can result from blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, or iatrogenic causes, and are more likely if the bladder is full. Management ranges from conservative treatment to surgical repair depending on the severity of injury.
2. Evaluation of suspected bladder trauma involves cystography, cystoscopy, and ultrasound to identify leaks or extravasation. Surgical repair is usually needed for penetrating injuries or injuries inside the abdominal cavity.
3. Conservative management involves catheter drainage, antibiotics, and monitoring for healing without repair. Surgical repair is done by closing mucosa and muscle layers. Complications can include infection, leaks, or fistulas if not properly treated.
Certain Gastrointestinal Disorders Can Be Life Threatening And Require Emerge...

Certain gastrointestinal disorders like abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, and abdominal abscesses can require emergency surgery. Doctors must quickly determine if surgery is needed to identify and treat the underlying problem. Abdominal abscesses in particular cause pain and other symptoms depending on their location, and are usually diagnosed using imaging tests before being treated by draining pus and antibiotics. Abdominal hernias, which cause bulging but little pain, are also common and usually repaired through elective surgery to prevent potential incarceration or strangulation of intestine tissue.
Certain Gastrointestinal Disorders Can Be Life Threatening And Require Emerge...

Certain gastrointestinal disorders like abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, and abdominal abscesses can require emergency surgery. Doctors must quickly determine if surgery is needed to identify and treat the underlying problem. Abdominal abscesses in particular cause pain and other symptoms depending on their location, and are usually diagnosed using imaging tests before being treated by draining pus and antibiotics. Abdominal hernias, which cause bulging but little pain, are also common and usually repaired through elective surgery to prevent potential incarceration or strangulation of intestine tissue.
Lower urinary tract trauma

This document discusses lower urinary tract trauma, specifically bladder and urethral trauma. It classifies bladder trauma as either intrapritoneal or extraperitoneal, and caused by either non-iatrogenic or iatrogenic means. Common signs and symptoms of bladder trauma include visible hematuria and suprapubic pain. Diagnostic tests include cystography and cystoscopy. Treatment depends on the type and severity of injury, but may involve conservative management, surgical repair, or a combination of both. Urethral trauma is also discussed, separating anterior male urethral injuries from posterior male and female urethral injuries.
urology trauma english.pptx

The document describes injury scales for the kidney and outlines the diagnostic evaluation and management of various genitourinary traumas, including kidney injuries, ureteral trauma, bladder trauma, urethral trauma, and penile fracture. It provides grading scales for kidney injuries and outlines recommended diagnostic imaging tests and surgical or conservative treatment approaches for different types and severities of genitourinary injuries.
Ureteric injuries in gynecological surgeries

Urinary tract injury during female pelvic surgery occurs in 0.3-1% of procedures but can be as high as 2.4%. Risk factors include prior pelvic surgery, endometriosis, and pelvic masses. The ureters pass through the pelvis and can be injured at various points, most commonly when ligating the ovarian or uterine vessels. Identifying and isolating the ureters and bladder during surgery is important to prevent injury from other surgical maneuvers.
ABDOMINAL TRAUMA.pptx

Abdominal trauma can result from blunt force, stab wounds, or penetrating injuries. Diagnosis is challenging as the patient may be unconscious, and other injuries can distract from abdominal issues. Investigations include ultrasound, CT scan, diagnostic peritoneal lavage. Laparotomy is often needed for significant injuries such as liver laceration or small bowel perforation. Management depends on injury type and severity but may involve organ resection, suturing, or drainage. Complications can be serious if not addressed promptly.
Similar to bladder trauma.ppt (20)
LECTURE NOTE ON URETHRAL STRICTURES AND STENOSIS.pdf

LECTURE NOTE ON URETHRAL STRICTURES AND STENOSIS.pdf
Certain Gastrointestinal Disorders Can Be Life Threatening And Require Emerge...

Certain Gastrointestinal Disorders Can Be Life Threatening And Require Emerge...
Certain Gastrointestinal Disorders Can Be Life Threatening And Require Emerge...

Certain Gastrointestinal Disorders Can Be Life Threatening And Require Emerge...
More from harpreet363708
1OVER VIEW OF NSG. MANAG.1.pptx vital..

This document provides an overview of nursing management and administration. It discusses the increasing role and need for nursing services as health services expand. The role of professional nurses now includes direct care, supervision of other caregivers, and administrative skills. Nursing management integrates business principles with nursing science to manage healthcare organizations. Key administrative functions discussed include planning, organizing, staffing, directing, controlling, and budgeting. Principles of administration like division of work and unity of command are also summarized. The document outlines the purposes and types of planning in healthcare administration.
DrHarrison-GALLSTONE-DISEASE-Presentation-06-2016-2.pptx

This document discusses gallstone disease and provides definitions and details regarding epidemiology, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. It covers conditions such as cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, choledocholithiasis, and gallstone pancreatitis. Complications are outlined including acute cholecystitis, acute cholangitis, and gallstone pancreatitis. Diagnostic tools such as ultrasound and MRCP are mentioned. Management depends on the condition but may involve antibiotics, drainage procedures, ERCP, or cholecystectomy.
simran buttar.pptx

Five nursing students presented research on assessing the knowledge of first-year BSC nursing students at Adesh College of Nursing in Sri Muktsar Sahib, Punjab regarding bio-medical waste management. The objectives were to assess the students' knowledge of bio-medical waste management and determine if socio-demographic variables were associated with students' knowledge levels.
Introduction to Microbiology 081210 FV.ppt

This document provides an overview of microbiology and the classification of microorganisms. It discusses the early history of microbiology including the development of germ theory and experiments by scientists like Redi, Pasteur, and Koch. Microbes are classified into six categories: fungi, protozoa, algae, bacteria, archaea, and small animals. Bacteria and archaea are further described. The document also discusses topics like biochemistry, genetics, emerging diseases, antibiotic resistance, and the future of microbiology.
Maternal-infections-overview.pdf

Maternal infections can negatively impact both mother and baby's health. Common infections include syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and group B streptococcus. Infections may cause issues like preterm birth, low birthweight, stillbirth, or congenital diseases in the baby. Screening and treatment programs aim to identify infections early to provide appropriate care and reduce risks. Prevention through education and behavior modification can also lower infection rates.
GASTIC DISORDERS.pptx

This document provides information on nursing care for patients with gastro-intestinal problems. It discusses assessment of gastro-intestinal issues including history taking, physical exam, and lab tests. Diagnostic studies like radiologic exams, endoscopy, and tests of gastric secretions are outlined. Common GI conditions like peptic ulcer disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, and intestinal obstruction are described along with their causes, signs/symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment/nursing care.
429512901-Unit-I-Nursing-History-ppt.ppt

The document provides a historical overview of nursing from ancient civilizations to modern times. It discusses how nursing evolved from early caretaking roles to a more formal profession. Key developments include Florence Nightingale establishing the first nursing school in 1860, the establishment of nursing programs in Pakistan in the 1940s-50s, and the Pakistan Nursing Council Act in 1952 that standardized nursing education. The document also outlines the historical periods, influential figures, and changing social factors that have shaped the field of nursing over time.
Acute Renal Failure 2.ppt

Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as a rapid loss of kidney function over hours to days. It occurs when the kidneys are unable to excrete daily toxins due to damage. To properly diagnose ARF, a thorough history, physical exam, and lab tests are required to determine the cause (pre-renal, intrinsic, post-renal) and severity. Treatment involves fluid resuscitation, electrolyte management, treating the underlying cause, and potentially renal replacement therapies like dialysis. The goal of treatment is to reverse ARF and restore kidney function if possible.
final renal seminar.pptx

The document discusses pyelonephritis, which is an inflammation of the renal pelvis and parenchyma caused by a bacterial infection. It can be caused by an ascending or hematogenous infection. Symptoms include flank pain, fever, vomiting and frequent urination. Diagnosis involves urine culture and sensitivity as well as imaging tests. Treatment aims to eliminate pathogenic organisms with antibiotics based on culture results and remove any contributing factors to decreased resistance. Mild cases may only require a short course of oral antibiotics while severe cases involving abscesses may require IV antibiotics or even drainage of abscesses.
Introduction on Hepatitis.pptx

The document summarizes the history and discovery of various hepatitis viruses including Hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. It discusses how Hepatitis B virus was discovered in 1967 and its vaccine developed in 1969. It also outlines the discovery of other hepatitis viruses between 1973-1983. The document then discusses WHO's global strategy to eliminate viral hepatitis by 2030 and its World Hepatitis Day. It provides information on the main hepatitis viruses and regional targets set by WHO Western Pacific region. Finally, it discusses Punjab government's focus on treating Hepatitis C patients but notes Hepatitis B must also be included.
liver anatomy.ppt

The liver is the largest gland in the body, located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen under the diaphragm. It has 4 lobes and produces bile which aids in fat digestion. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver. The liver performs many critical metabolic functions including synthesizing proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and coagulation factors. It also breaks down toxins, hormones, and hemoglobin. The liver regulates blood sugar levels through gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis.
final renal seminar.pptx

The document discusses the urinary system and renal disorders. It provides information on the structure and function of the kidneys, nephrons, and other components of the urinary system. It also covers different types of renal disorders like urinary incontinence, including stress, urge, overflow, and reflex incontinence. Causes, symptoms, diagnostic tests, and management of urinary incontinence are described. Both non-surgical and surgical treatment options are mentioned.
More from harpreet363708 (12)
DrHarrison-GALLSTONE-DISEASE-Presentation-06-2016-2.pptx

DrHarrison-GALLSTONE-DISEASE-Presentation-06-2016-2.pptx
Recently uploaded
Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...

Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
This presentation was provided by Steph Pollock of The American Psychological Association’s Journals Program, and Damita Snow, of The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), for the initial session of NISO's 2024 Training Series "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape." Session One: 'Setting Expectations: a DEIA Primer,' was held June 6, 2024.What is the purpose of studying mathematics.pptx

Students often ask about what the purpose is for their learning. This PowerPoint highlights some really important reasons to study Mathematics.
Top five deadliest dog breeds in America

Thinking of getting a dog? Be aware that breeds like Pit Bulls, Rottweilers, and German Shepherds can be loyal and dangerous. Proper training and socialization are crucial to preventing aggressive behaviors. Ensure safety by understanding their needs and always supervising interactions. Stay safe, and enjoy your furry friends!
Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx![Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
This is part 2 of my Java Learning Journey. This contains Hashing, ArrayList, LinkedList, Date and Time Classes, Calendar Class and more.
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS Template 2023-2024 by: Irene S. Rueco
Advantages and Disadvantages of CMS from an SEO Perspective

Advantages and Disadvantages of CMS from an SEO Perspective
A Survey of Techniques for Maximizing LLM Performance.pptx

A Survey of Techniques for Maximizing LLM Performance
June 3, 2024 Anti-Semitism Letter Sent to MIT President Kornbluth and MIT Cor...

Letter from the Congress of the United States regarding Anti-Semitism sent June 3rd to MIT President Sally Kornbluth, MIT Corp Chair, Mark Gorenberg
Dear Dr. Kornbluth and Mr. Gorenberg,
The US House of Representatives is deeply concerned by ongoing and pervasive acts of antisemitic
harassment and intimidation at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Failing to act decisively to ensure a safe learning environment for all students would be a grave dereliction of your responsibilities as President of MIT and Chair of the MIT Corporation.
This Congress will not stand idly by and allow an environment hostile to Jewish students to persist. The House believes that your institution is in violation of Title VI of the Civil Rights Act, and the inability or
unwillingness to rectify this violation through action requires accountability.
Postsecondary education is a unique opportunity for students to learn and have their ideas and beliefs challenged. However, universities receiving hundreds of millions of federal funds annually have denied
students that opportunity and have been hijacked to become venues for the promotion of terrorism, antisemitic harassment and intimidation, unlawful encampments, and in some cases, assaults and riots.
The House of Representatives will not countenance the use of federal funds to indoctrinate students into hateful, antisemitic, anti-American supporters of terrorism. Investigations into campus antisemitism by the Committee on Education and the Workforce and the Committee on Ways and Means have been expanded into a Congress-wide probe across all relevant jurisdictions to address this national crisis. The undersigned Committees will conduct oversight into the use of federal funds at MIT and its learning environment under authorities granted to each Committee.
• The Committee on Education and the Workforce has been investigating your institution since December 7, 2023. The Committee has broad jurisdiction over postsecondary education, including its compliance with Title VI of the Civil Rights Act, campus safety concerns over disruptions to the learning environment, and the awarding of federal student aid under the Higher Education Act.
• The Committee on Oversight and Accountability is investigating the sources of funding and other support flowing to groups espousing pro-Hamas propaganda and engaged in antisemitic harassment and intimidation of students. The Committee on Oversight and Accountability is the principal oversight committee of the US House of Representatives and has broad authority to investigate “any matter” at “any time” under House Rule X.
• The Committee on Ways and Means has been investigating several universities since November 15, 2023, when the Committee held a hearing entitled From Ivory Towers to Dark Corners: Investigating the Nexus Between Antisemitism, Tax-Exempt Universities, and Terror Financing. The Committee followed the hearing with letters to those institutions on January 10, 202
PCOS corelations and management through Ayurveda.

This presentation includes basic of PCOS their pathology and treatment and also Ayurveda correlation of PCOS and Ayurvedic line of treatment mentioned in classics.
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশের অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা ২০২৪ [Bangladesh Economic Review 2024 Bangla.pdf] কম্পিউটার , ট্যাব ও স্মার্ট ফোন ভার্সন সহ সম্পূর্ণ বাংলা ই-বুক বা pdf বই " সুচিপত্র ...বুকমার্ক মেনু 🔖 ও হাইপার লিংক মেনু 📝👆 যুক্ত ..
আমাদের সবার জন্য খুব খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ একটি বই ..বিসিএস, ব্যাংক, ইউনিভার্সিটি ভর্তি ও যে কোন প্রতিযোগিতা মূলক পরীক্ষার জন্য এর খুব ইম্পরট্যান্ট একটি বিষয় ...তাছাড়া বাংলাদেশের সাম্প্রতিক যে কোন ডাটা বা তথ্য এই বইতে পাবেন ...
তাই একজন নাগরিক হিসাবে এই তথ্য গুলো আপনার জানা প্রয়োজন ...।
বিসিএস ও ব্যাংক এর লিখিত পরীক্ষা ...+এছাড়া মাধ্যমিক ও উচ্চমাধ্যমিকের স্টুডেন্টদের জন্য অনেক কাজে আসবে ...
Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective Upskilling

Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective UpskillingExcellence Foundation for South Sudan
Strategies for Effective Upskilling is a presentation by Chinwendu Peace in a Your Skill Boost Masterclass organisation by the Excellence Foundation for South Sudan on 08th and 09th June 2024 from 1 PM to 3 PM on each day.clinical examination of hip joint (1).pdf

described clinical examination all orthopeadic conditions .
How to Manage Your Lost Opportunities in Odoo 17 CRM

Odoo 17 CRM allows us to track why we lose sales opportunities with "Lost Reasons." This helps analyze our sales process and identify areas for improvement. Here's how to configure lost reasons in Odoo 17 CRM
Recently uploaded (20)
Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...

Pollock and Snow "DEIA in the Scholarly Landscape, Session One: Setting Expec...
Digital Artefact 1 - Tiny Home Environmental Design

Digital Artefact 1 - Tiny Home Environmental Design
Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf

Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3
Advantages and Disadvantages of CMS from an SEO Perspective

Advantages and Disadvantages of CMS from an SEO Perspective
Film vocab for eal 3 students: Australia the movie

Film vocab for eal 3 students: Australia the movie
A Survey of Techniques for Maximizing LLM Performance.pptx

A Survey of Techniques for Maximizing LLM Performance.pptx
June 3, 2024 Anti-Semitism Letter Sent to MIT President Kornbluth and MIT Cor...

June 3, 2024 Anti-Semitism Letter Sent to MIT President Kornbluth and MIT Cor...
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf
Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective Upskilling

Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective Upskilling
How to Manage Your Lost Opportunities in Odoo 17 CRM

How to Manage Your Lost Opportunities in Odoo 17 CRM
Pride Month Slides 2024 David Douglas School District

Pride Month Slides 2024 David Douglas School District
bladder trauma.ppt
- 2. INTRODUCTION The urinary bladder occupies the deep pelvic cavity and is well protected. Because the bladder is located within the bony structures of the pelvis, it is protected from most external forces. This is the reason it is rarely traumatized. However it can suffer traumas which can cause extraperitoneal and intraperitoneal ruptures
- 3. DEFINITION It is the injury to the urinary bladder caused by either blunt or penetrating accidents. The probability of bladder injury varies according to the degree of bladder distention; therefore, a full bladder is more likely to become injured than an empty one.
- 4. INCIDENCE 60 - 85% - Blunt injuries 15 - 40% - Penetrating injury 10 - 29% - Pelvic fractures 0.3% - Caesarean section 30% - Bladder biopsy
- 5. ETIOLOGY Penetrating and blunt trauma (main causes of bladder injury) during accidents. Iatrogenic causes include surgical misadventures from gynecologic, urologic, and orthopedic operations near the urinary bladder. Spontaneous or idiopathic bladder injuries without an obvious underlying pathology constitute the remainder.
- 6. Contd… Other causes include: Surgeries of the pelvis or groin (including hernia repair and abdominal hysterectomy) Tears, cuts, bruises, and other injuries to the urethra (most common in men) Straddle injuries (direct force accidents that injure the scrotum area between a man's legs) Deceleration injury (for example, a motor vehicle accident that occurs with a full bladder while wearing seatbelt)
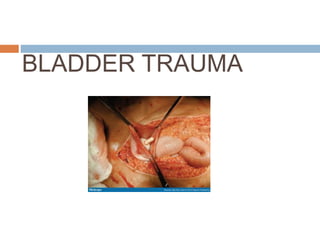
- 7. TYPES OF BLADDER TRAUMA
- 8. Blunt trauma ◦ The most common mechanisms of blunt trauma are road traffic accidents (87%), falls (7%), and assaults (6%). Deceleration injuries usually produce both bladder trauma (perforation) and pelvic fractures. ◦ Approximately 10% of patients with pelvic fractures also have significant bladder injuries.
- 9. Contd… ◦ The likelihood of the bladder to sustain injury is related to its degree of distention at the time of trauma. ◦ Injury may occur if there is a blow to the pelvis that is severe enough to break the bones and cause bone fragments to penetrate the bladder wall. ◦ Generally the bladder injury in these cases is associated with other injuries as well, the commonest being to the spleen and rectum.
- 10. Penetrating trauma The most common cause of penetrating trauma is gunshot wounds (85%), followed by stabbings (15%). It is also associated with abdominal and/or pelvic organ injuries. Combined penetrating trauma of the rectum and urinary bladder is rare. The combination of penetrating trauma to both rectum and the urinary system is associated with high morbidity and mortality.
- 11. Obstetric trauma During prolonged labor or a difficult forceps delivery, persistent pressure from the fetal head against the mother's pubis can lead to bladder necrosis. Direct laceration of the urinary bladder is reported in 0.3% of women undergoing a Caesarean delivery. Previous Caesarean deliveries, and the adhesions that can remain subsequently, are a risk factor.
- 12. Gynecological trauma Bladder injury may occur during a vaginal or abdominal hysterectomy. Blind dissection in the incorrect tissue plane between the base of the bladder and the cervical fascia results in bladder injury.
- 13. Urologic trauma Perforation of the bladder during a bladder biopsy, cystolitholapaxy, transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), or transurethral resection of a bladder tumor (TURBT) is common. Incidence of bladder perforation is reportedly as high as 36% following bladder biopsy.
- 14. Orthopedic trauma Orthopedic pins and screws can commonly perforate the urinary bladder, particularly during internal fixation of pelvic fractures. Thermal injuries to the bladder wall may occur during the setting of cement substances used to seat arthroplasty prosthetics.
- 15. Idiopathic bladder trauma Alcoholics and those individuals who chronically drink large quantities of fluids are susceptible to this type of injury (bladder over distension ) Person who holds urine for long time during over distension.
- 16. Classification Type I injuries are partial tears of the mucosa. This is the most common injury pattern of multisystem trauma patients and is associated with blunt trauma. Type II or intraperitoneal bladder ruptures. This is usually the result of a direct blow to the distended organ.
- 17. Contd… Type III or interstitial pattern. This is an intramural or partial-thickness laceration of the intact serosa. CT cystography is used to diagnose this. Intramural contrast is shown within the bladder wall. This condition is usually the result of blunt trauma. Type IV bladder injury is extraperitoneal. It is the most common bladder rupture. It is subdivided into simple and complex injuries.
- 18. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Extraperitoneal bladder ruptures • Traumatic extraperitoneal ruptures are usually associated with pelvic fractures (89%-100%). The bladder rupture is most often due to a direct burst injury or the shearing force of the deforming pelvic ring. • These ruptures are usually associated with fractures of the anterior pubic arch, and they may occur from a direct laceration of the bladder by the bony fragments of the osseous pelvis.
- 19. Contd… • The anterolateral aspect of the bladder is typically perforated by bony spicules. Forceful disruption of the bony pelvis tear the wall of the bladder. • The degree of bladder injury is directly related to the severity of the fracture. • The classic cystographic finding is contrast extravasation around the base of the bladder confined to the perivesical space
- 21. Contd… • With a more complex injury, the contrast material extends to the thigh, penis, perineum, or into the anterior abdominal wall. • The bladder may assume a teardrop shape from compression by a pelvic hematoma.
- 22. Intraperitoneal injury Classic intraperitoneal bladder ruptures are described as large horizontal tears in the dome of the bladder. The dome is the least supported area and the only portion of the adult bladder covered by peritoneum. The mechanism of injury is a sudden large increase in intravesical pressure in a full bladder.
- 23. Contd… When full, the bladder's muscle fibers are widely separated and the entire bladder wall is relatively thin, offering relatively little resistance to perforation from sudden large changes in intra vesical pressure. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture occurs as the result of a direct blow to a distended urinary bladder.
- 24. Contd… This type of injury is common among patients diagnosed with alcoholism or those sustaining a seatbelt or steering wheel injury. Since urine may continue to drain into the abdomen, intraperitoneal ruptures may go undiagnosed from days to weeks.
- 25. Contd… Electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyperkalemia , hypernatremia, uremia, acidosis) may occur as urine is reabsorbed from the peritoneal cavity. Such patients may appear anuric, and the diagnosis is established when urinary ascites are recovered during paracentesis.
- 26. Contd… Intraperitoneal ruptures demonstrate contrast extravasation into the peritoneal cavity, often outlining loops of bowel and pooling under the diaphragm. An intraperitoneal rupture is more common in children because of the relative intra- abdominal position of the bladder. The bladder usually descends into the pelvis by age 20 years.
- 28. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Clinical signs of bladder injury are relatively nonspecific; however, a triad of symptoms are often present: GROSS HEMATURIA SUPRAPUBIC PAIN OR TENDERNESS DIFFICULTY OR INABILITY TO VOID
- 29. Contd… Hematuria invariably accompanies all bladder injuries. Gross hematuria is the hallmark of a bladder rupture. More than 98% of bladder ruptures are associated with gross hematuria, and 10% are associated with microscopic hematuria.
- 30. Contd… An abdominal examination may reveal distention, guarding, or rebound tenderness. Absent bowel sounds and signs of peritoneal irritation indicate a possible intraperitoneal bladder rupture. A rectal examination should be performed to exclude rectal injury.
- 31. Contd… Shock or hemorrhage (the symptoms include) Increased heart rate Pale skin Sweating Skin cool to touch Drowsiness Lethargy Decreased alertness Coma
- 32. Diagnostic tests History of trauma Gross hematuria Suprapubic pain Difficulty to void Abdominal tenderness Foley’s catheter CT scanning Cystography
- 33. CT scan It is often the first test performed in patients with blunt abdominal trauma. The CT scan of the pelvis provides information on the status of the pelvic organs and bony pelvis . It most sensitive test for bladder perforation
- 34. MANAGEMENT The European Association of Urology (EAU) developed guidelines for the appropriate management of genito-urinary trauma. In suspected renal injuries the hemodynamic situation of the patient is the benchmark for the diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm.
- 35. Contd… Most extraperitoneal ruptures can be managed safely with simple catheter drainage (ie, urethral or Suprapubic). Leave the catheter in for 7-10 days and then obtain a cystogram. All extraperitoneal bladder injuries heal within 3 weeks
- 36. Surgical Management Intraperitoneal bladder rupture Most require surgical exploration, as they do not heal with catheterization alone. Urine continues to leak into the abdominal cavity, resulting in urinary ascites, abdominal distention, and electrolyte disturbances. All wounds should be explored and should be surgically repaired.
- 37. Contd… Extraperitoneal extravasation Bladders with extensive extraperitoneal extravasation are often repaired surgically. Early surgical intervention in these cases decreases the length of hospitalization and potential complications. It also promotes early recovery.
- 38. Complications Hemorrhage Pelvic infection Peritonitis Urge incontinence Urinary extravasation Wound dehiscence Obstructive uropathy
- 39. Follow-up The patient should return in 7-10 days for staple removal and wound check. The X-ray cystogram should be done 10-14 days after surgery. If the cystogram finding is normal, the urethral catheter can be removed. Advise the patient that they may return to normal activity 4-6 weeks after surgery.
- 40. Nursing Management Nursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis
- 41. Nursing Diagnosis 1) Hypovolemia related to gross hemorrhage. 2) High risk for infection related to extravasation of urine and open wounds. 3) Acute pain related to injury of the bladder. 4) Fluid and electrolyte imbalance related to hemorrhage. 5) Anemia related to gross hematuria.