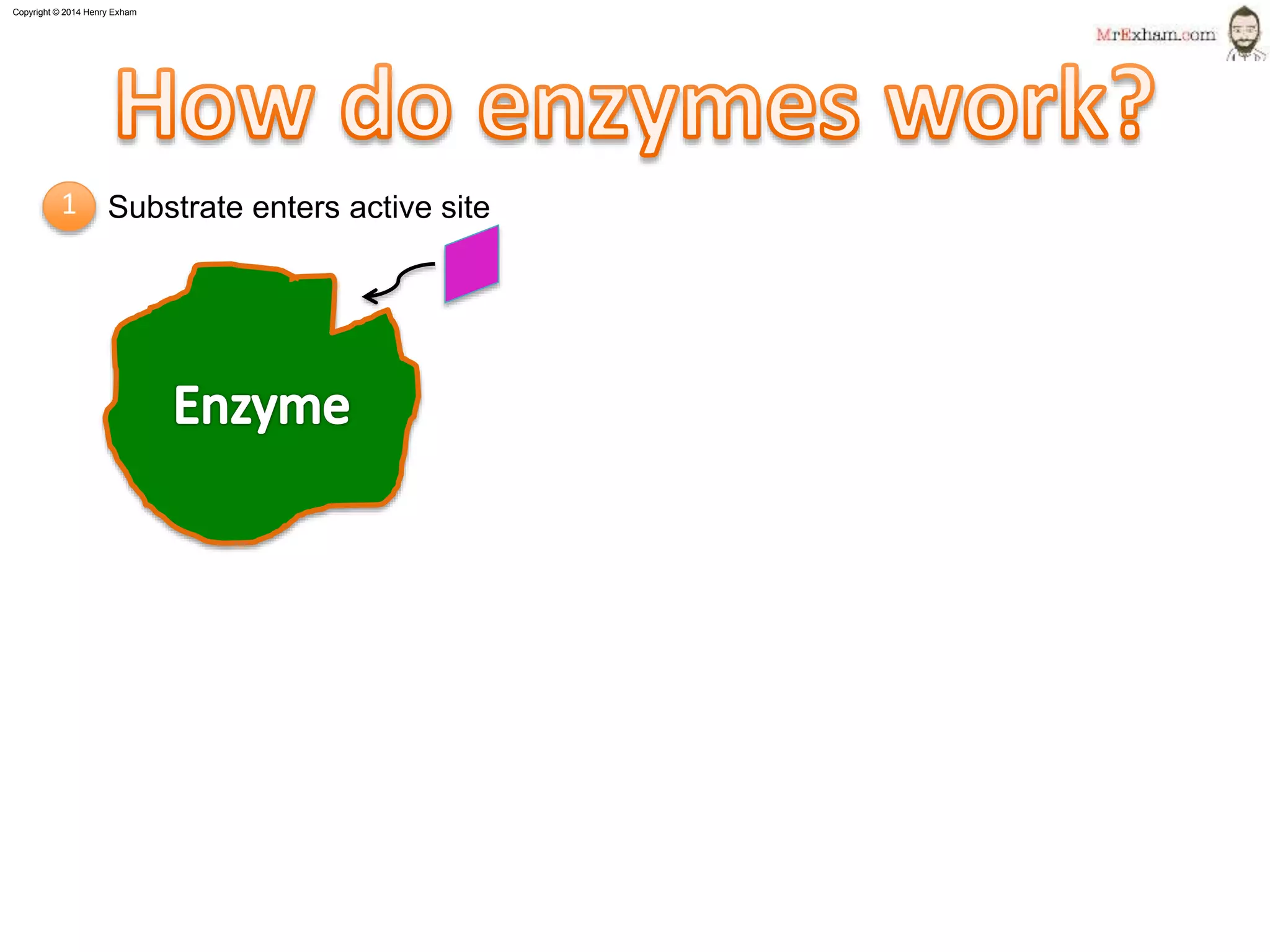
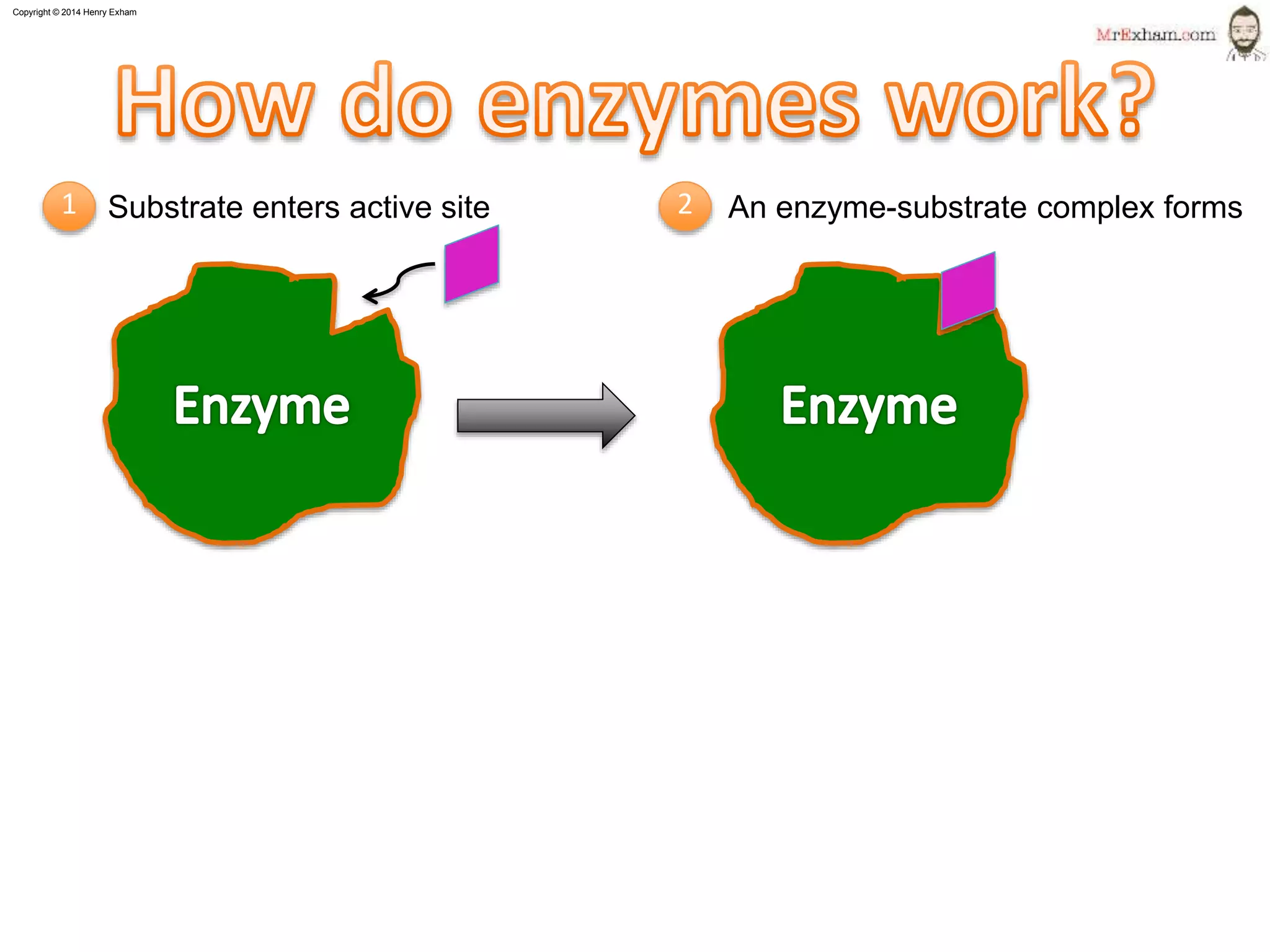
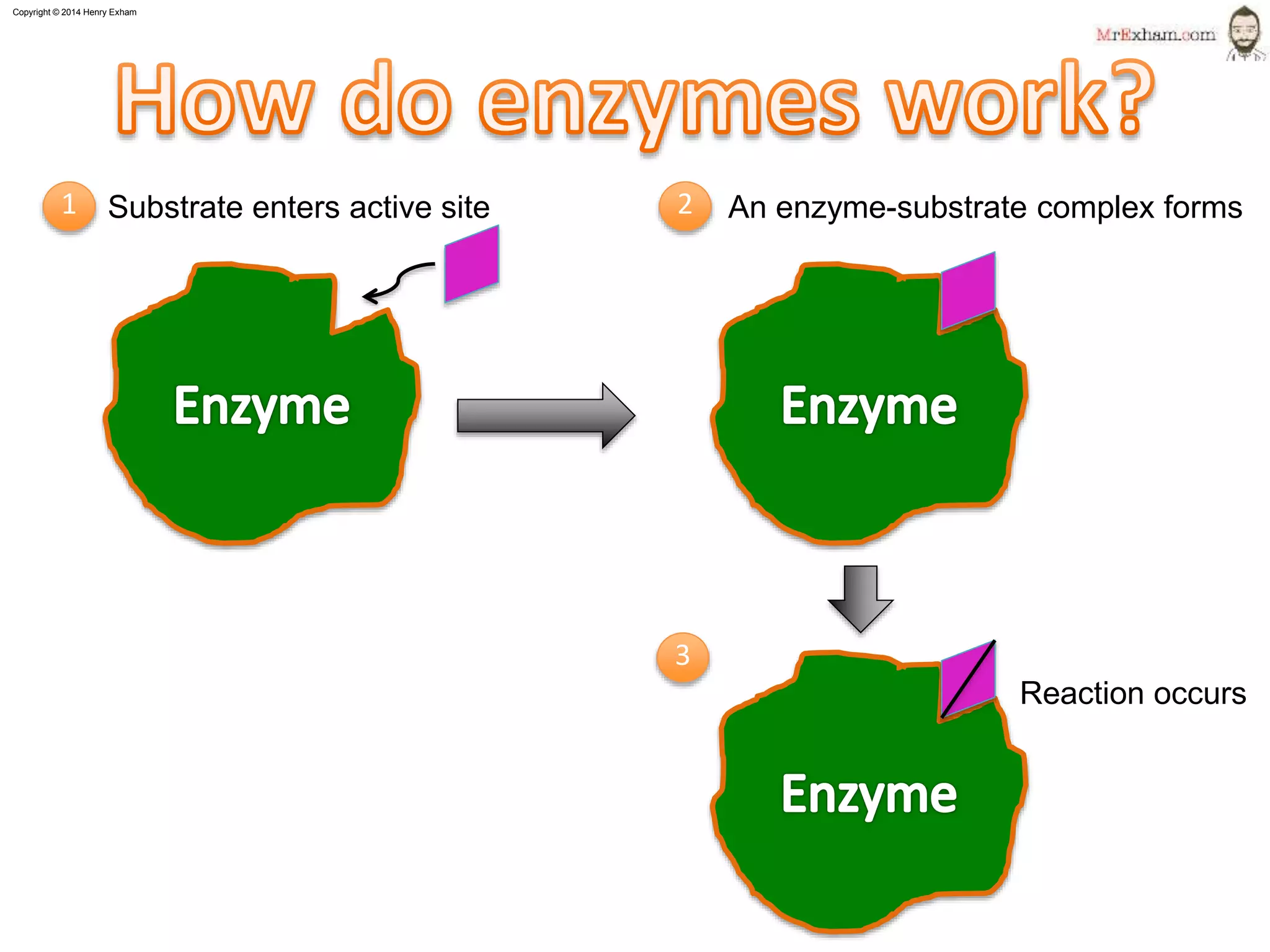
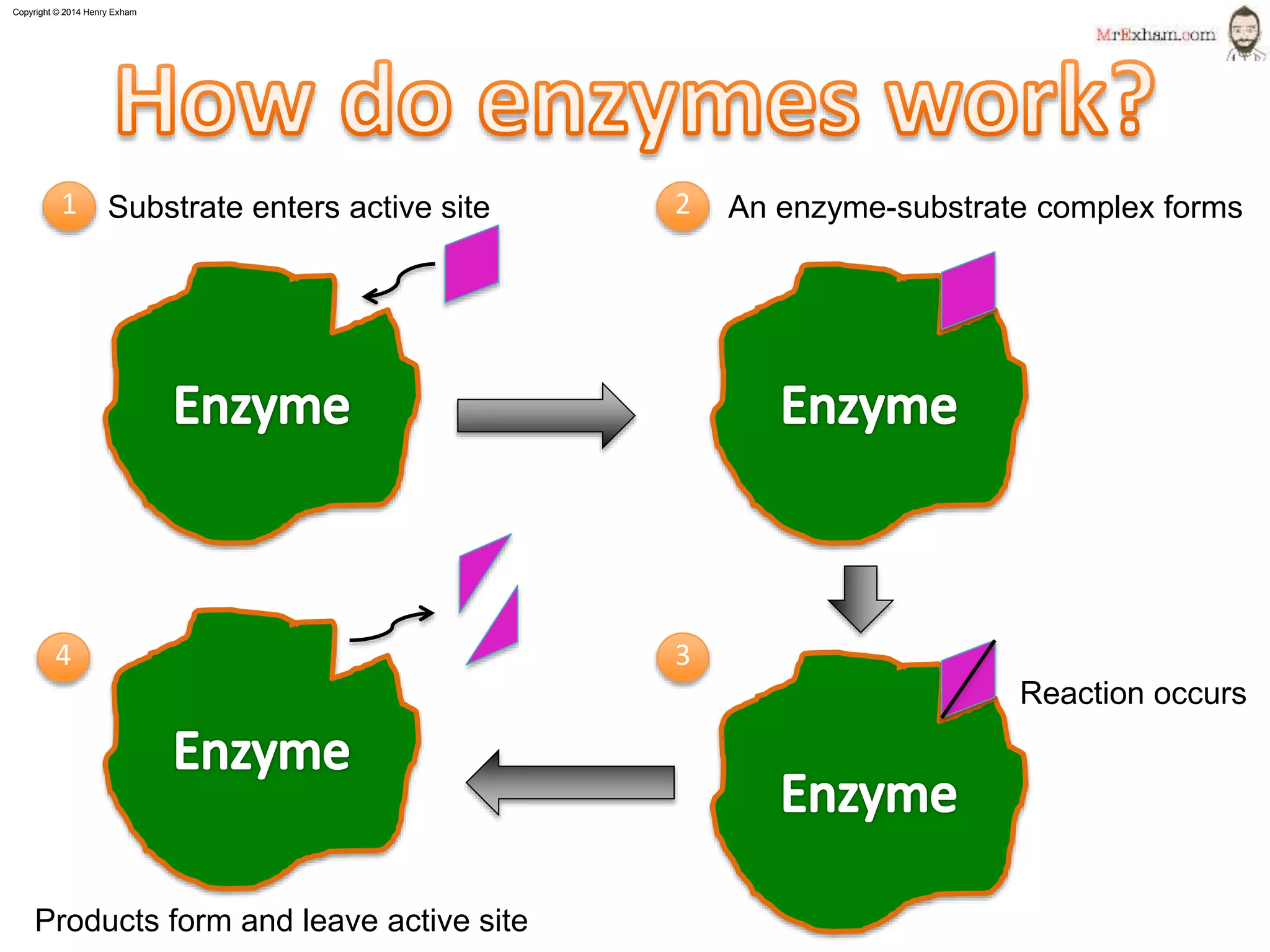
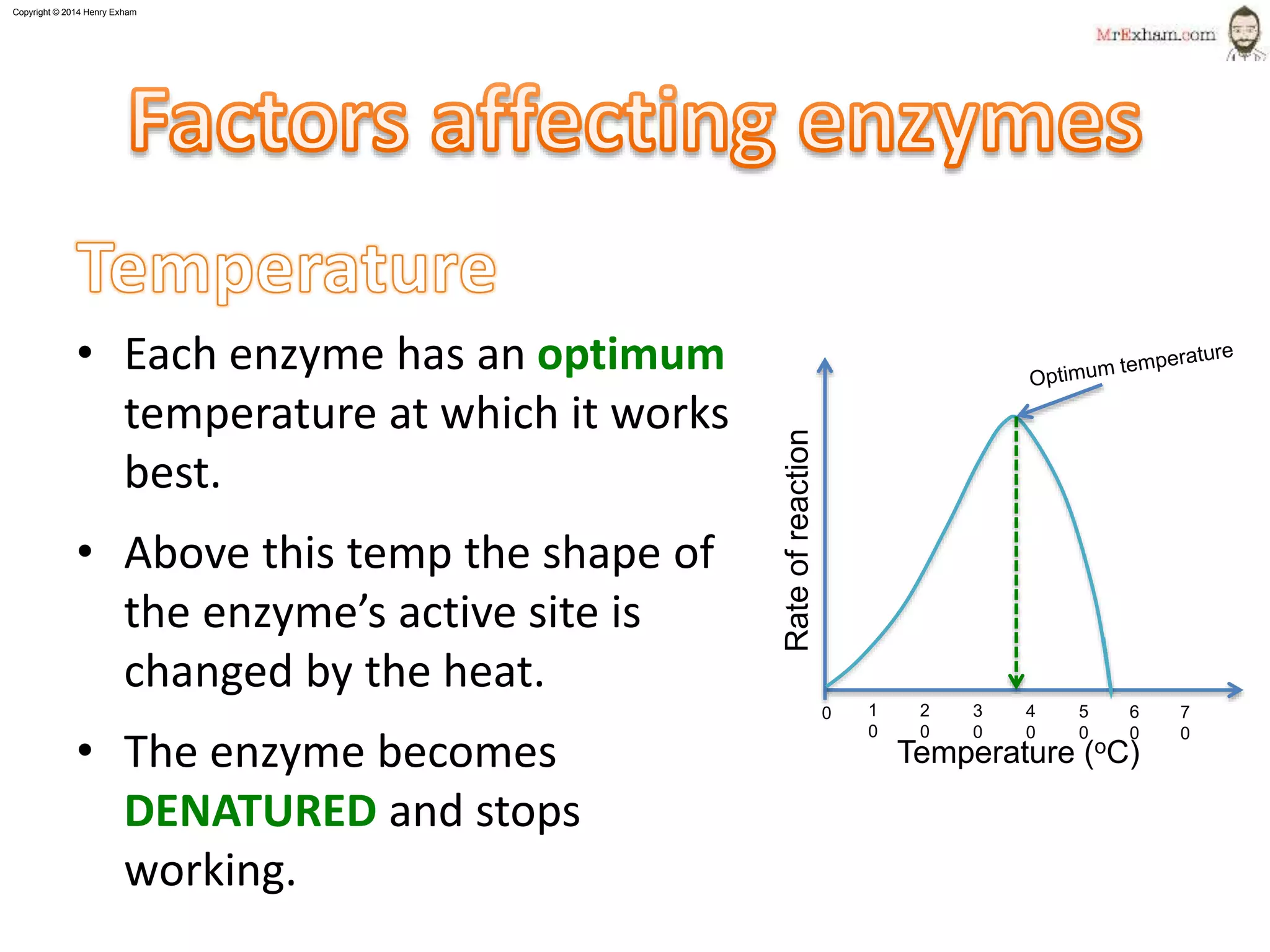
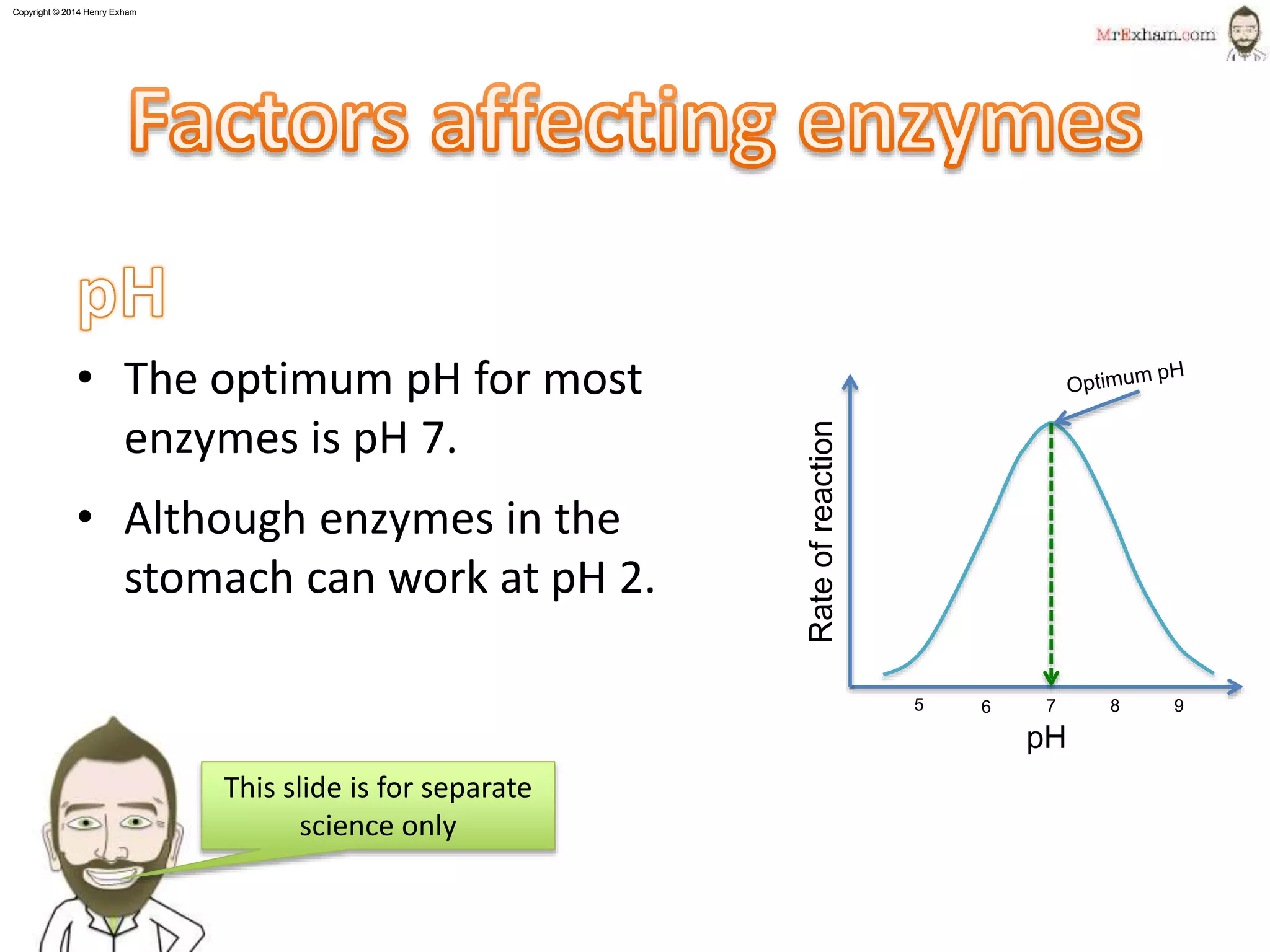
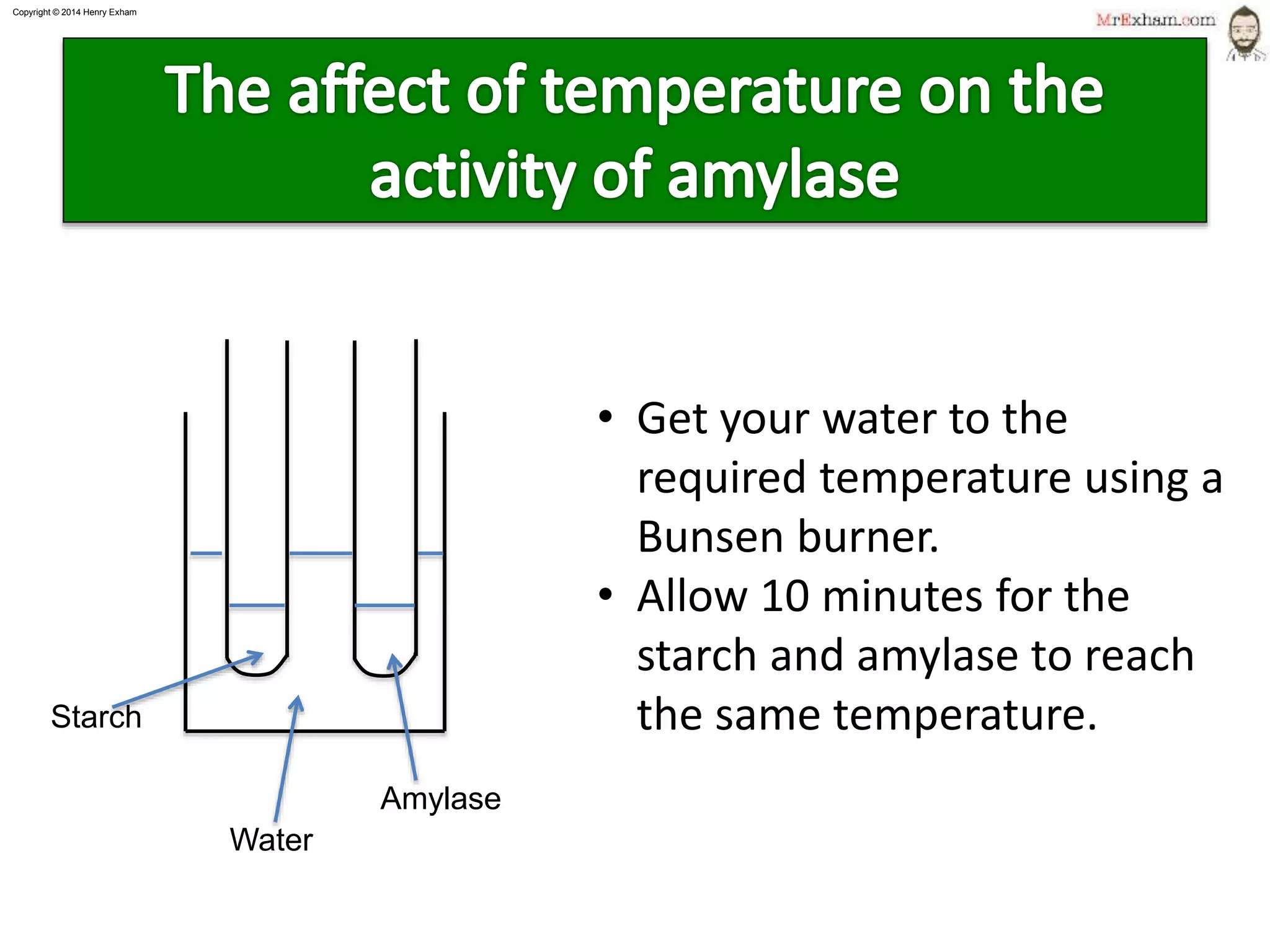
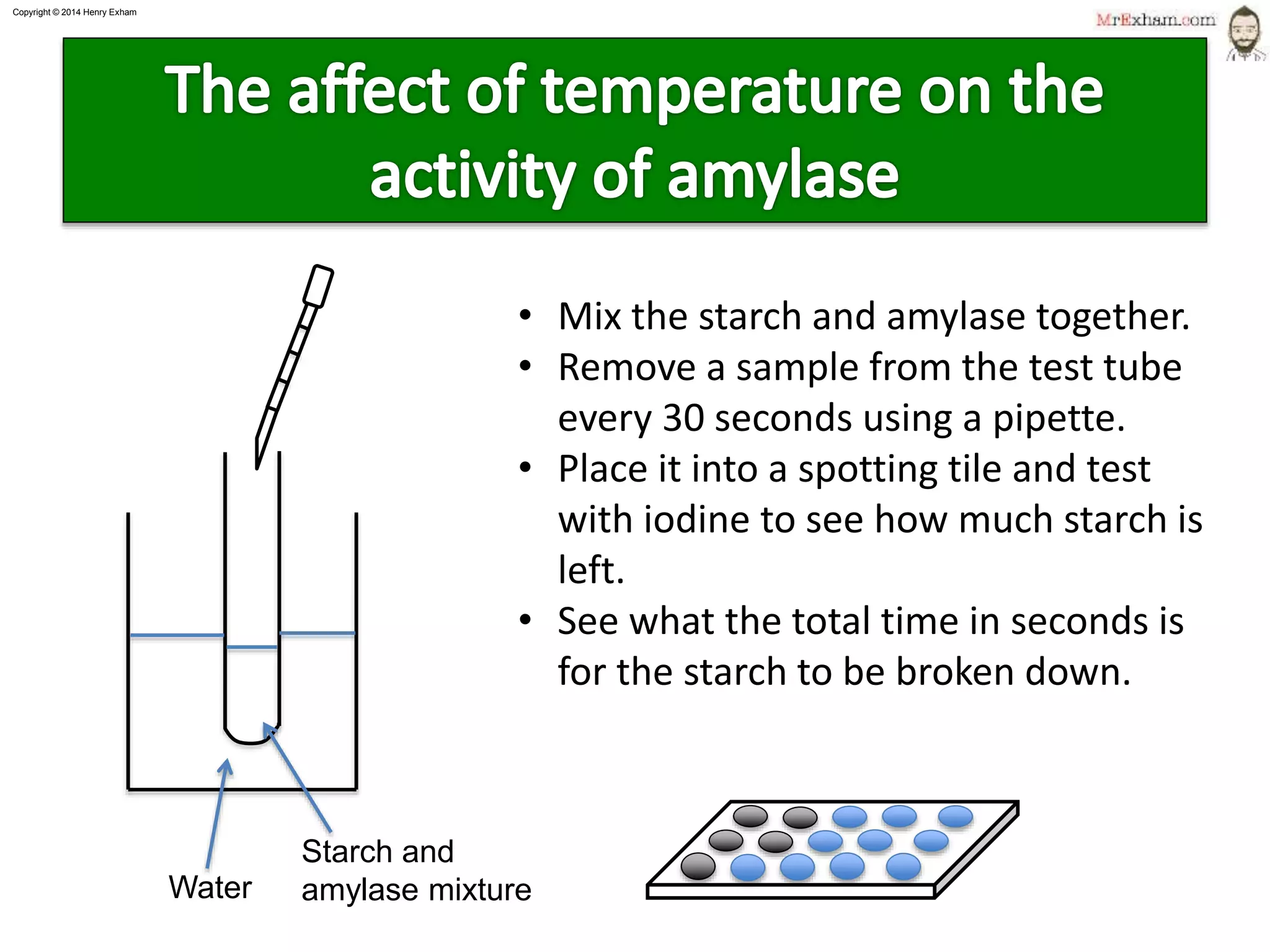
This document provides information about enzymes and how they function as biological catalysts in metabolic reactions. It discusses that enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in cells and do not get used in the reactions. The document describes how enzymes have an active site that binds to substrate molecules in a lock-and-key mechanism. It explains that temperature and pH can affect the shape of the active site and enzyme function, with most enzymes working best around body temperature and pH 7. It proposes a simple experiment using the enzyme amylase to show how reaction time is affected by temperature.