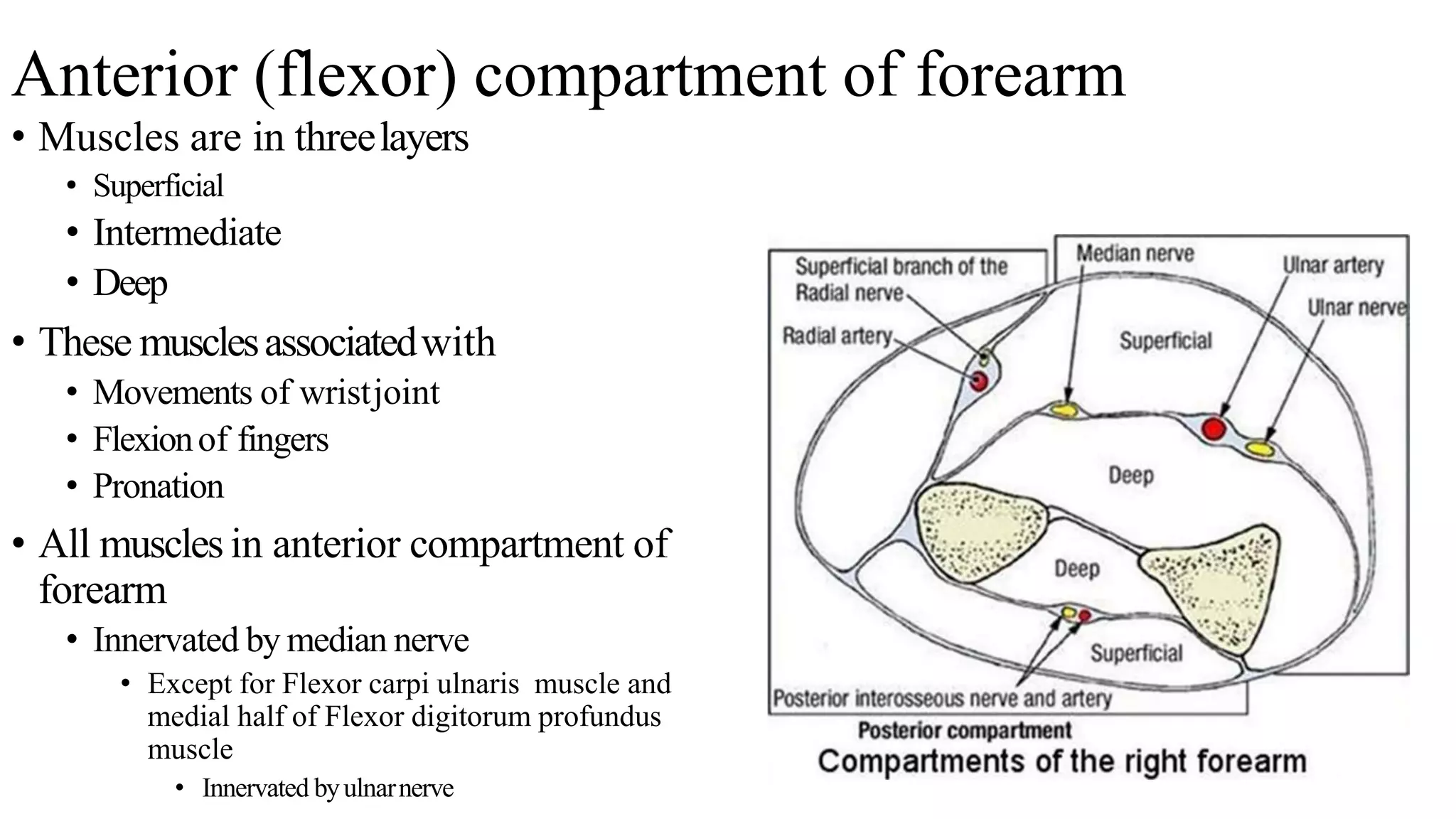
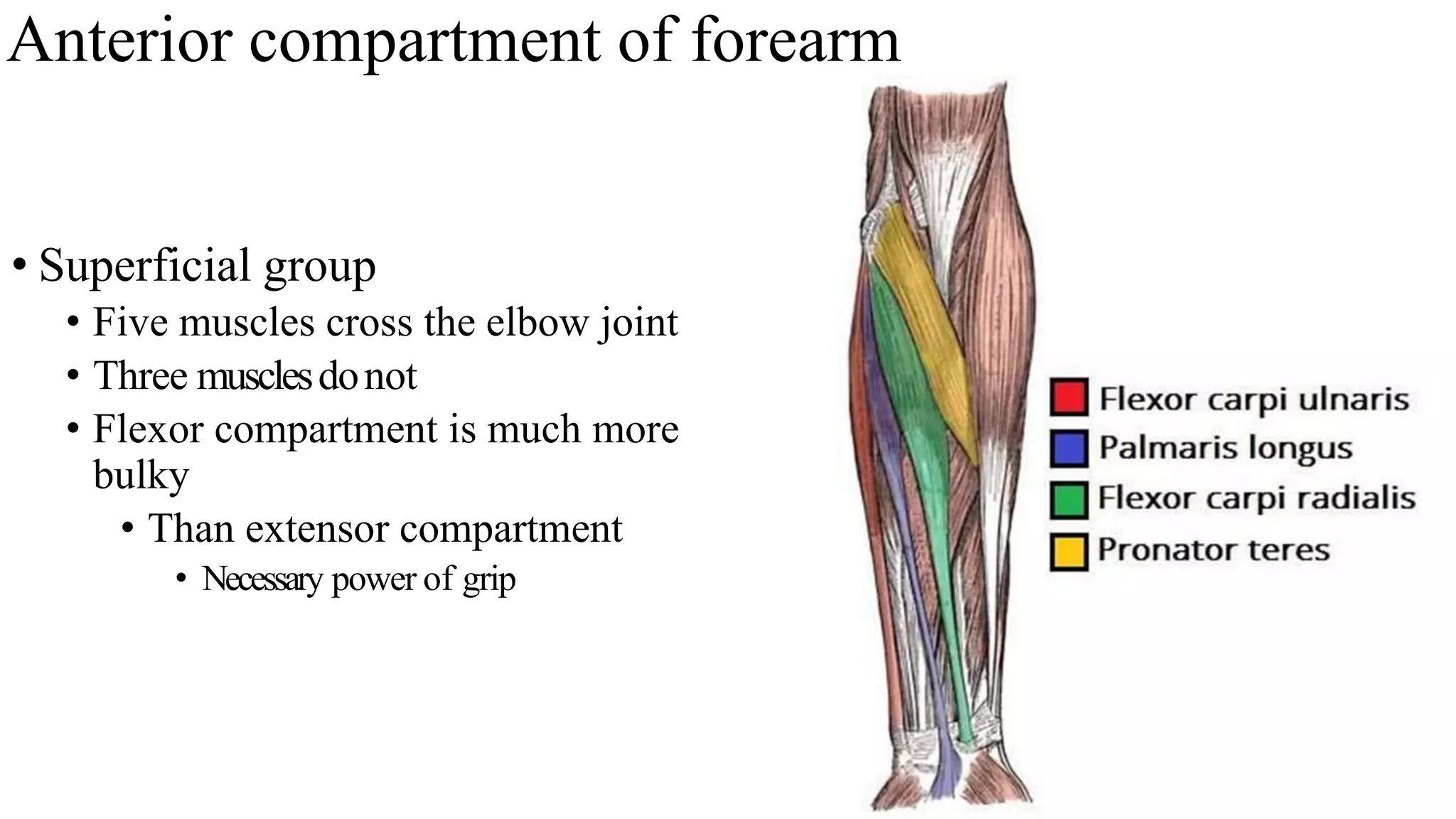
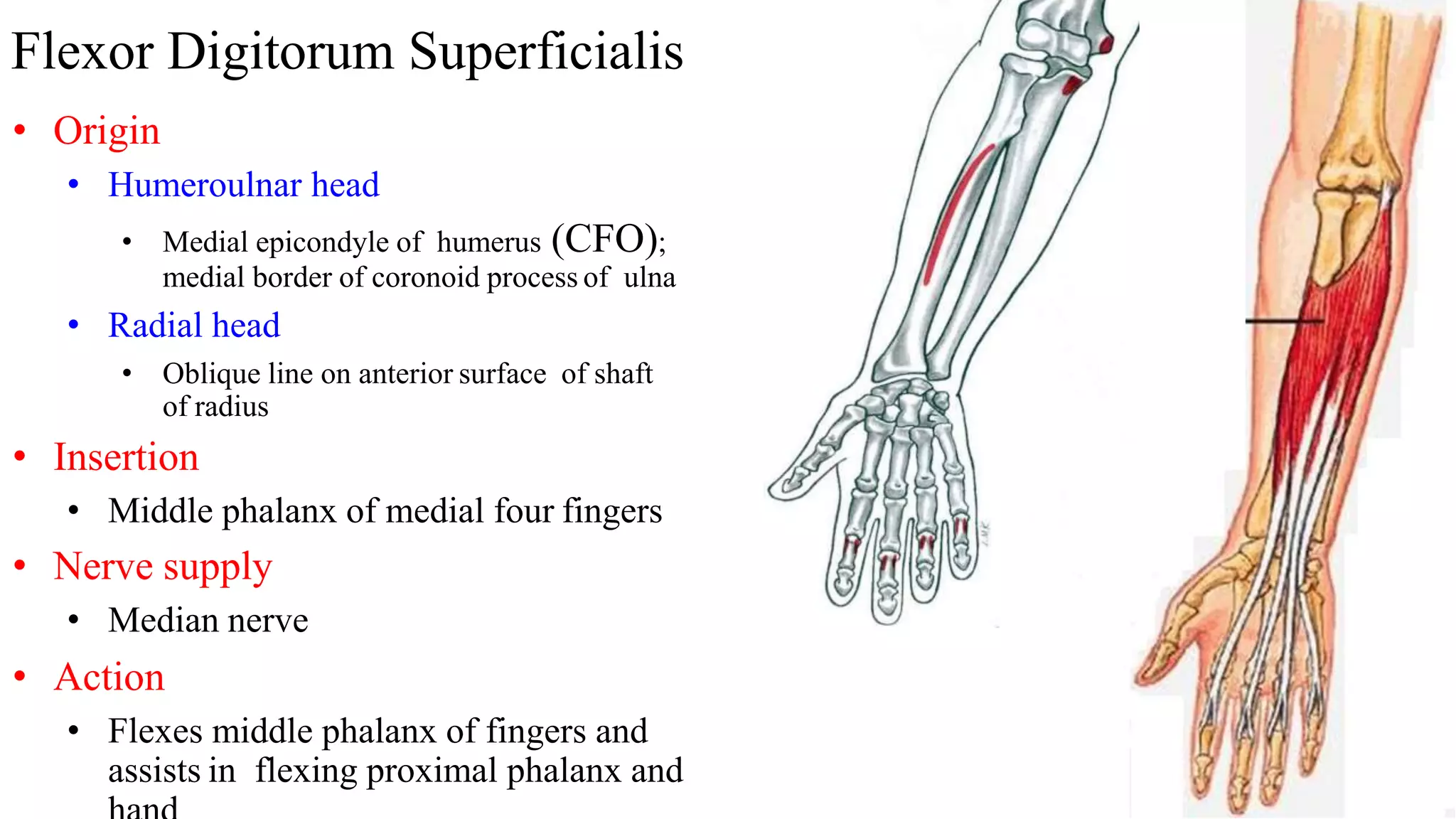
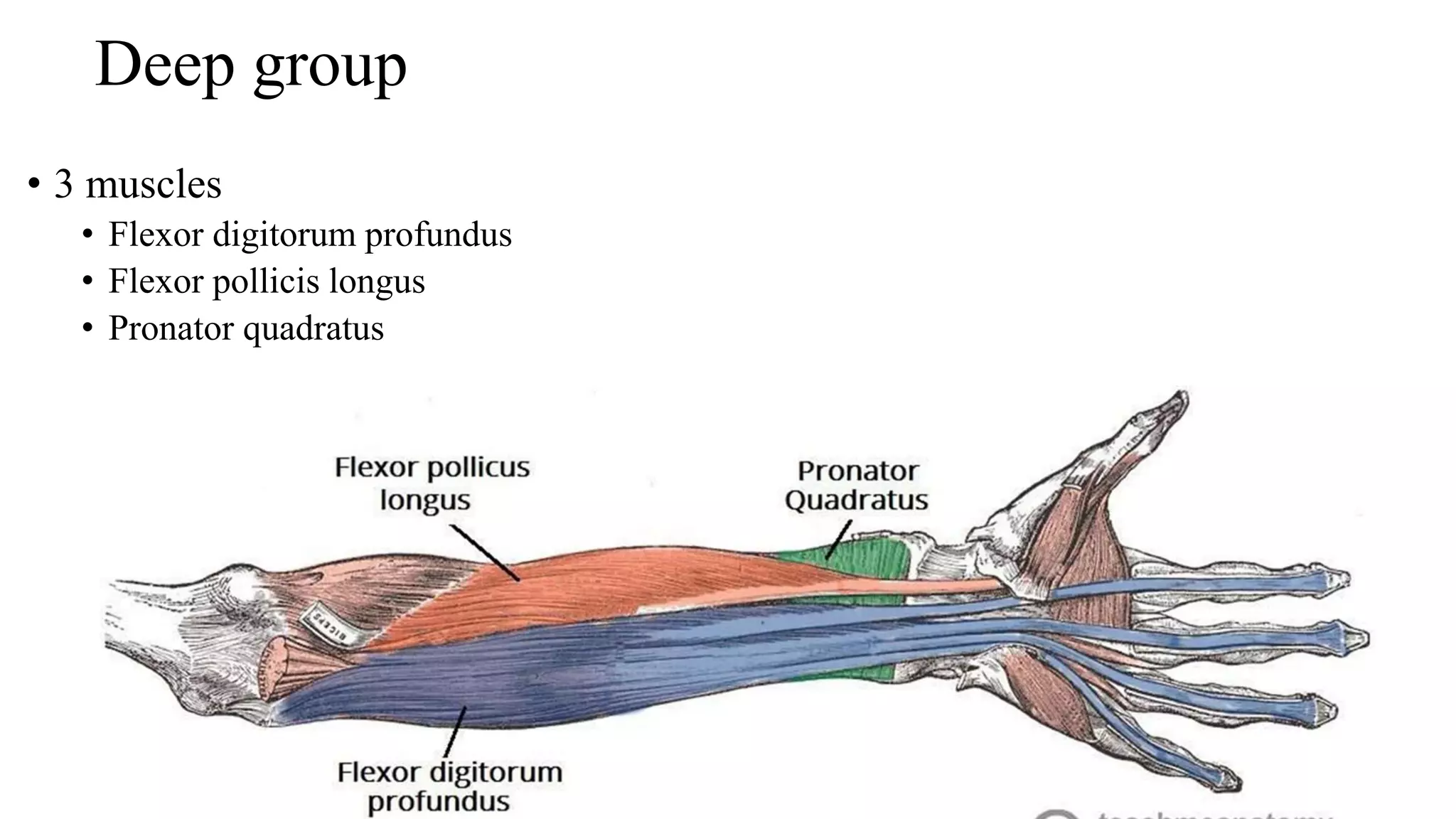
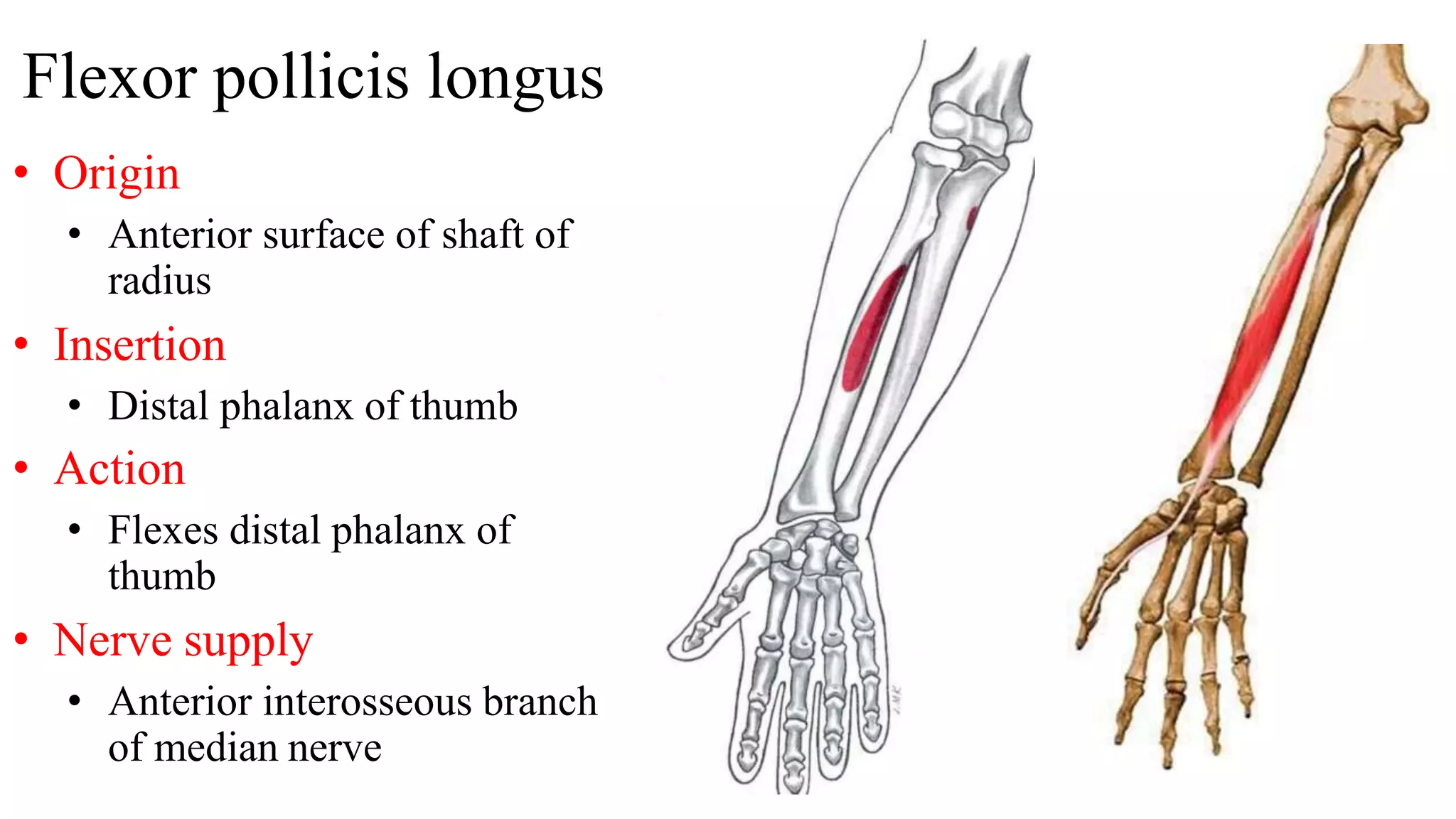
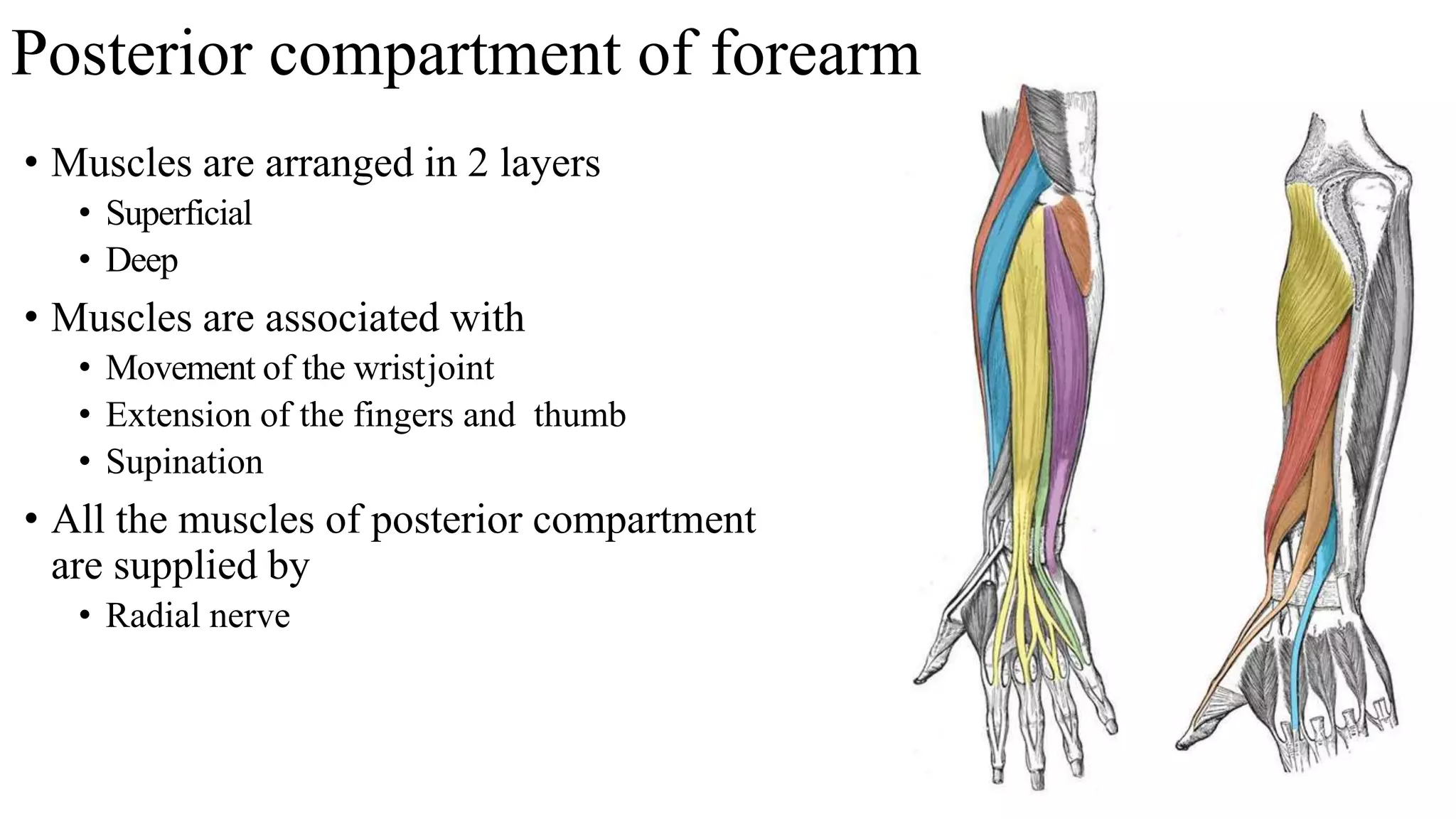
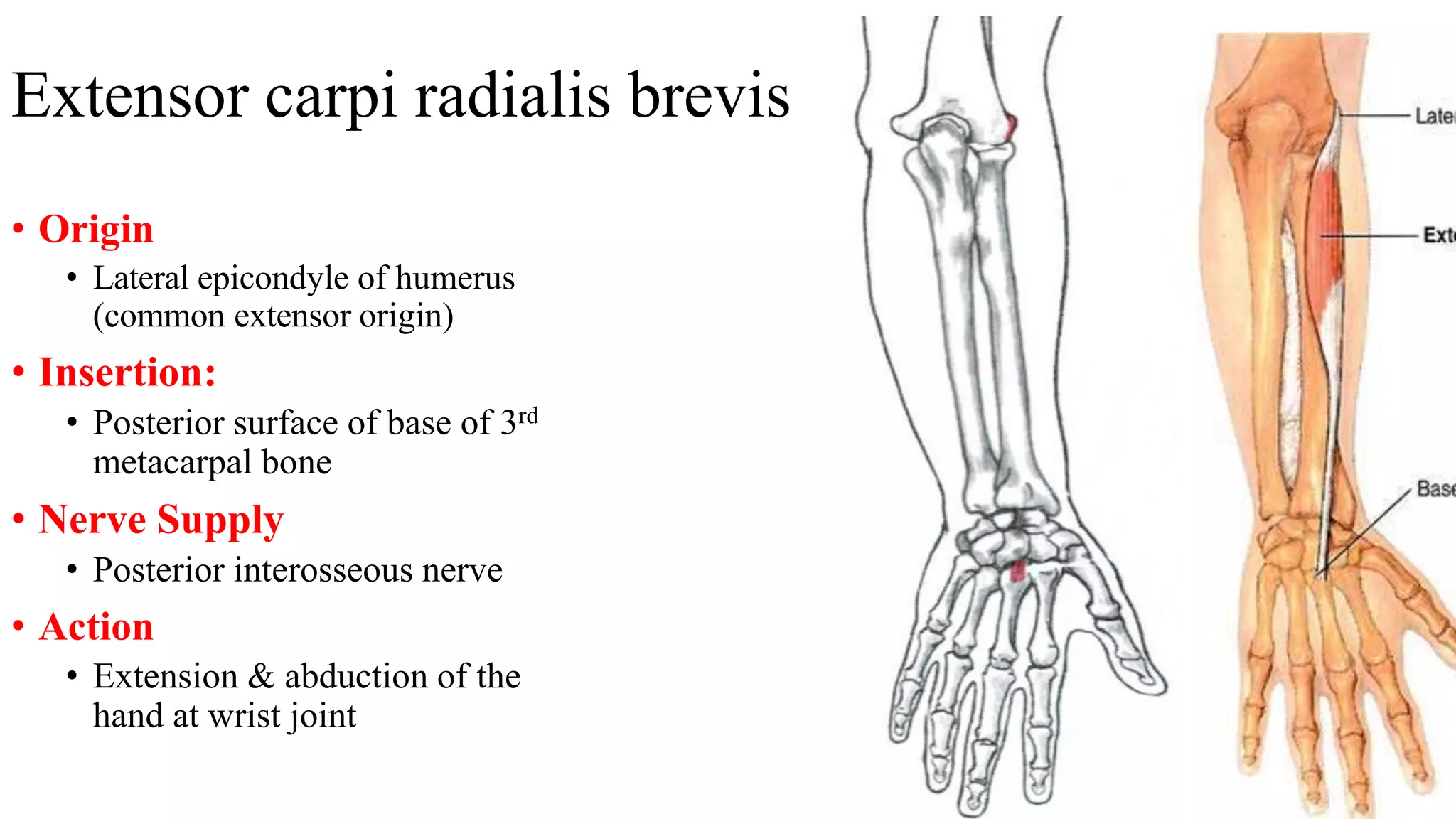
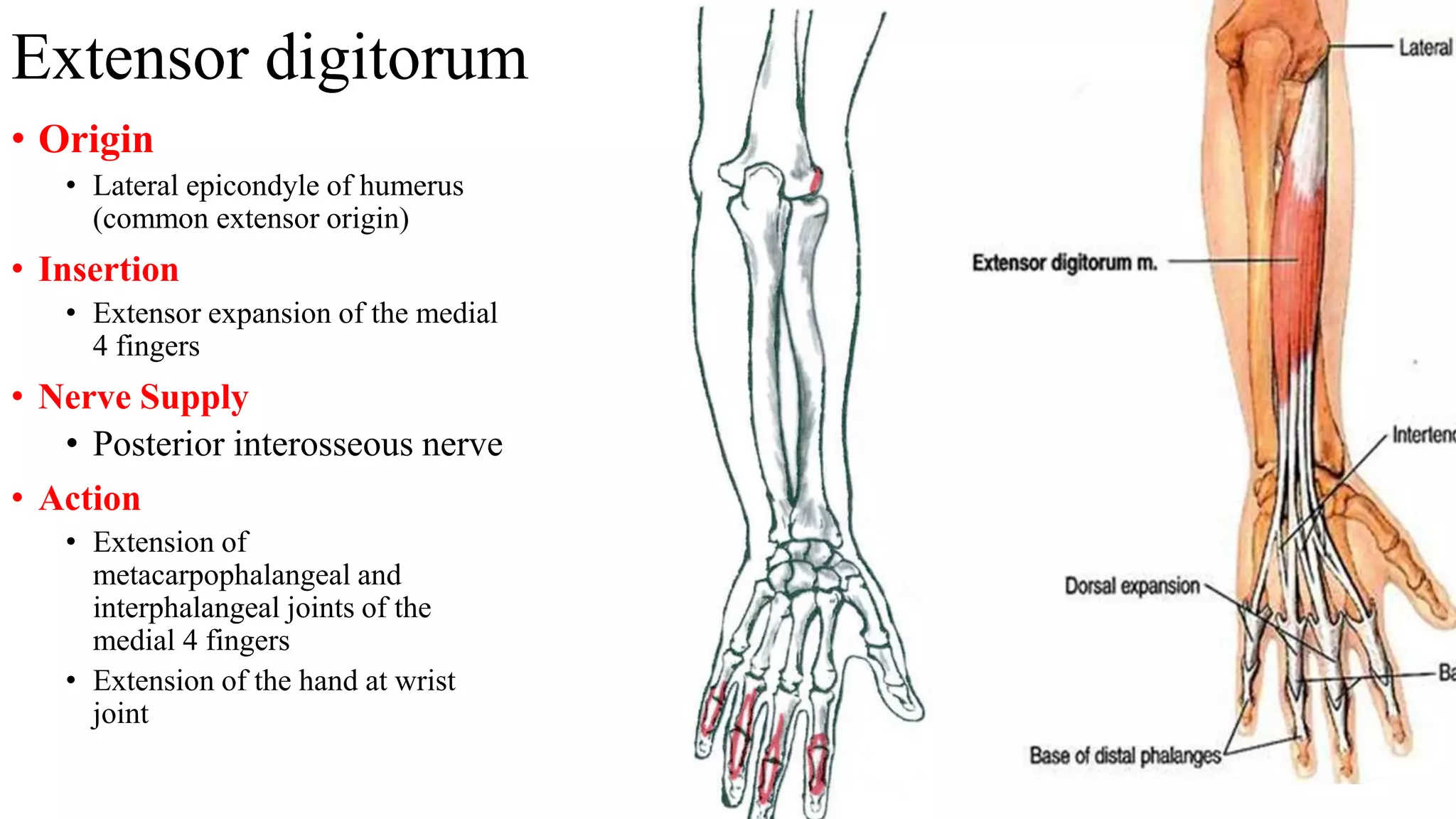
The forearm is divided into anterior and posterior compartments by septa. The anterior compartment contains flexor muscles in superficial, intermediate, and deep layers that flex the fingers and wrist. These muscles are innervated by the median nerve except for two muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve. The posterior compartment contains extensor muscles in superficial and deep layers that extend the fingers and wrist. These muscles are innervated by the radial nerve. Wrist drop is a sign of radial nerve injury where the extensor muscles are paralyzed, allowing unopposed flexion of the wrist by the flexor muscles.