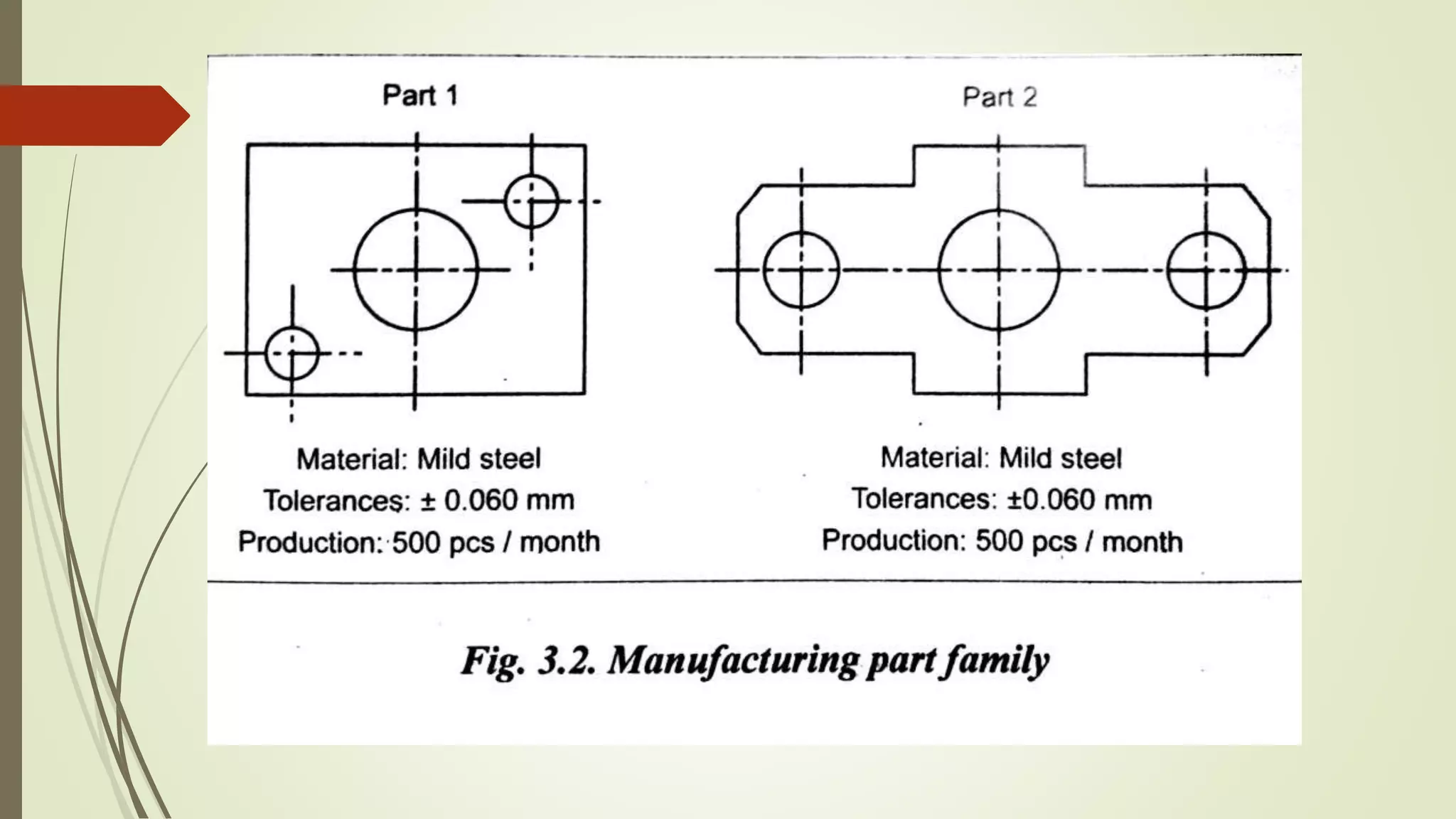
This document discusses cellular manufacturing and group technology. It describes group technology as organizing manufacturing by grouping parts with similar shapes, dimensions, or manufacturing processes. This justifies batch production and increases efficiency. Cellular manufacturing involves designing machine cells and layouts to group similar production processes together. The document discusses various part classification and coding methods used to analyze production flow and form part families based on design and manufacturing attributes. This includes visual inspection and coding schemes involving hierarchical, attribute, or decision tree codes.