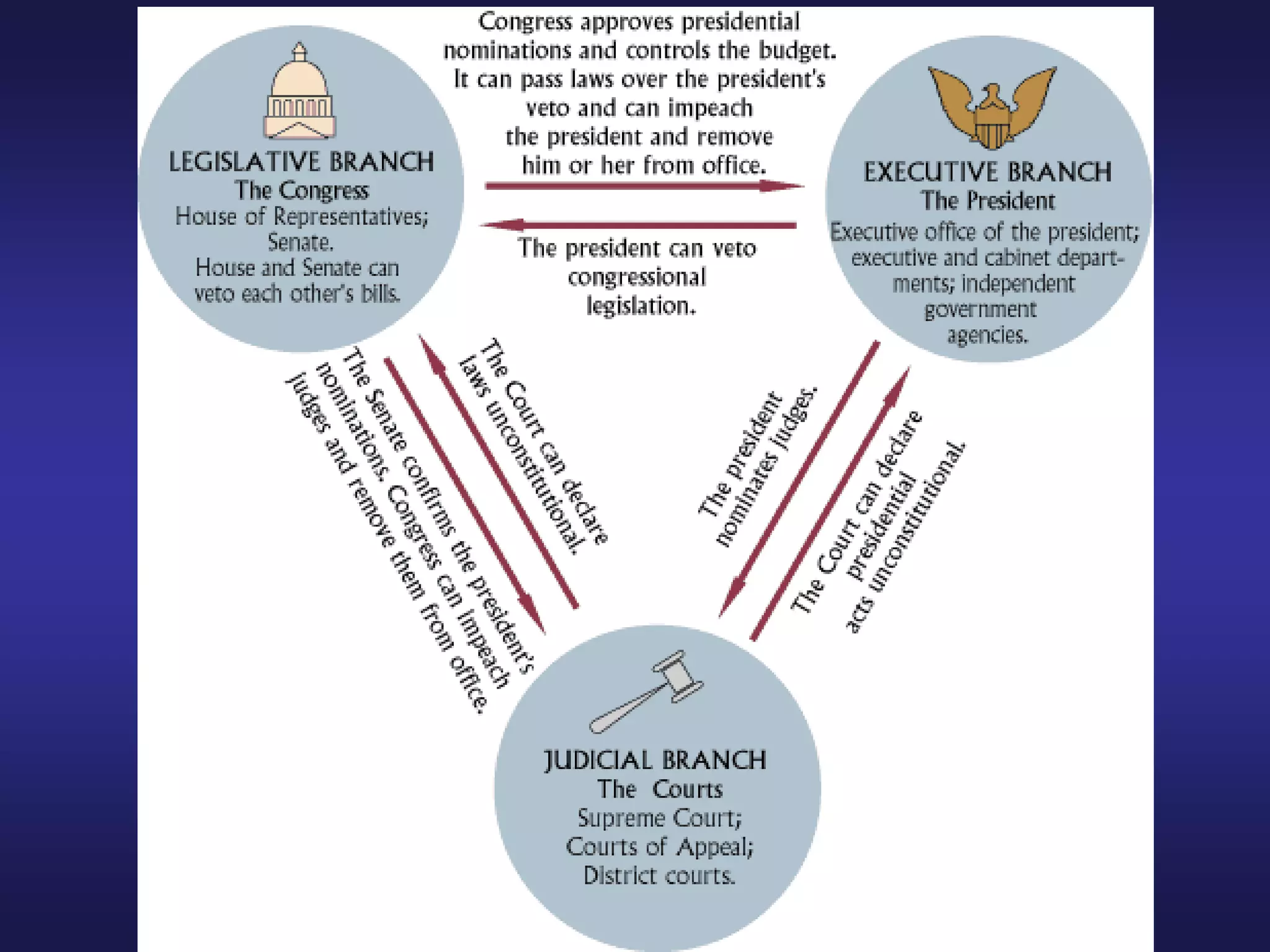
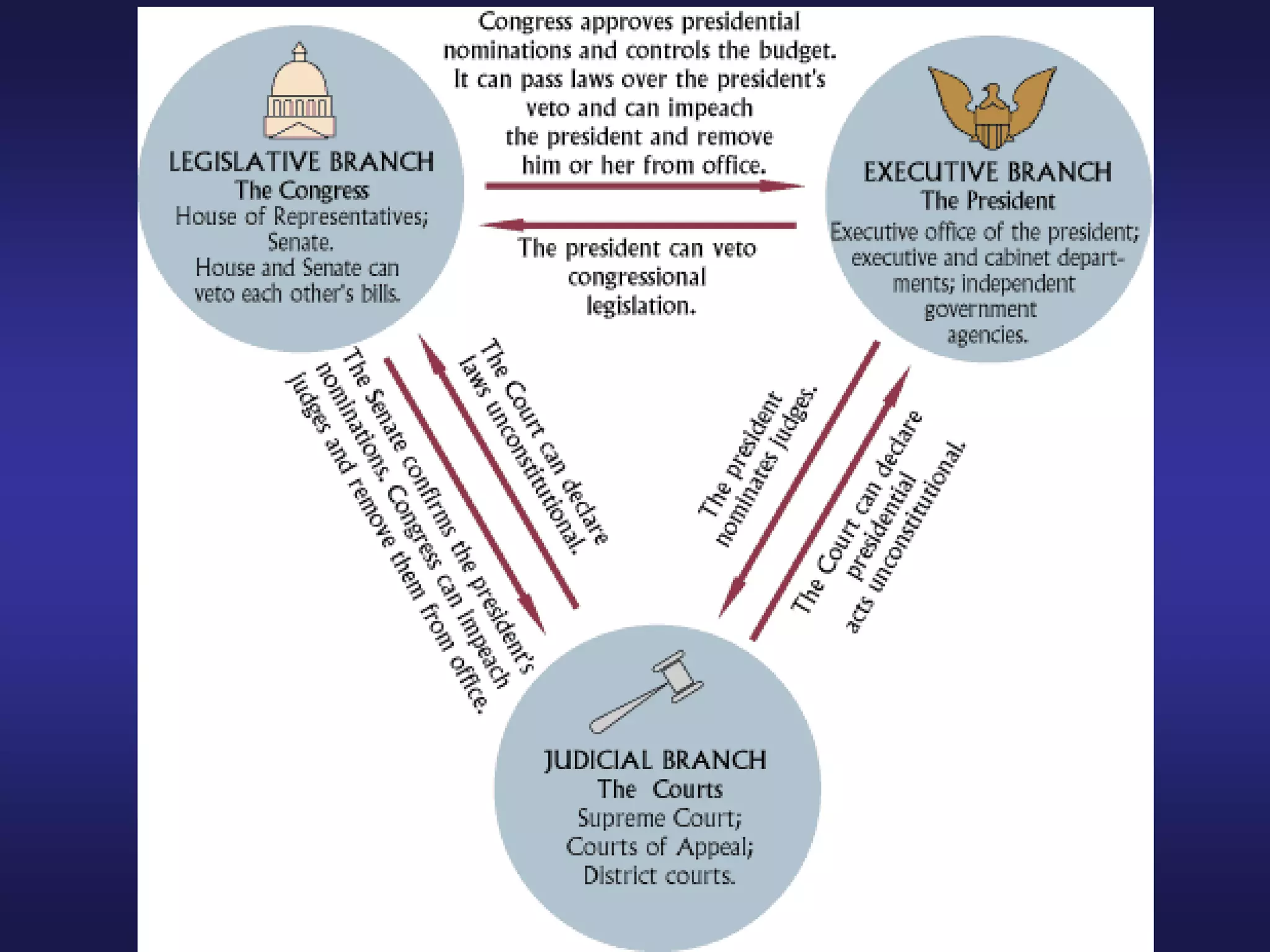
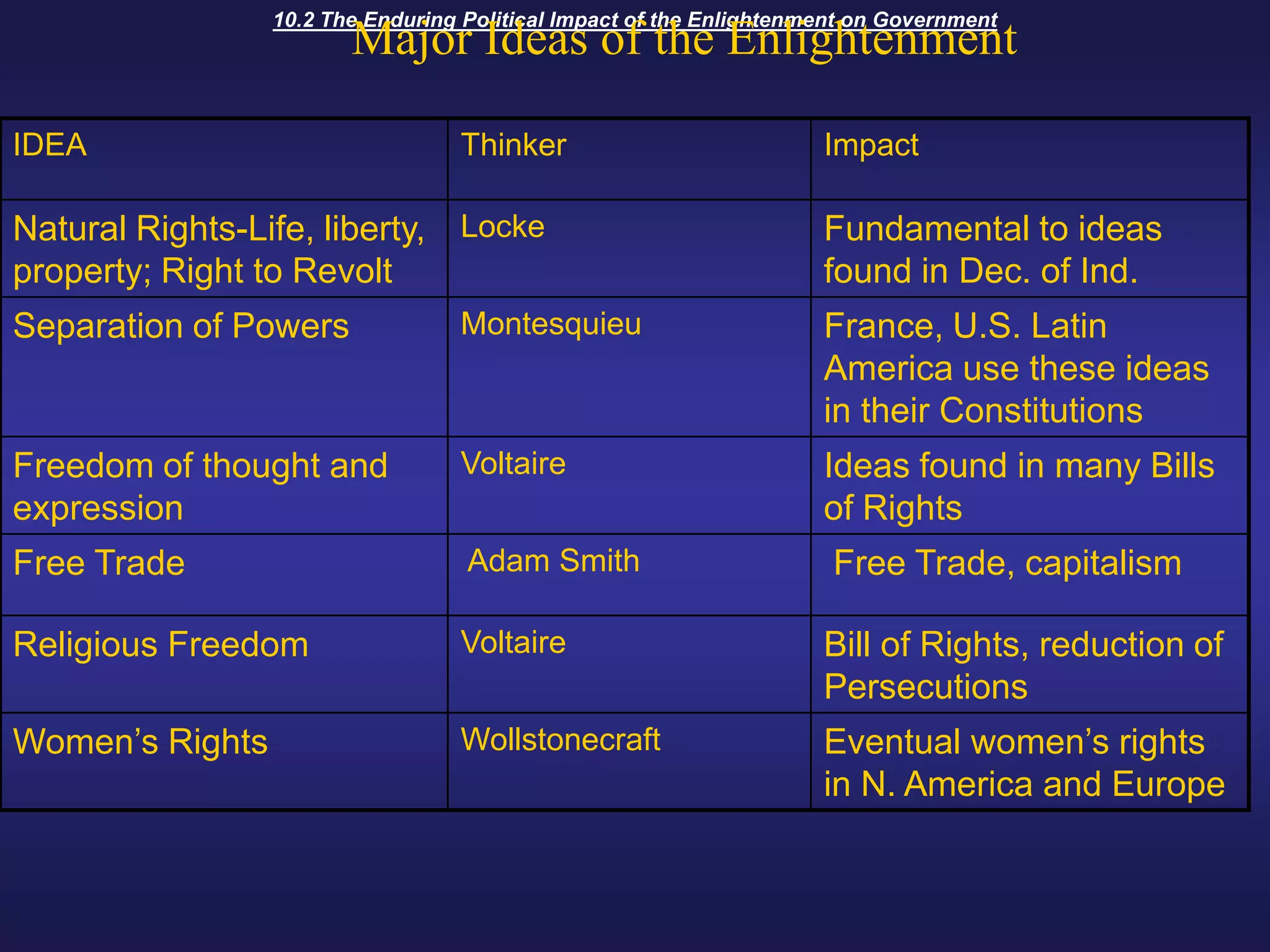
The Enlightenment promoted the use of reason and science to understand the world, influenced by thinkers like Locke and Newton. It advocated for religious tolerance in Britain and spread ideas through print culture. Voltaire, Diderot, and Beccaria used their writings to promote tolerance and reform unjust laws. Adam Smith advocated for free markets and criticized mercantilism. Montesquieu's ideas of separation of powers and checks and balances influenced the U.S. Constitution. Rousseau believed people were originally good but corrupted by society. Though most Enlightenment thinkers did not advocate for women's rights, salons run by women and works by Wollstonecraft began expanding women's role.