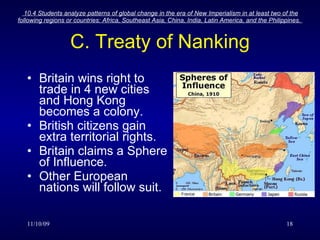
China viewed itself as the center of civilization and was culturally chauvinistic, looking down on Europe. The Opium Wars resulted from China's attempts to stop the opium trade and Britain's victory allowed it to impose trade and territorial concessions on China. China struggled against European dominance through rebellions like the Taiping Rebellion and Boxer Rebellion and attempts to modernize, but was ultimately unable to prevent European powers from colonizing parts of China and gaining spheres of influence.