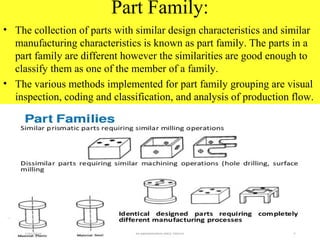
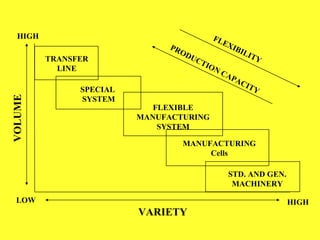
This document discusses Group Technology (GT), which is a manufacturing methodology where similar parts are grouped into families based on their design and manufacturing characteristics. The key aspects covered include:
- GT aims to identify and group similar parts that can be processed together efficiently to reduce setup times and costs.
- Parts are classified into families and production machines are arranged into cells dedicated to producing one or more part families.
- Implementing GT involves tasks like developing coding systems to classify parts, identifying part families, and rearranging machines into production cells.
- Benefits of GT include reduced lead times, setup times, inventory levels, and costs through specialized production of groups of similar parts.