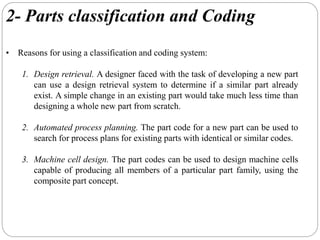
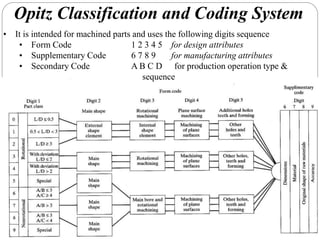
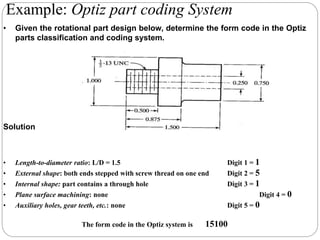
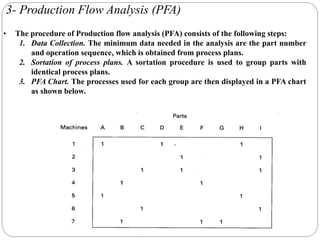
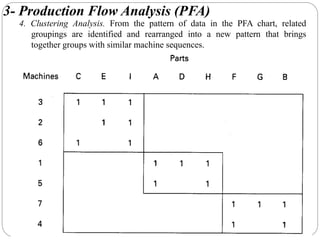
This document discusses group technology and part families. It defines group technology as identifying similar parts and grouping them into families based on their design and manufacturing characteristics. The two main tasks for implementing group technology are identifying part families and rearranging production machines into cells. There are three methods for determining part families: visual inspection, part coding systems, and production flow analysis. Part coding systems involve assigning codes to parts' design and manufacturing attributes to facilitate grouping similar parts.