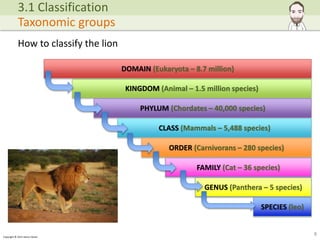
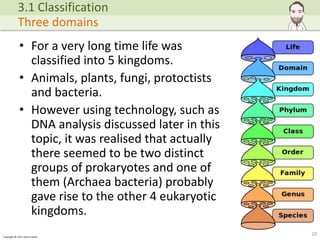
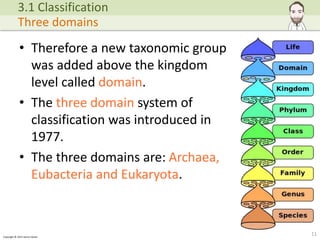
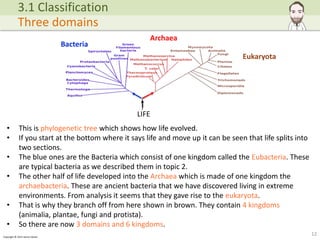
The document discusses the classification of organisms, tracing historical approaches starting with Aristotle and Carl Linnaeus, who developed a hierarchical and binomial naming system. It also covers advancements in classification methods due to modern technologies such as DNA analysis, leading to the acceptance of the three-domain system of life: Archaea, Eubacteria, and Eukaryota. The importance of biodiversity and the role of classification in understanding evolutionary relationships and species monitoring is emphasized.