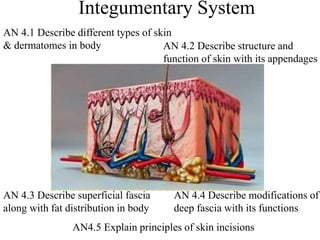
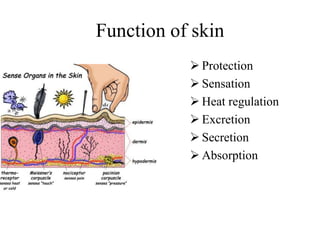
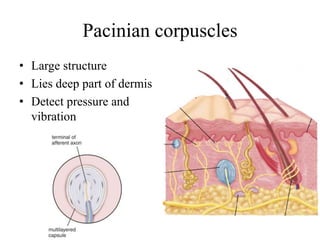
The document describes the structure and function of the integumentary system. It discusses the different layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis), the cells found in each layer and their roles in protection, sensation, and regulation. It also describes skin appendages like hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands. The document outlines the types, layers and functions of fascia beneath the skin, and modifications like septa and sheaths. Finally, it discusses skin color changes that can provide diagnostic clues for medical conditions.