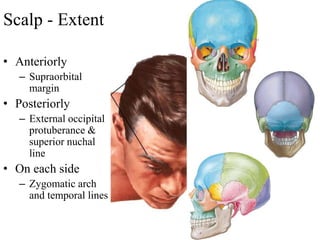
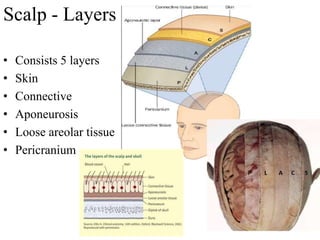
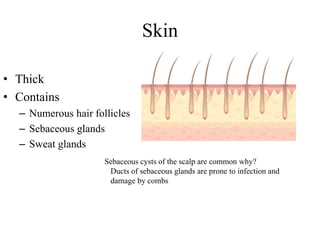
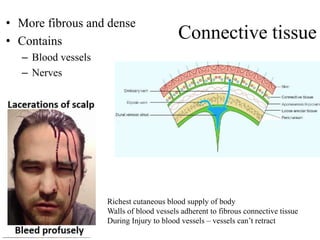
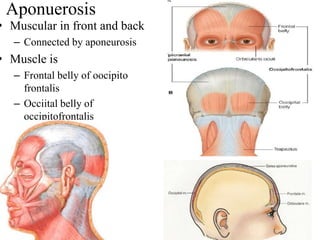
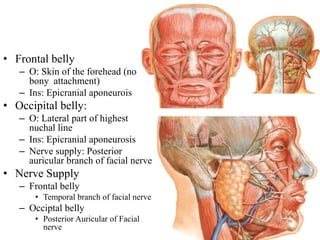
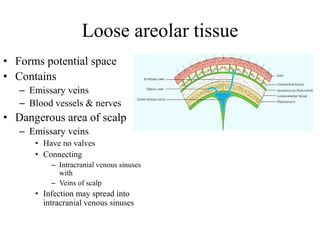
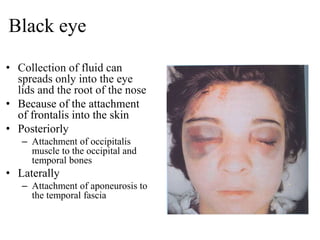
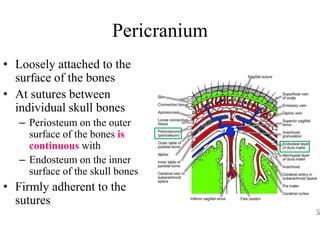
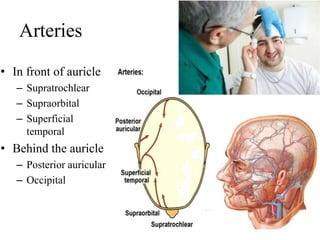
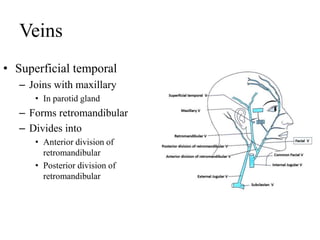
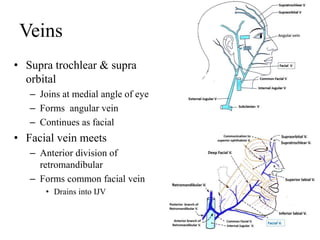
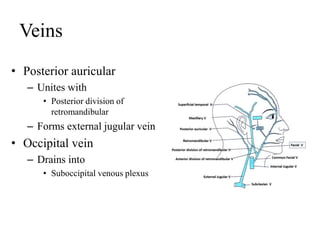
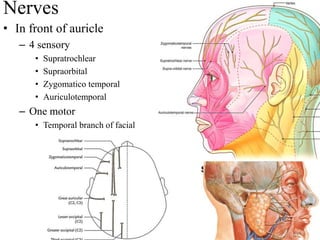
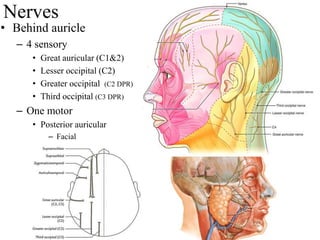
The scalp consists of 5 layers - skin, connective tissue, aponeurosis, loose areolar tissue, and pericranium. The skin is thick and contains numerous hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. The connective tissue below is dense and fibrous, containing a rich blood supply where vessels are adherent. Below this is the aponeurosis layer, containing two muscle bellies connected by the epicranial aponeurosis. The loose areolar tissue below forms a potential space containing emissary veins that can allow spread of infection to intracranial sinuses. The outermost pericranium layer is loosely attached to skull bones and firmly