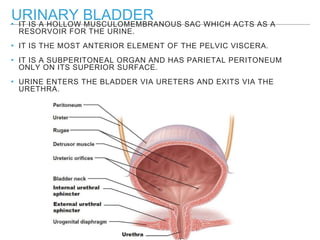
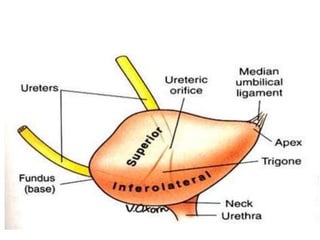
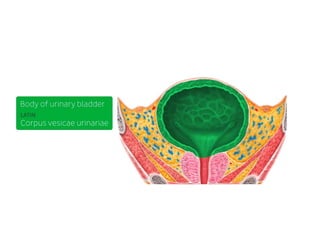
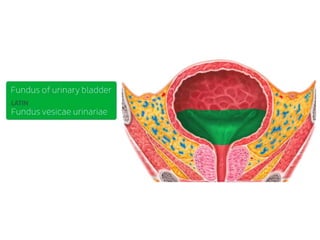
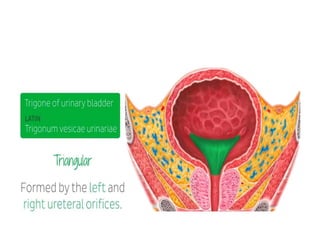
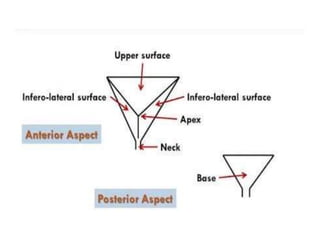
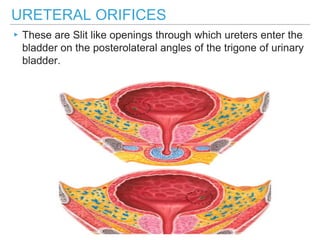
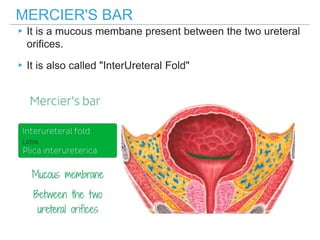
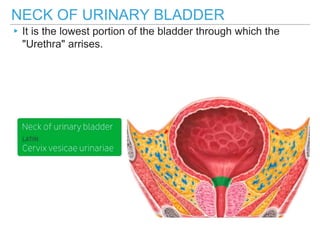
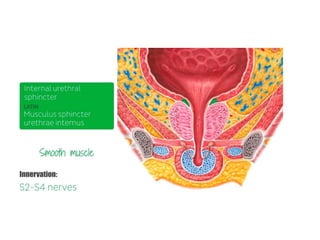
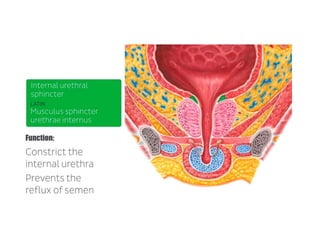
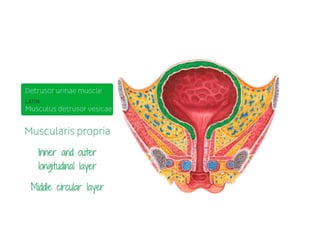
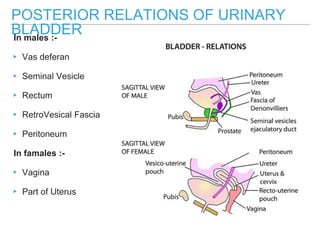
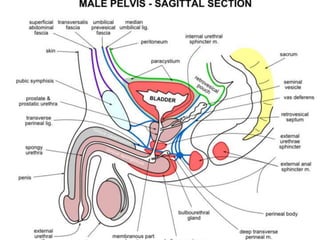
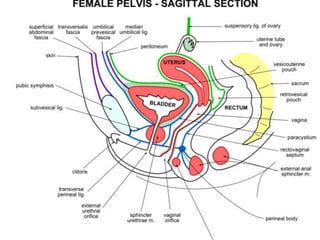
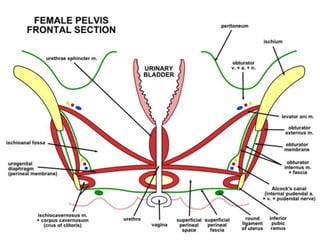
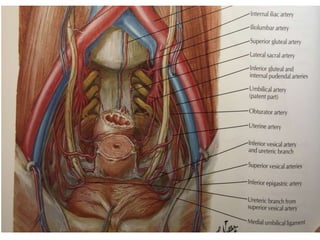
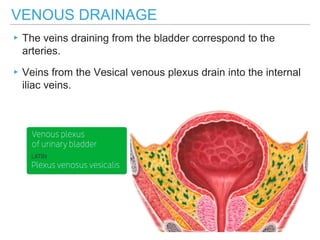
The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular sac located in the pelvis that acts as a reservoir for urine. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits through the urethra. The bladder has a superior surface covered by peritoneum and inferior surfaces that are not. As it fills, the bladder rises from the pelvis into the lower abdomen. The trigone is a triangular area where the ureters enter the bladder and is innervated to signal the need to void. The detrusor muscle surrounds the bladder wall and contracts to empty urine during urination.