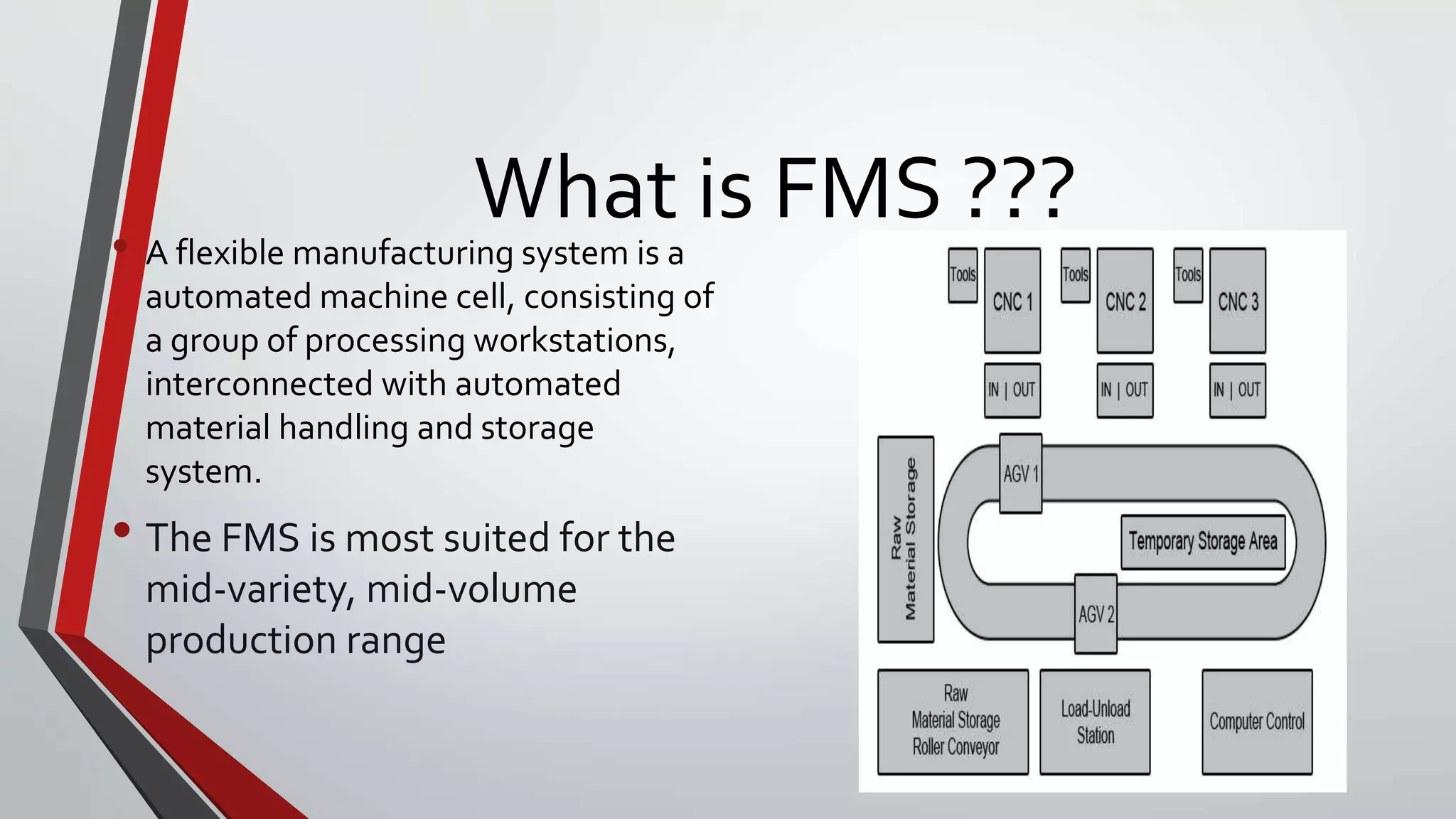
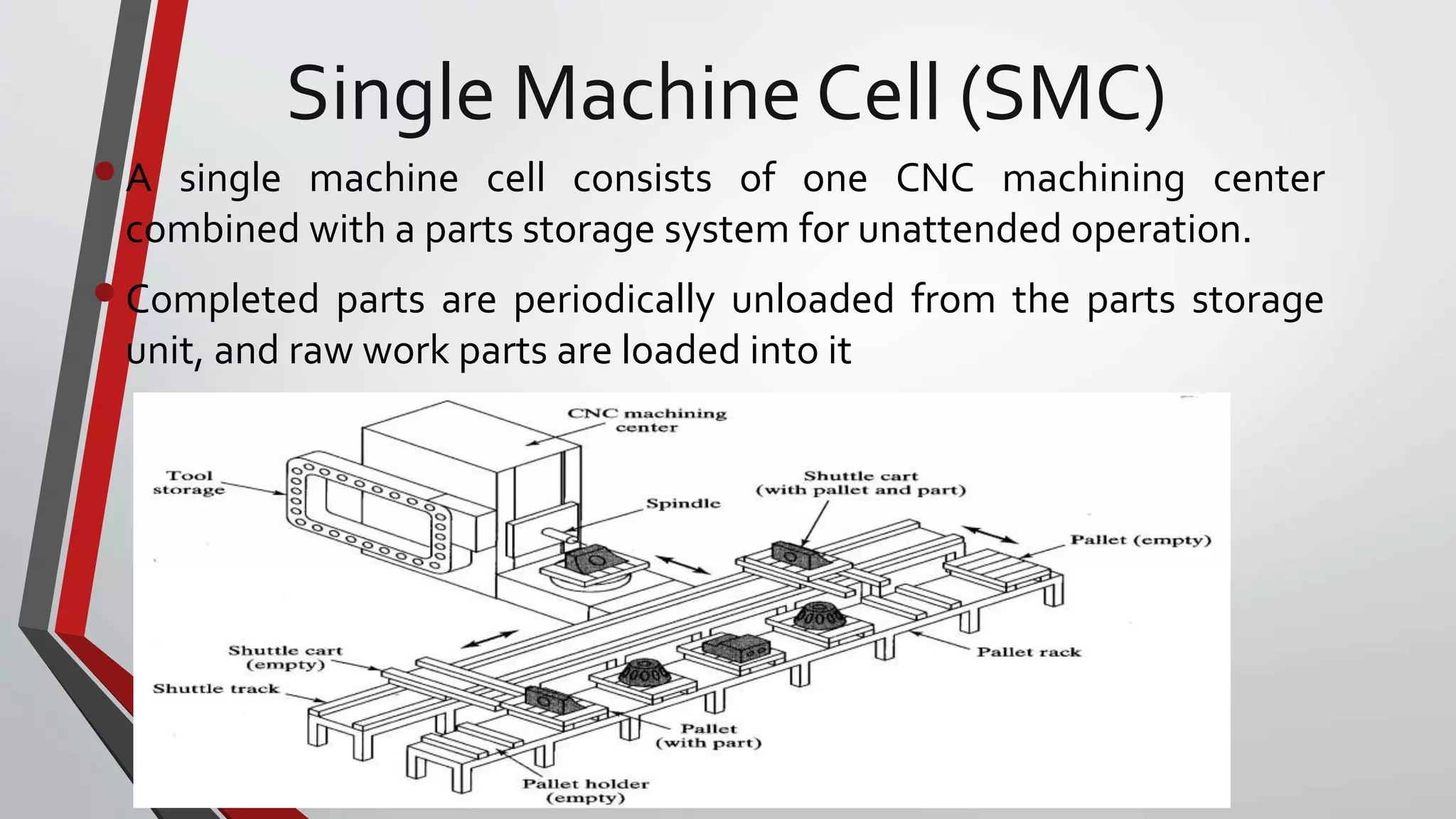
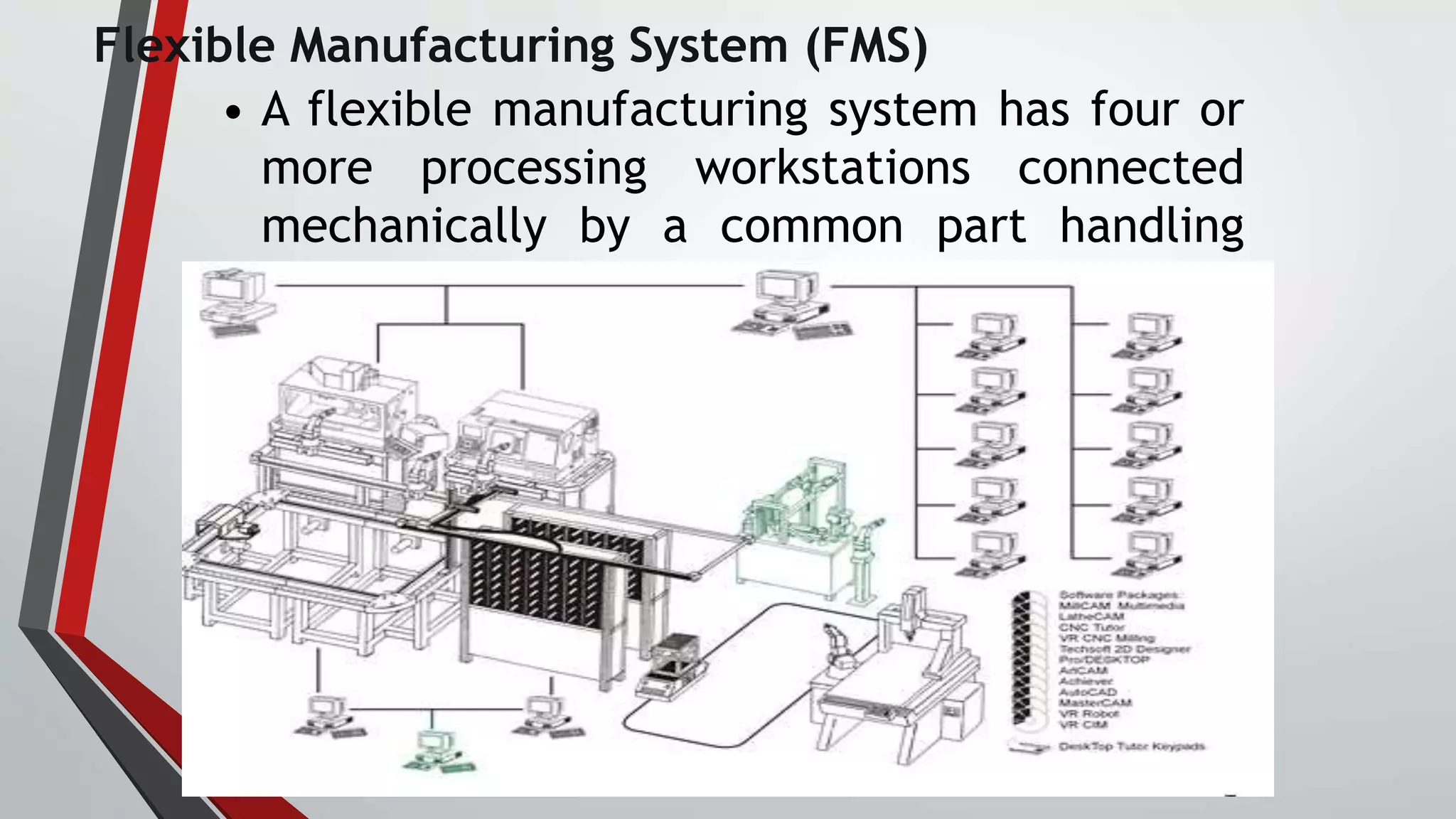
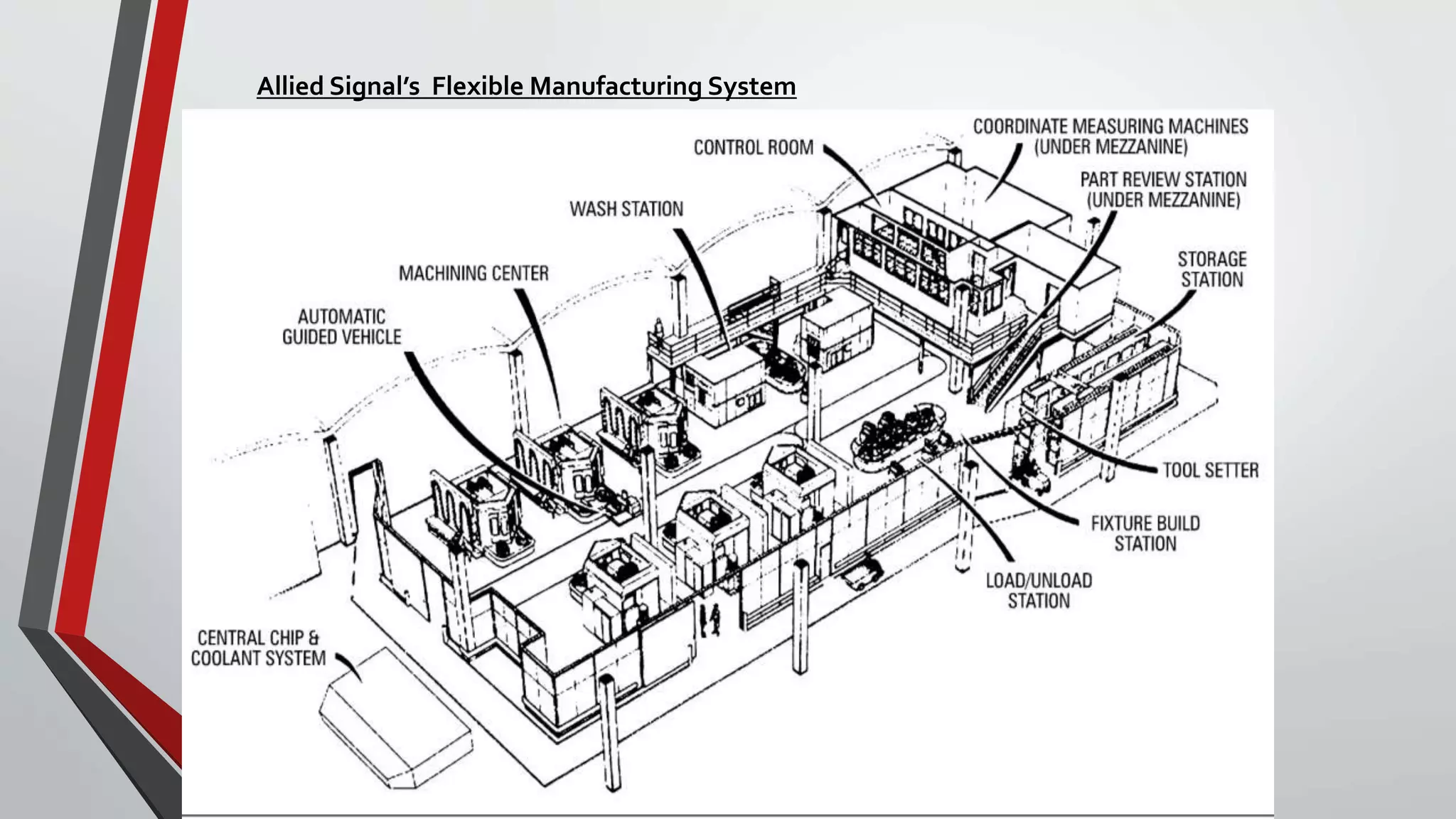
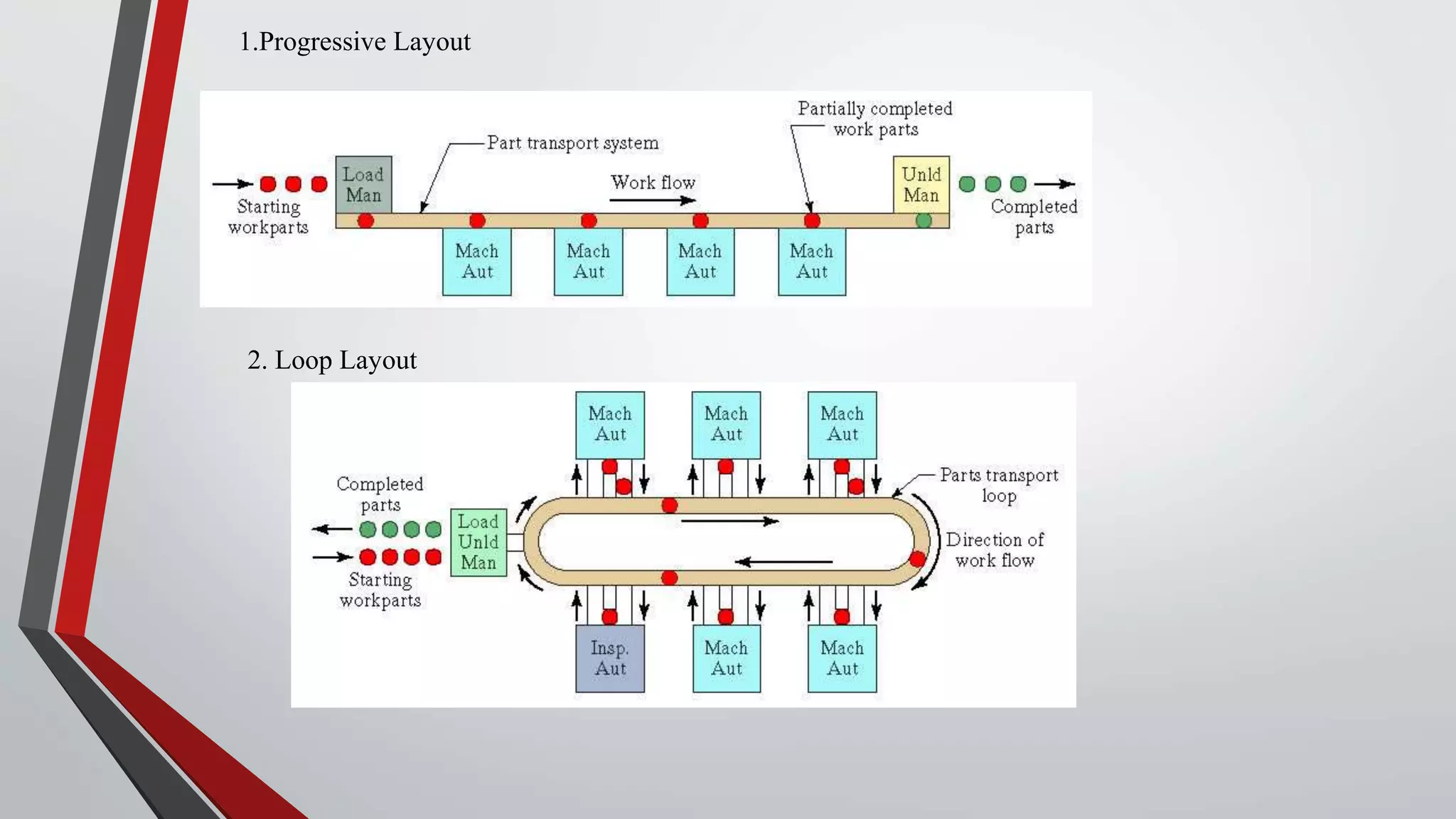
The document discusses flexible manufacturing systems (FMS). It provides a history of FMS, describing how the concept originated in the 1960s and was first implemented by companies in the US, Germany, Russia, and Japan. It defines an FMS as an automated machine cell consisting of interconnected processing workstations and automated material handling. FMS offers benefits like reduced costs, optimized cycle times, and flexibility to handle different part styles and quick changeovers. It classifies FMS based on the number of machines and describes common components and layouts of FMS. Potential applications and advantages are also outlined, along with challenges associated with implementing FMS.