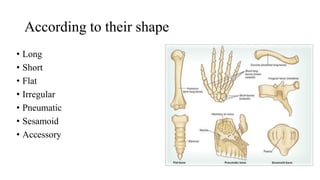
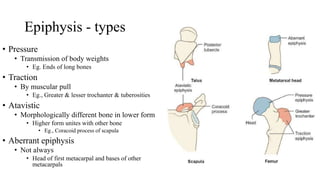
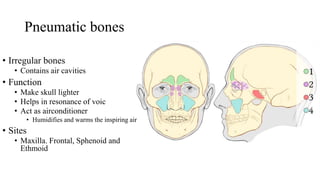
This document provides information about bones, including their classification, structure, and development. It discusses the four main classifications of bones by position, shape, structure, and ossification. Key points include:
- Bones provide structure, protection, movement, and store minerals. There are 206 total bones in the human body.
- Bones are classified as either axial (skull, vertebrae, ribs) or appendicular (shoulder bones, arm/leg bones).
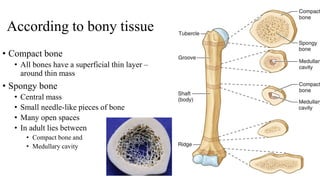
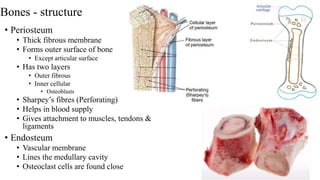
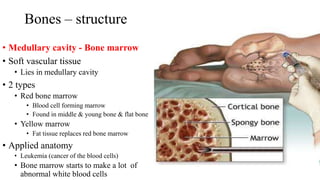
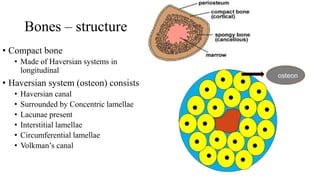
- The structure of bones includes compact bone, spongy bone, periosteum, endosteum, marrow cavity, and bone cells.
- Ossification is the process of bone formation, which can occur through intrame