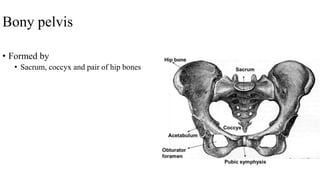
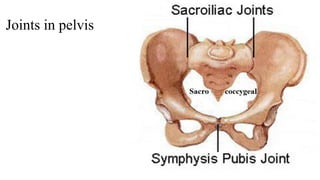
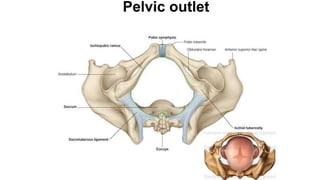
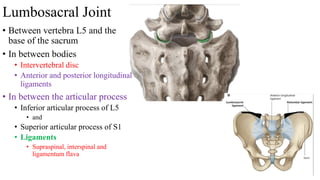
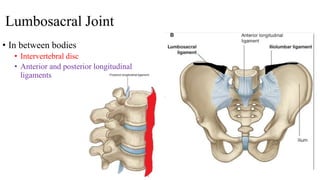
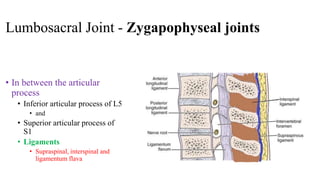
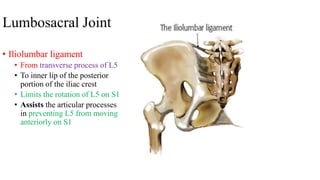
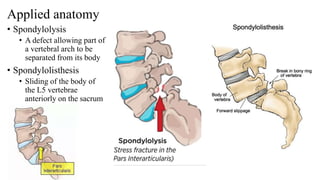
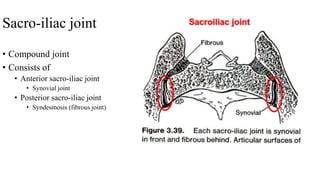
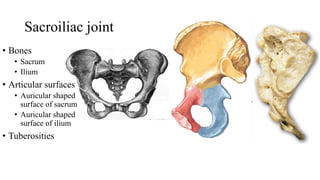
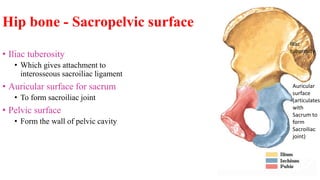
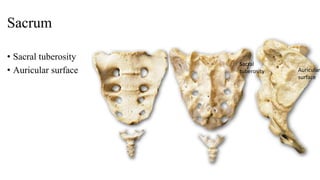
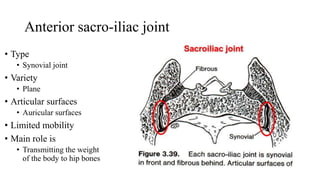
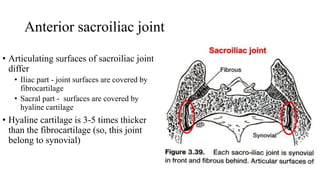
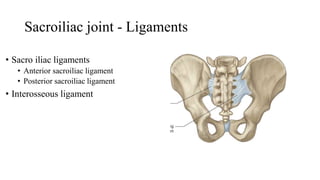
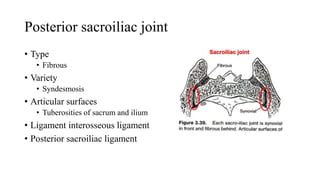
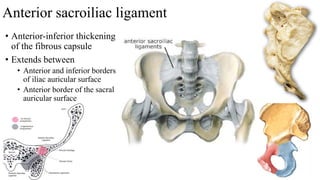
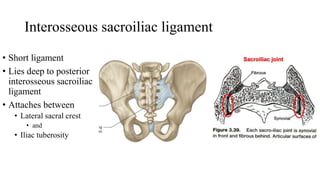
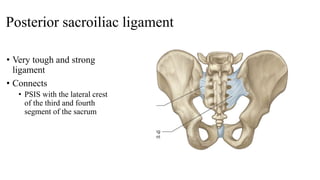
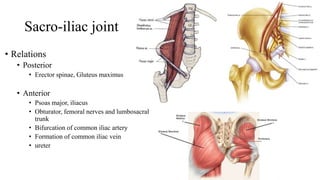
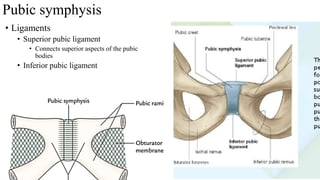
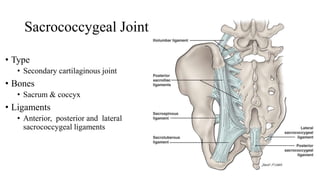
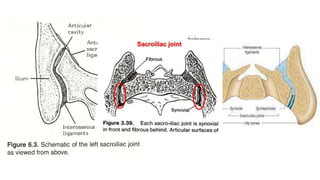
The document describes the joints in the pelvis, including the lumbosacral joint between the L5 vertebrae and sacrum, the sacroiliac joint between the sacrum and ilium, and the pubic symphysis and sacrococcygeal joints. The lumbosacral joint contains intervertebral discs and ligaments that connect the vertebral processes. The sacroiliac joint is a synovial joint anteriorly and fibrous joint posteriorly, connected by strong ligaments. The pubic symphysis and sacrococcygeal joints are secondary cartilaginous joints held together by ligaments.