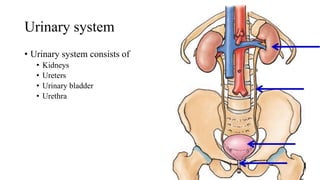
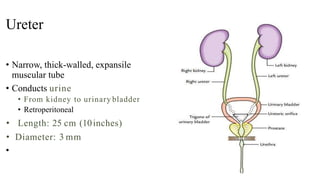
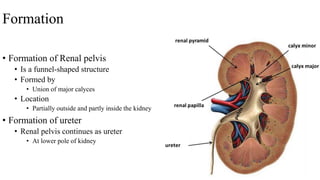
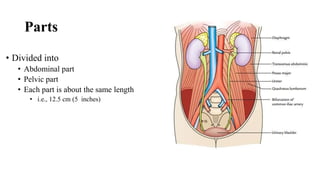
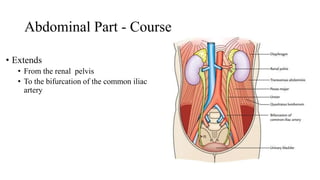
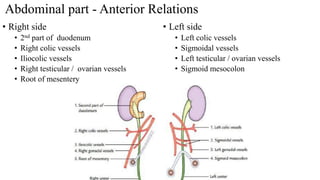
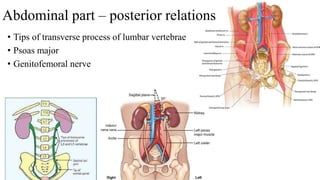
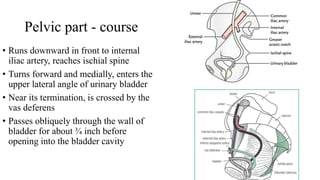
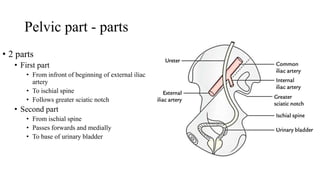
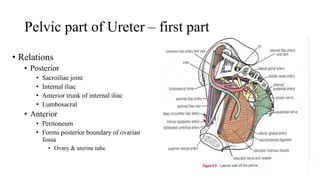
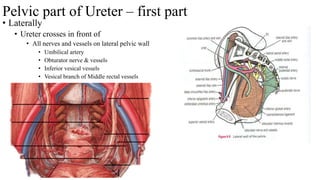
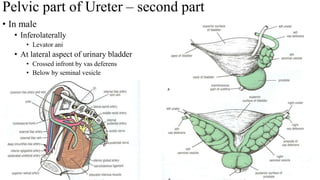
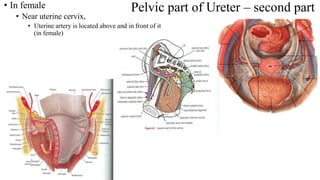
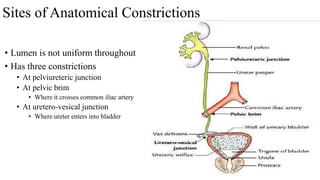
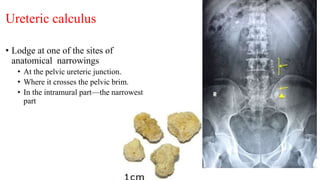
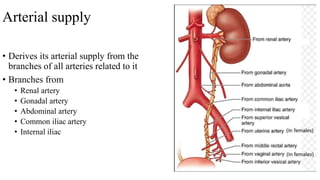
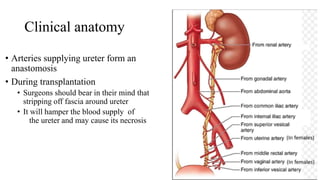
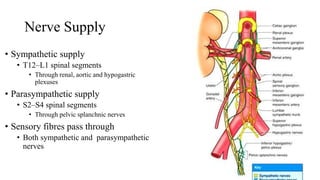
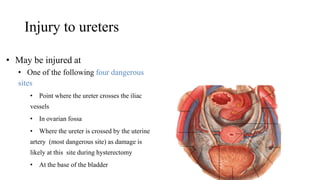
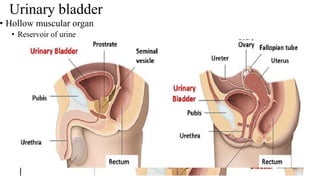
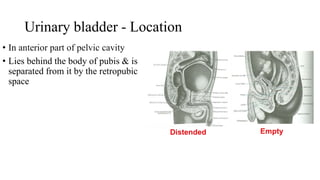
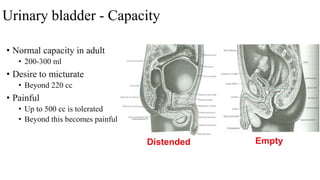
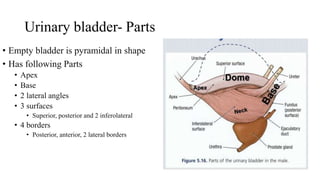
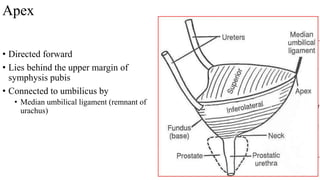
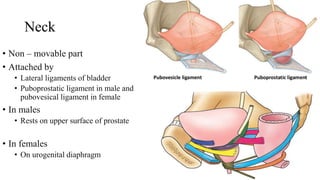
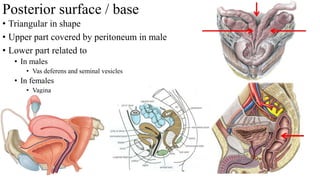
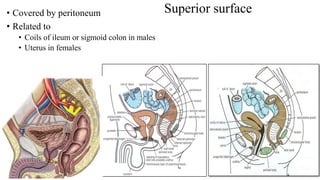
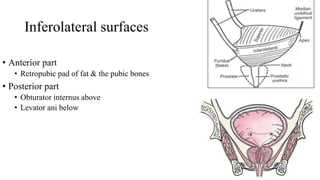
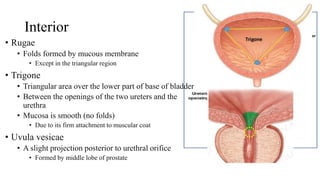
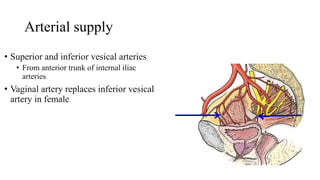
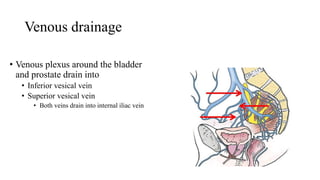
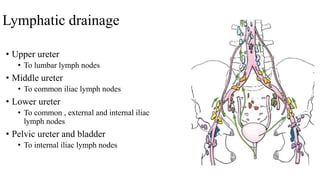
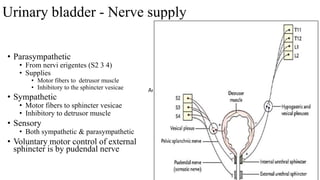
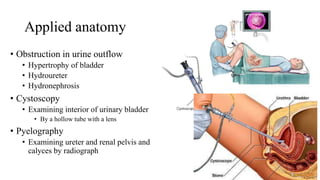
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The ureters are thin muscular tubes that conduct urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Each ureter is around 25 cm long and divided into abdominal and pelvic parts. The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ that acts as a reservoir for urine in the pelvis. It has a capacity of 200-300 ml in adults and is supplied by superior and inferior vesical arteries. The document provides detailed descriptions of the anatomy and relations of the ureters and urinary bladder.