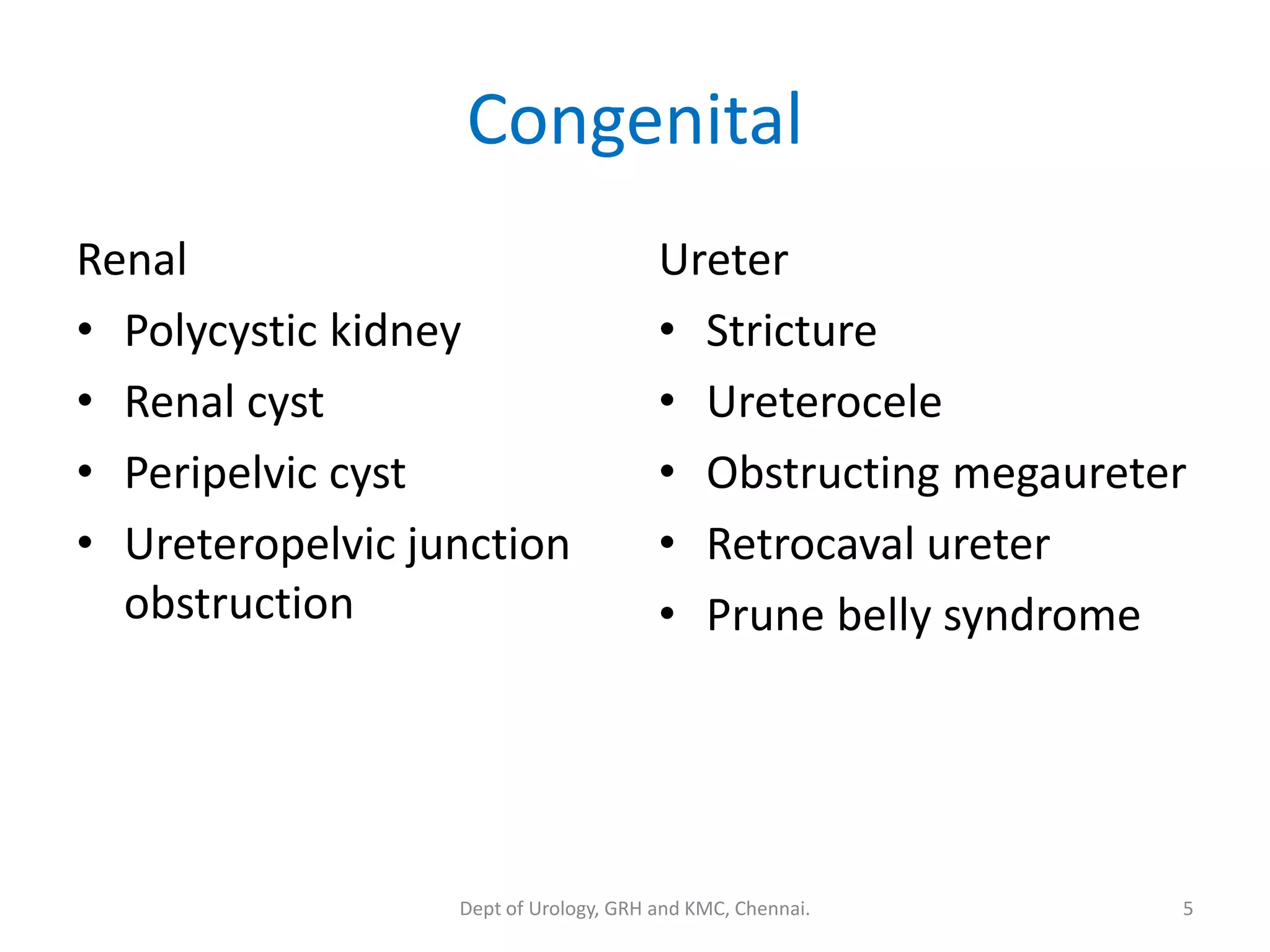
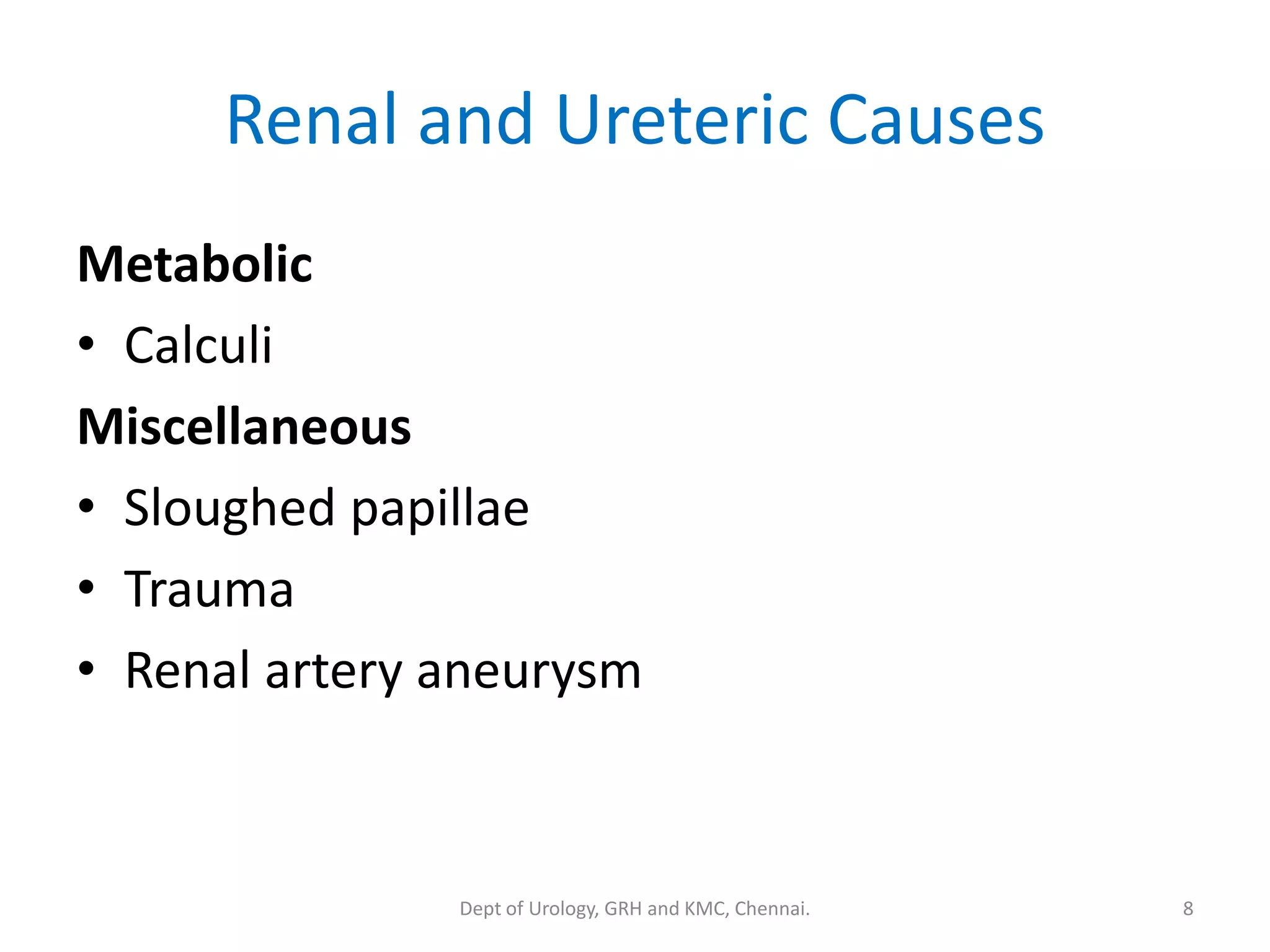
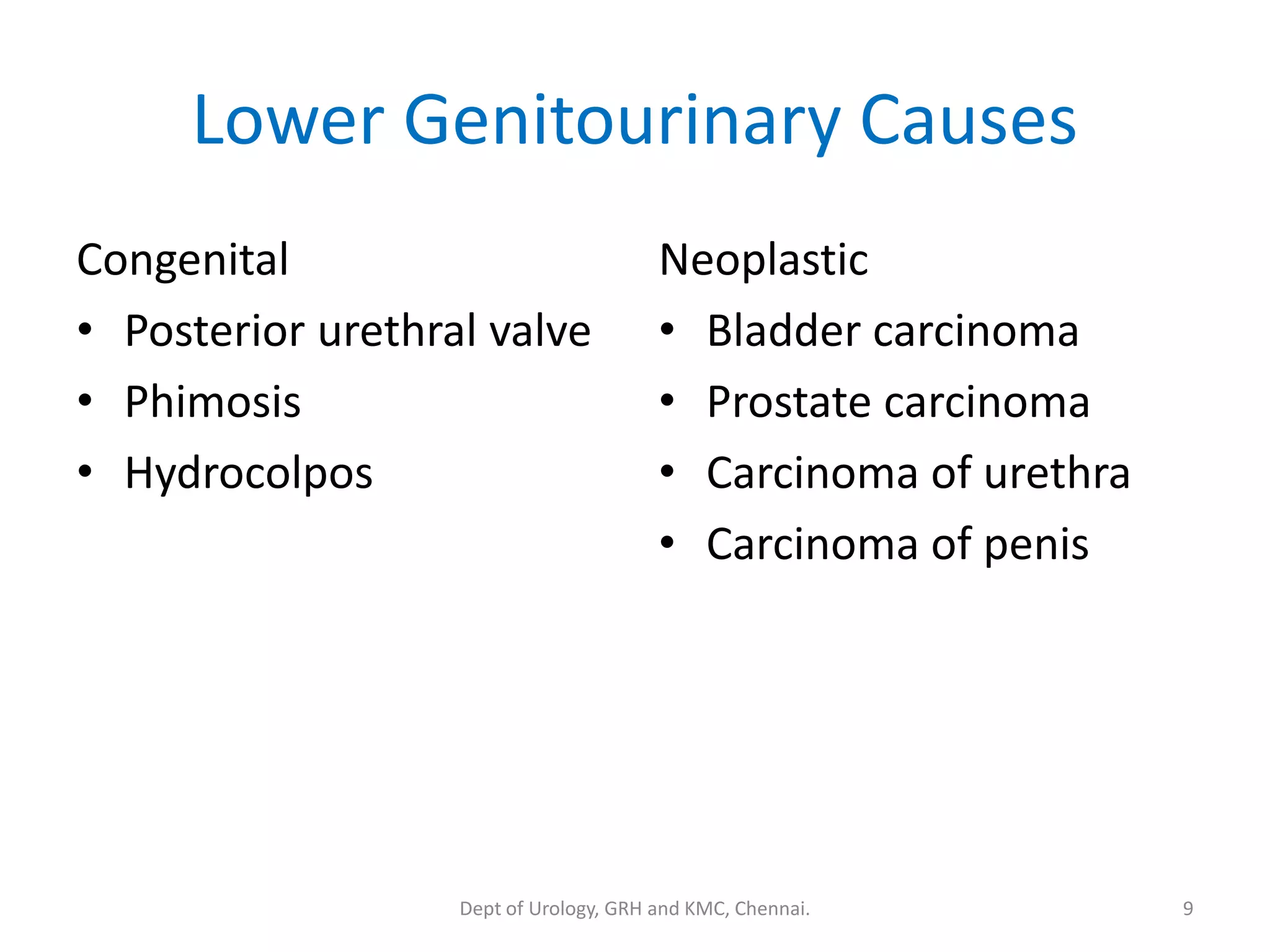
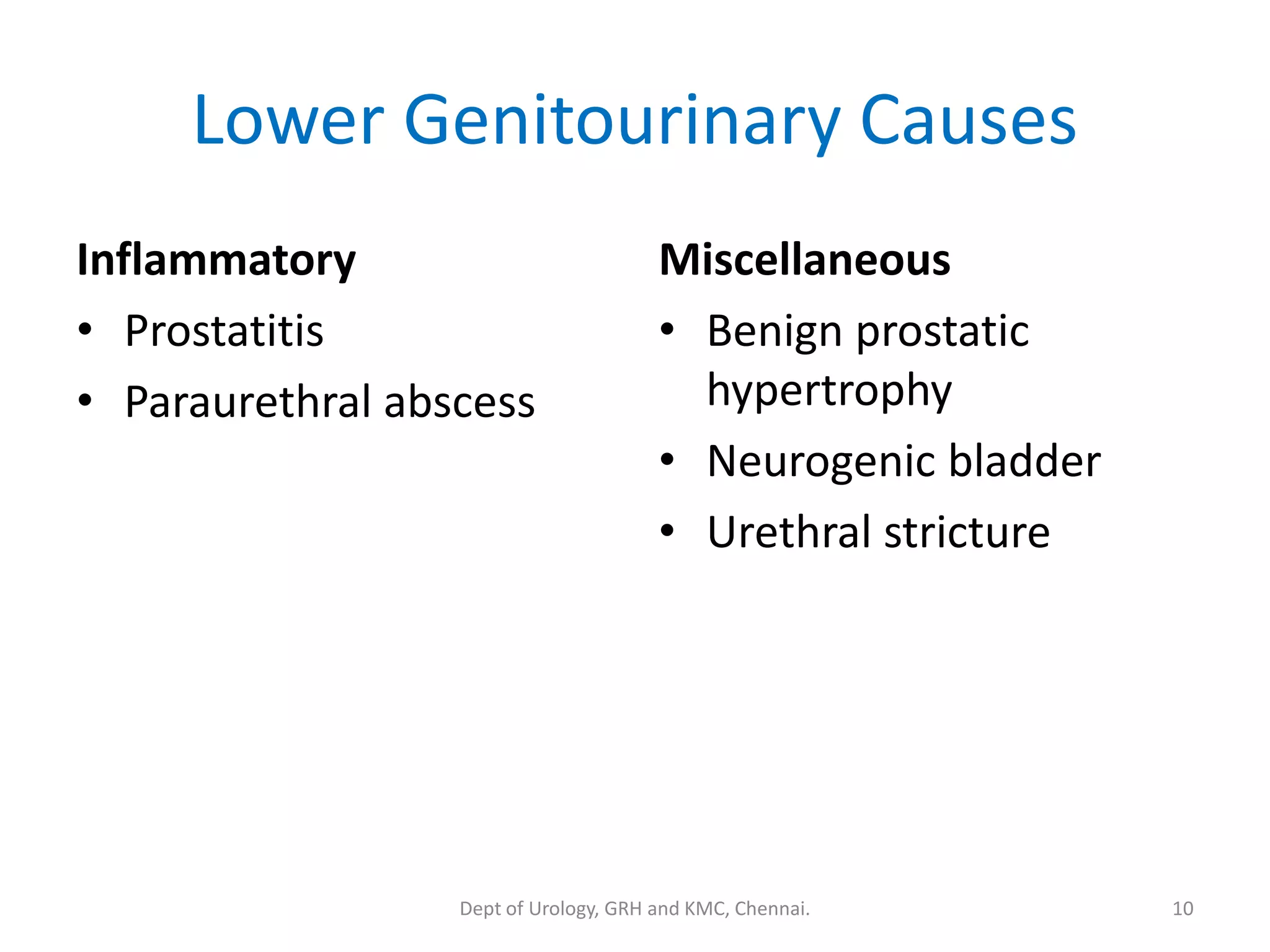
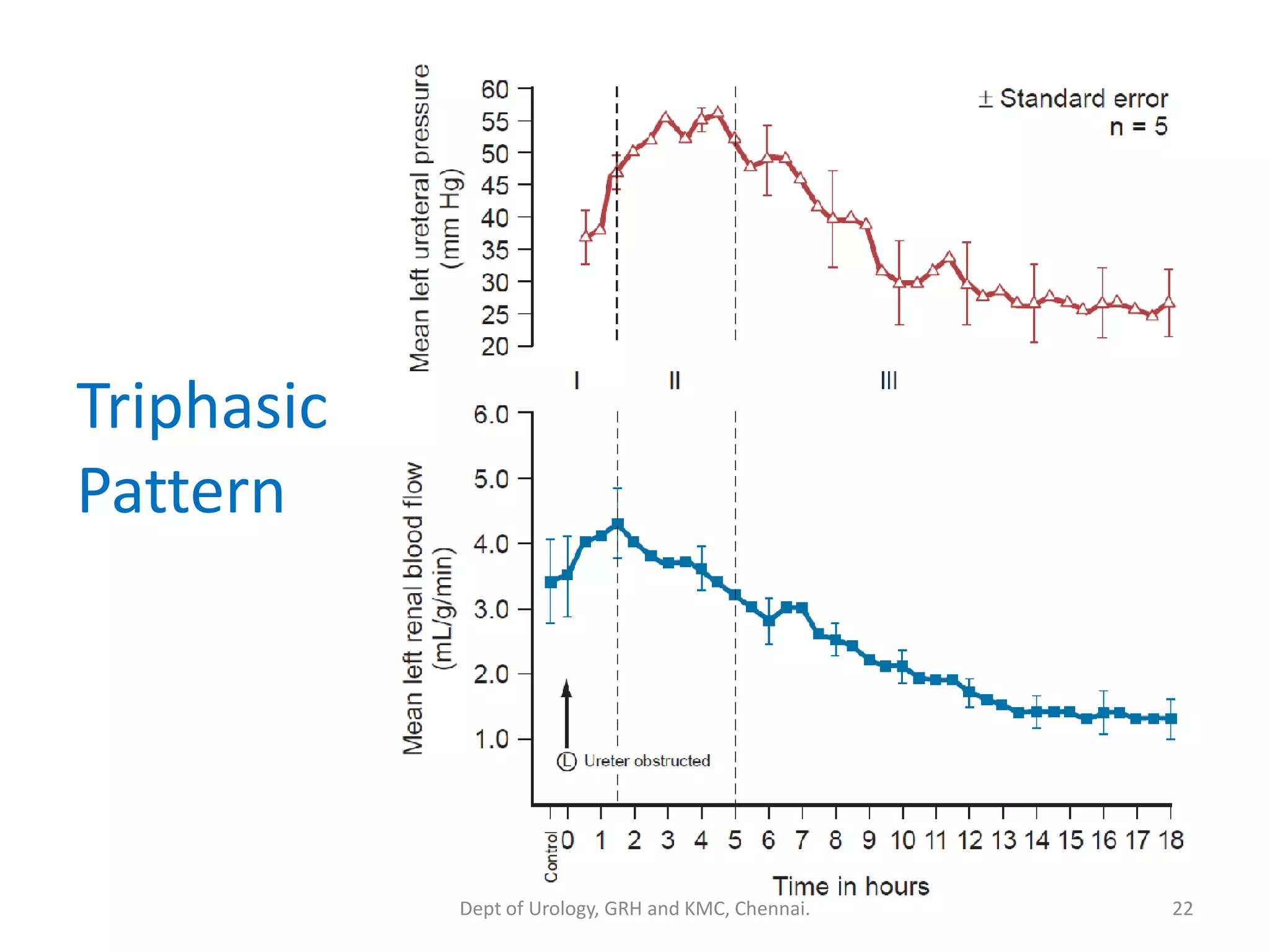
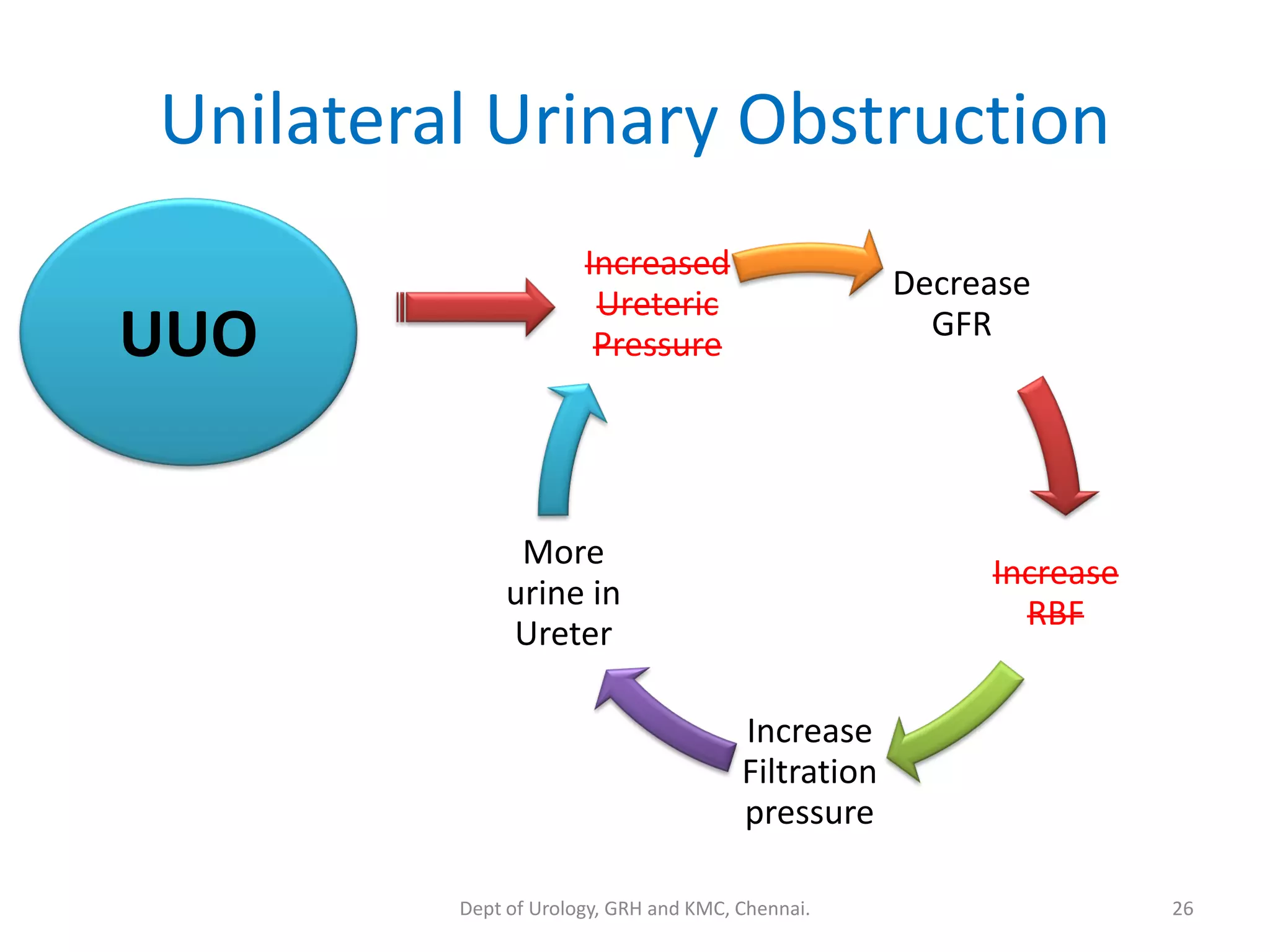
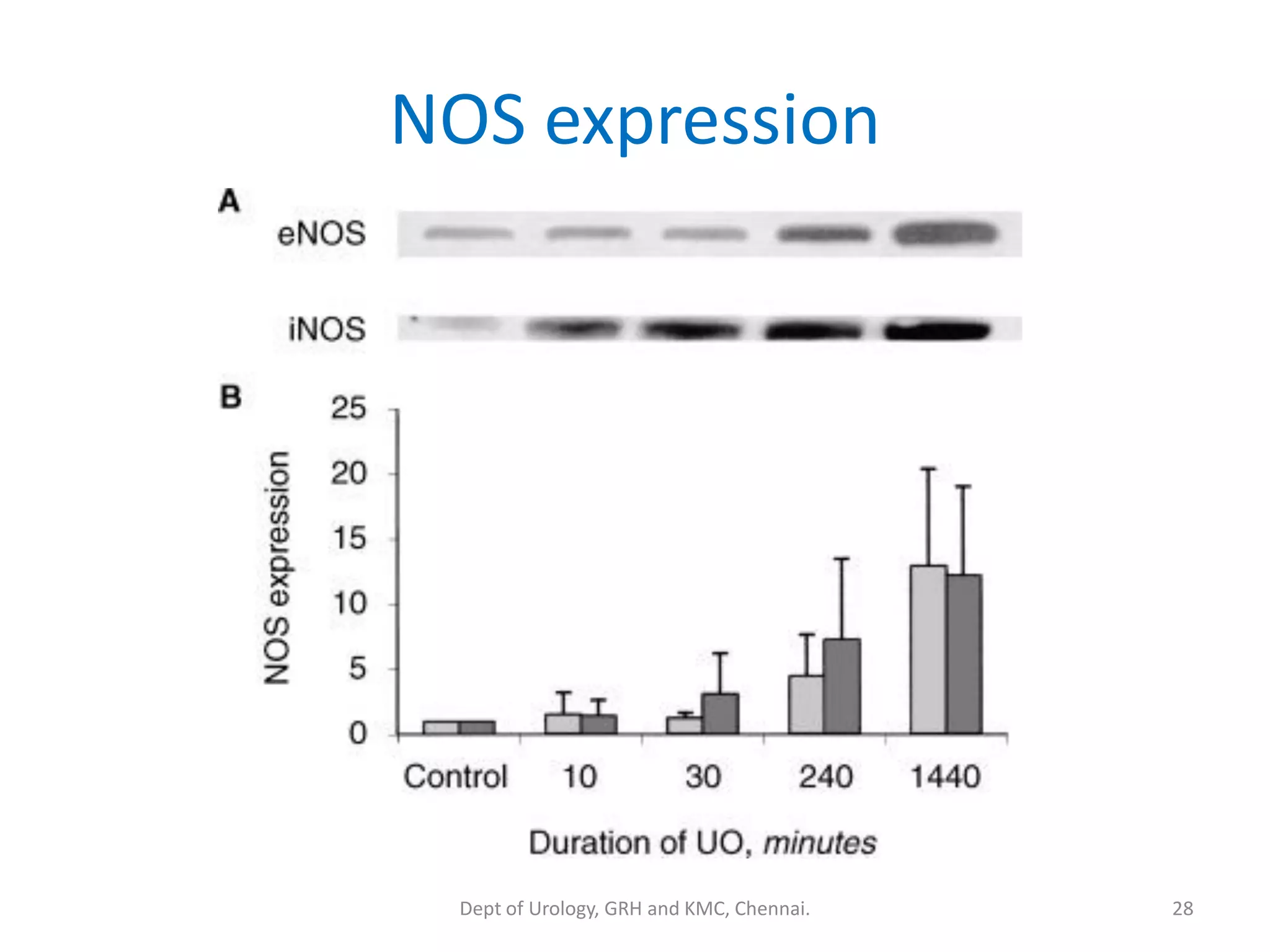
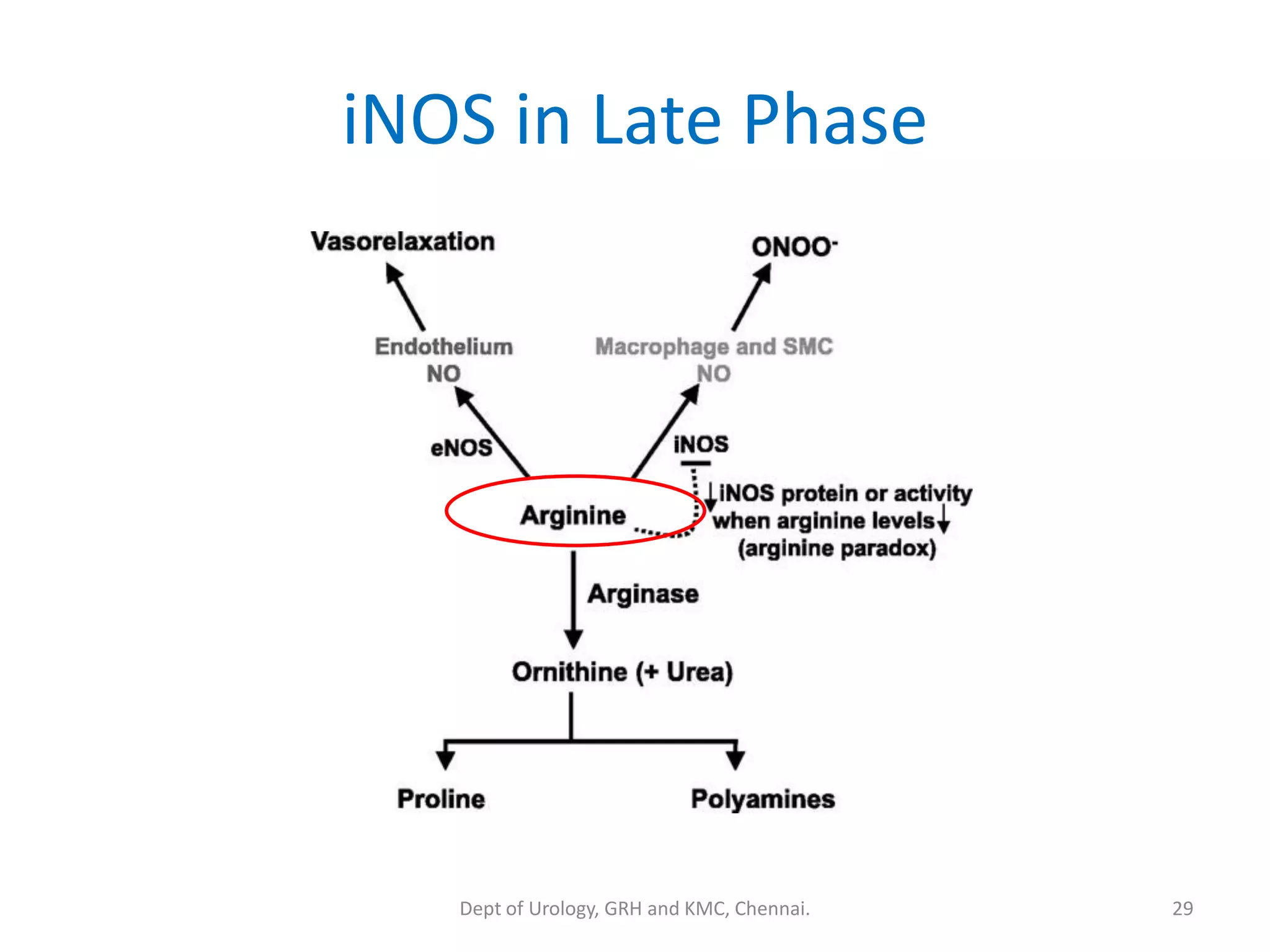
This document discusses urinary obstruction, including its pathophysiology, causes, effects on renal physiology and function, histological changes, clinical impact, and renal recovery after relief of obstruction. It provides an overview of how urinary obstruction can lead to permanent kidney damage depending on the severity, chronicity, and baseline kidney condition. Both unilateral and bilateral obstruction are examined, along with the triphasic response and changes in renal blood flow, filtration, and tubular transport that occur.