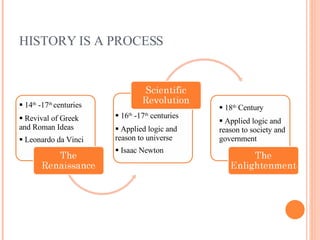
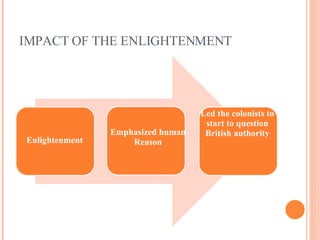
The document discusses how Enlightenment ideas from Europe impacted the English colonies in the 1700s. Enlightenment philosophers applied logic and reason to understand society, government, and the universe. Thinkers like Hobbes, Locke, Voltaire, and Montesquieu influenced revolutionary ideas by developing theories like social contract and separation of church and state. Their ideas questioning absolute rule and emphasizing natural rights and consent of the governed helped shape colonial political thought.