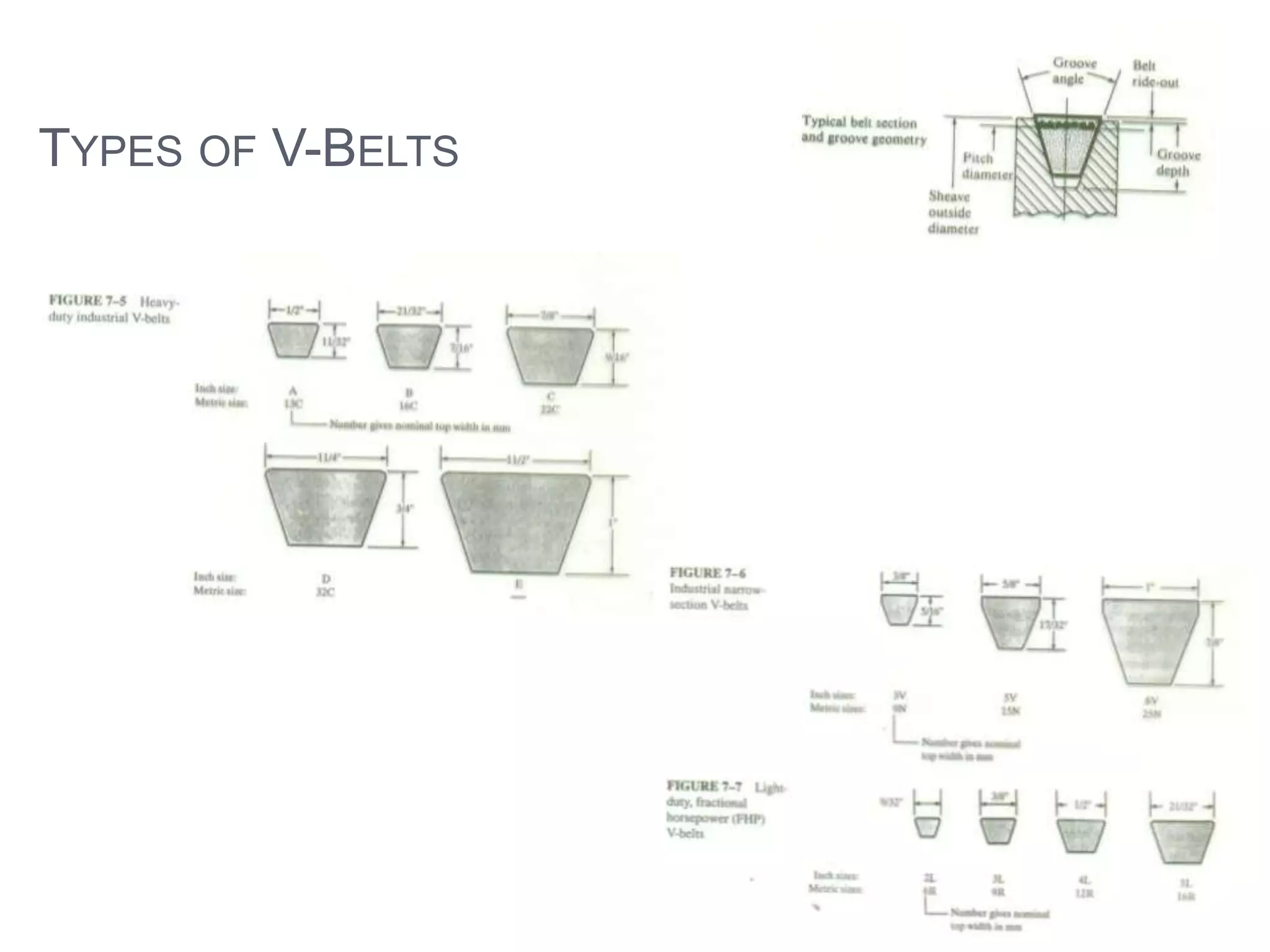
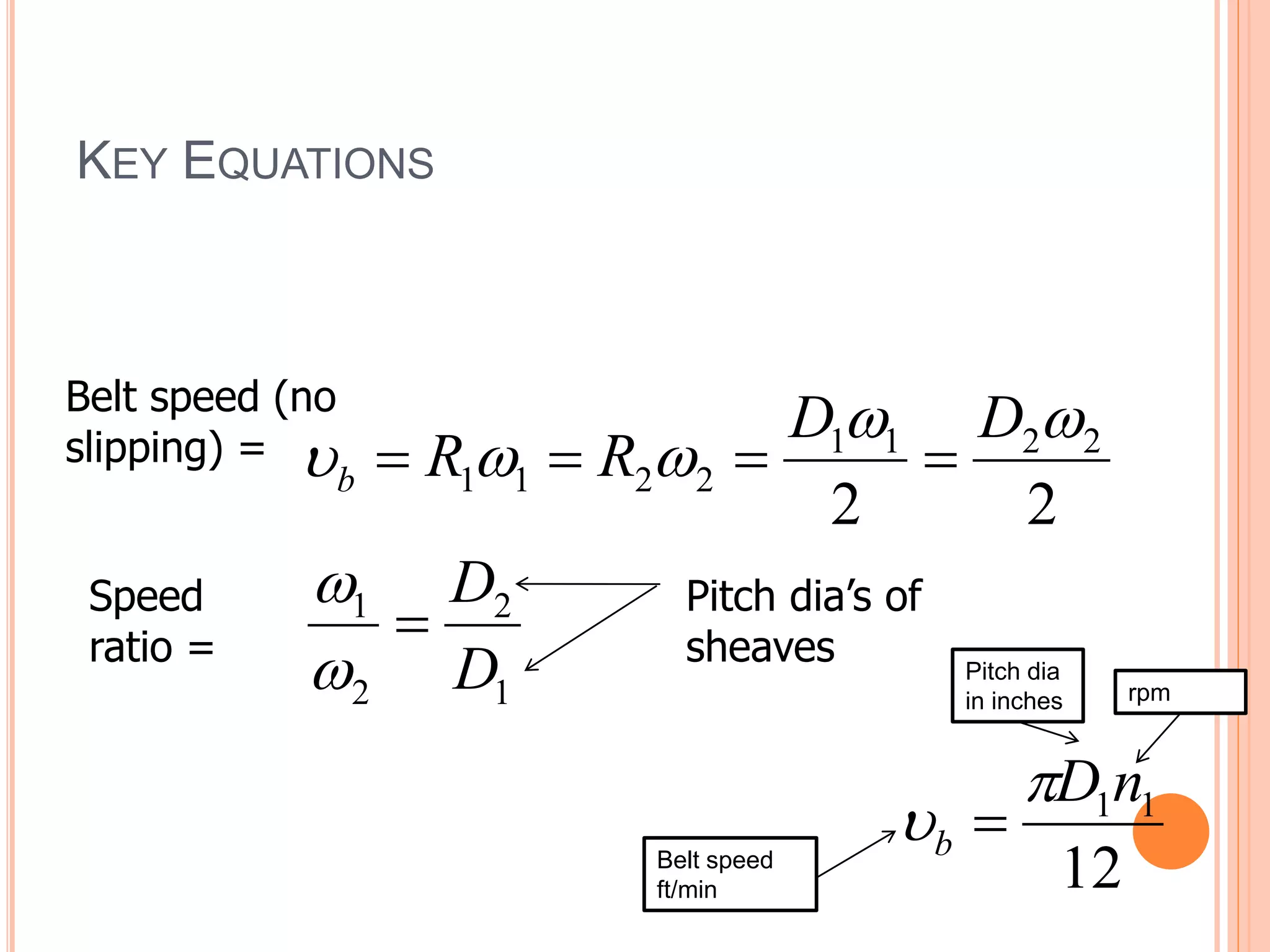
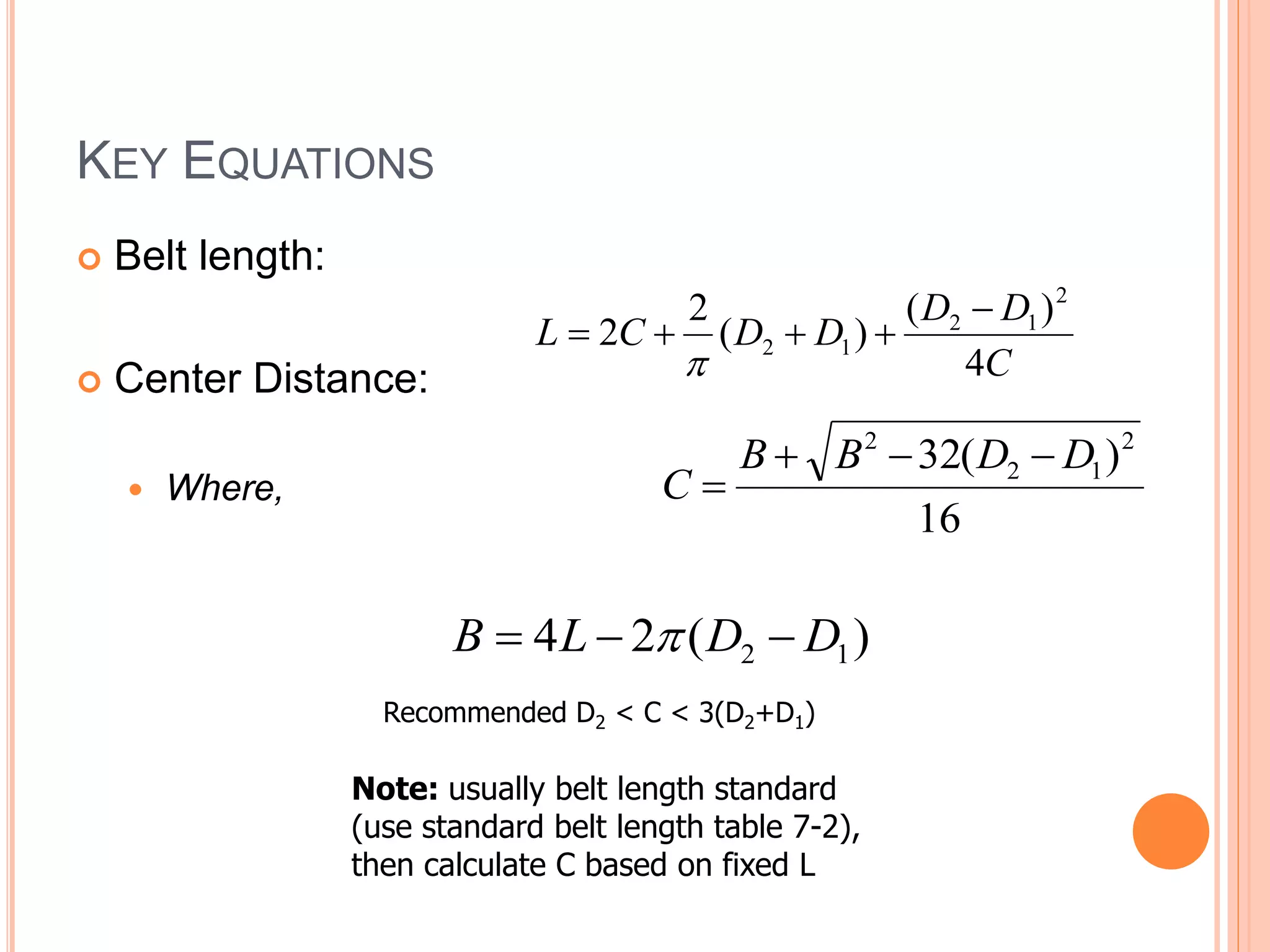
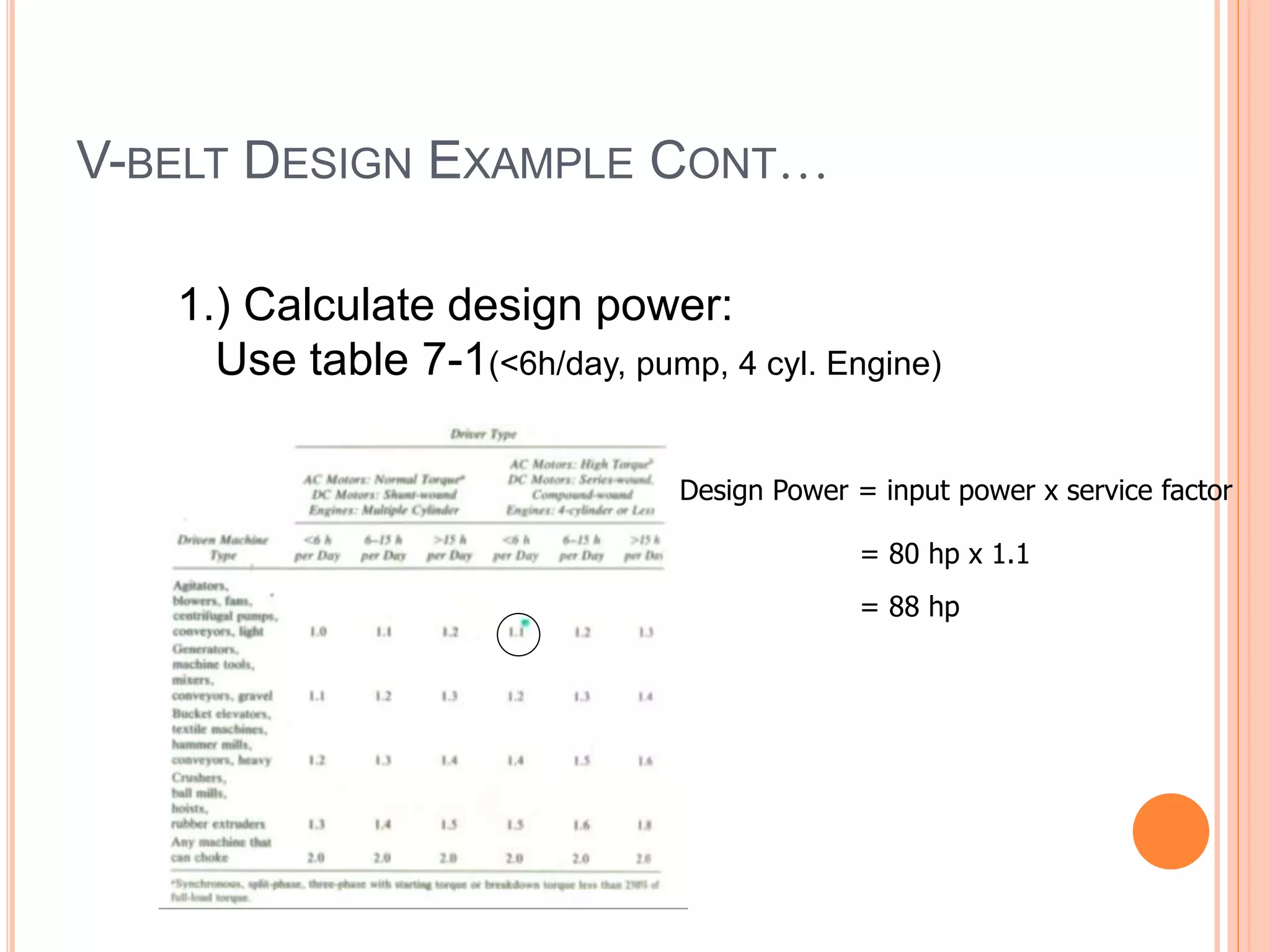
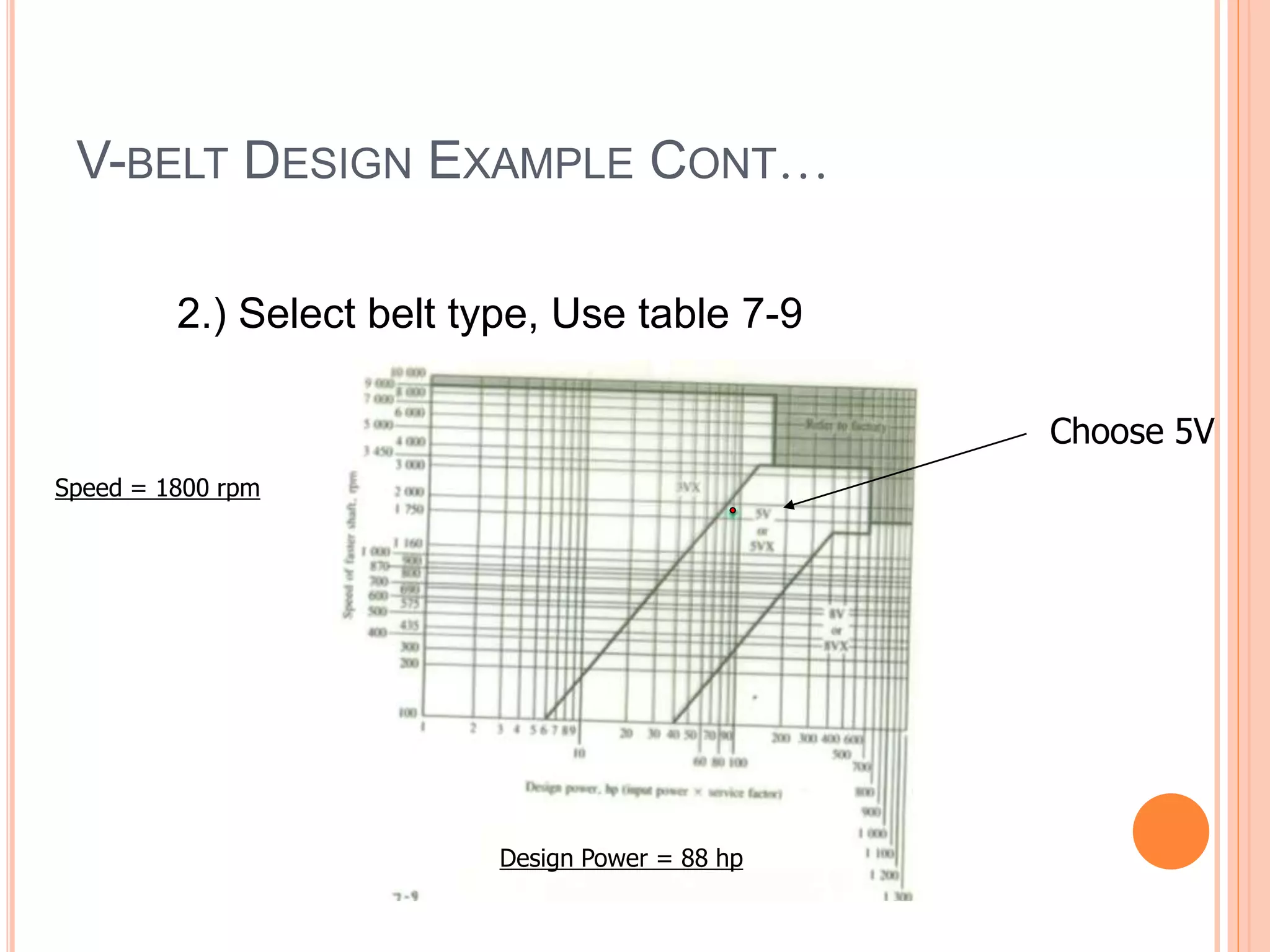
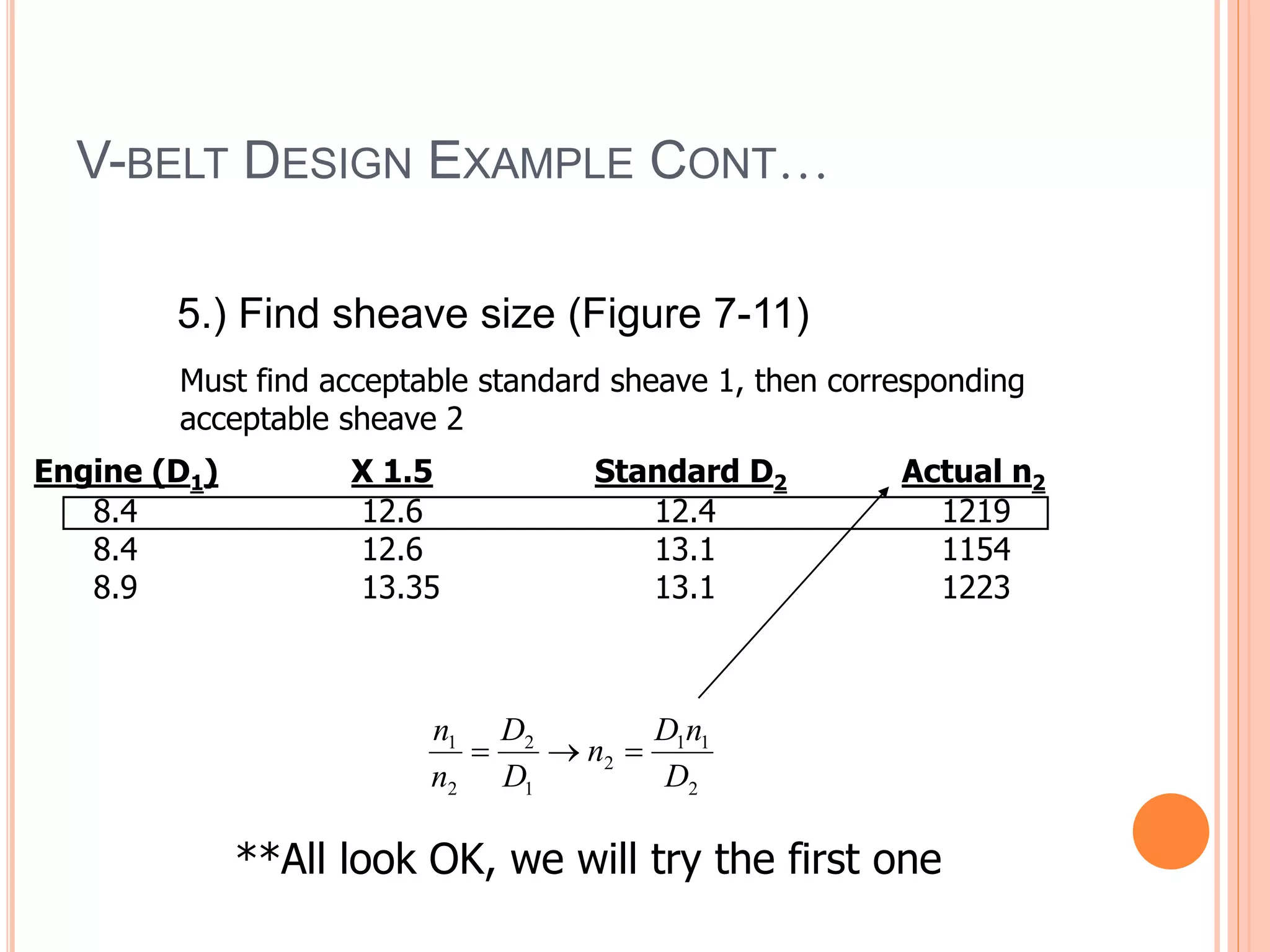
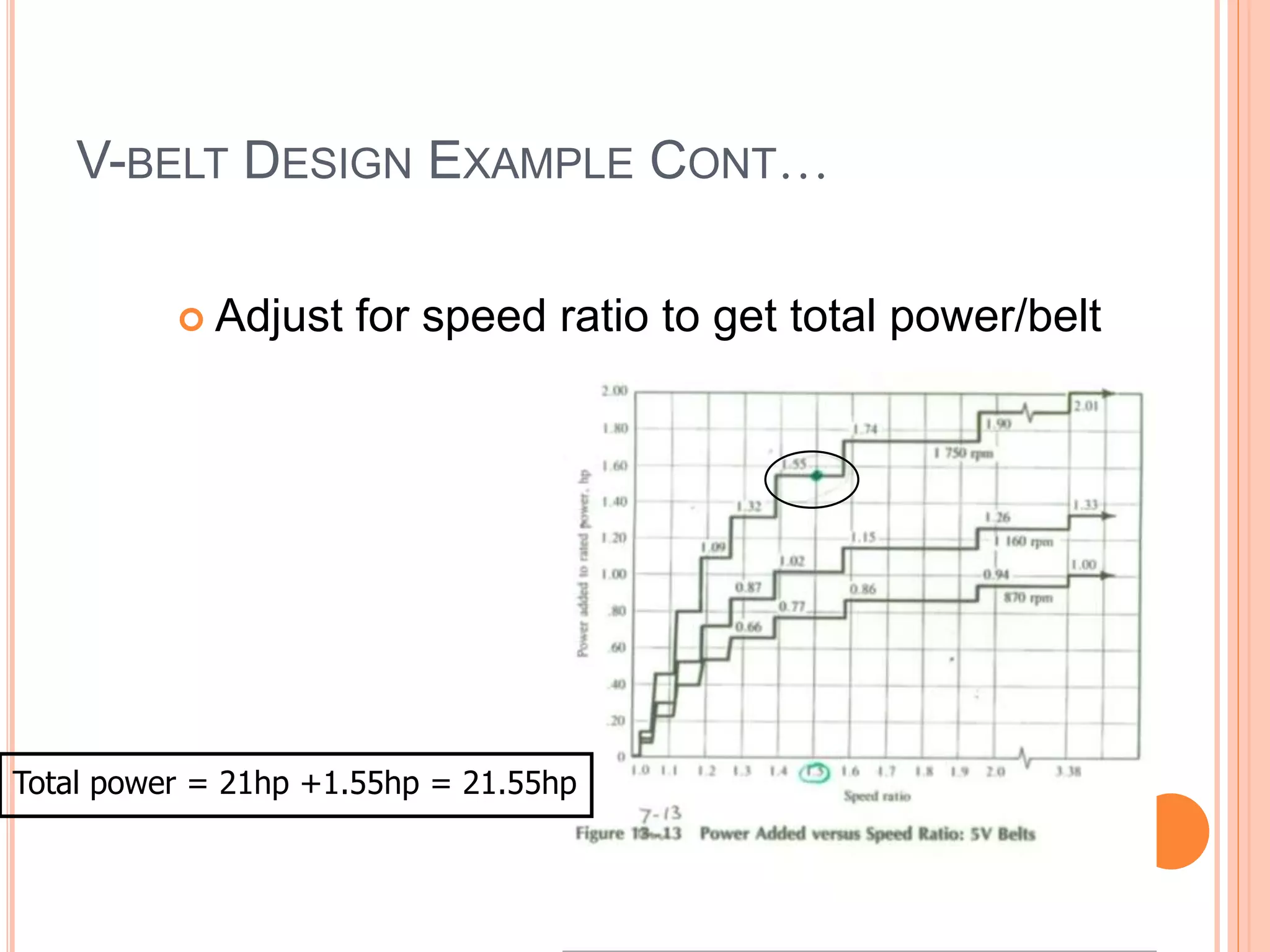
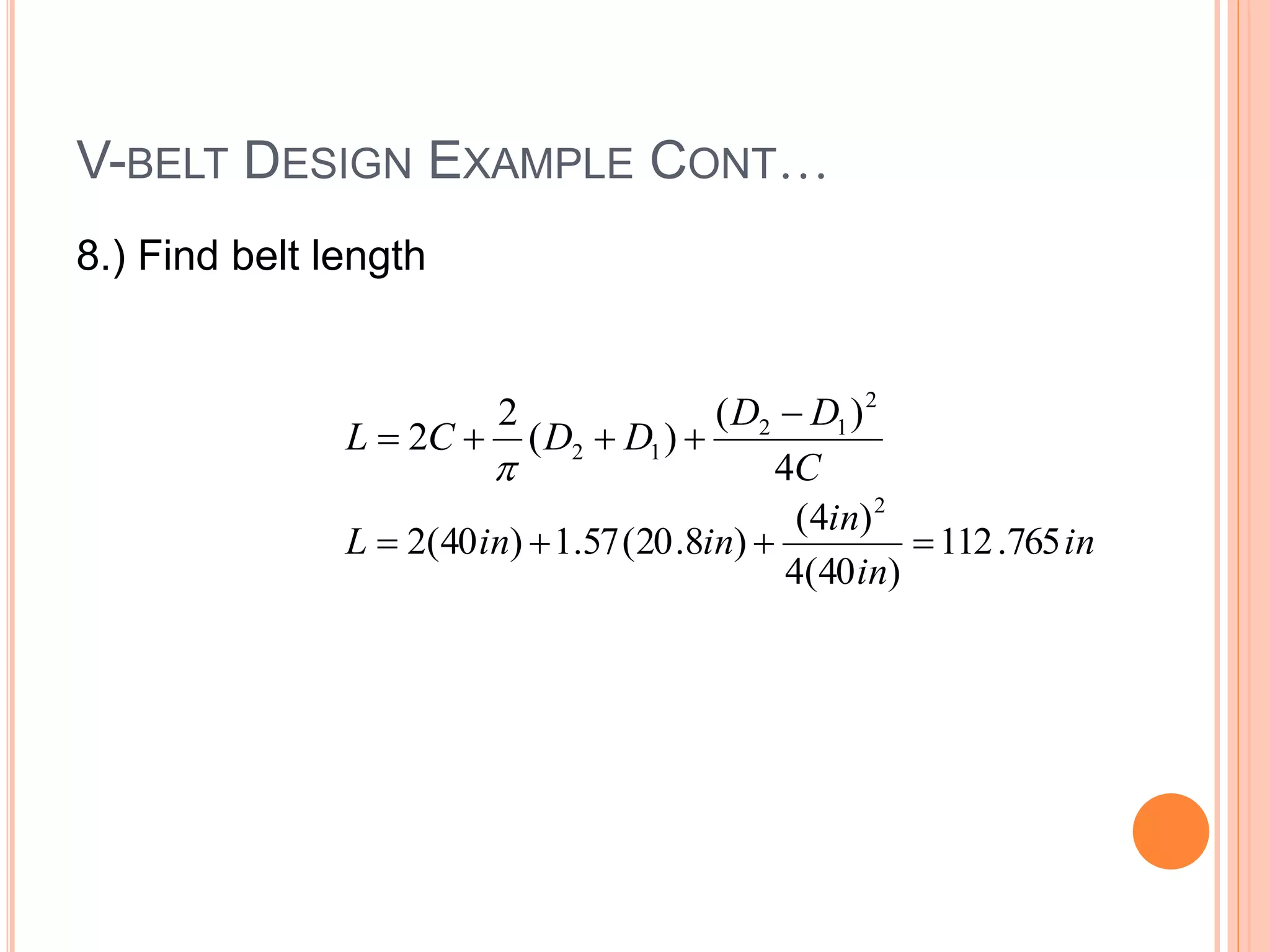
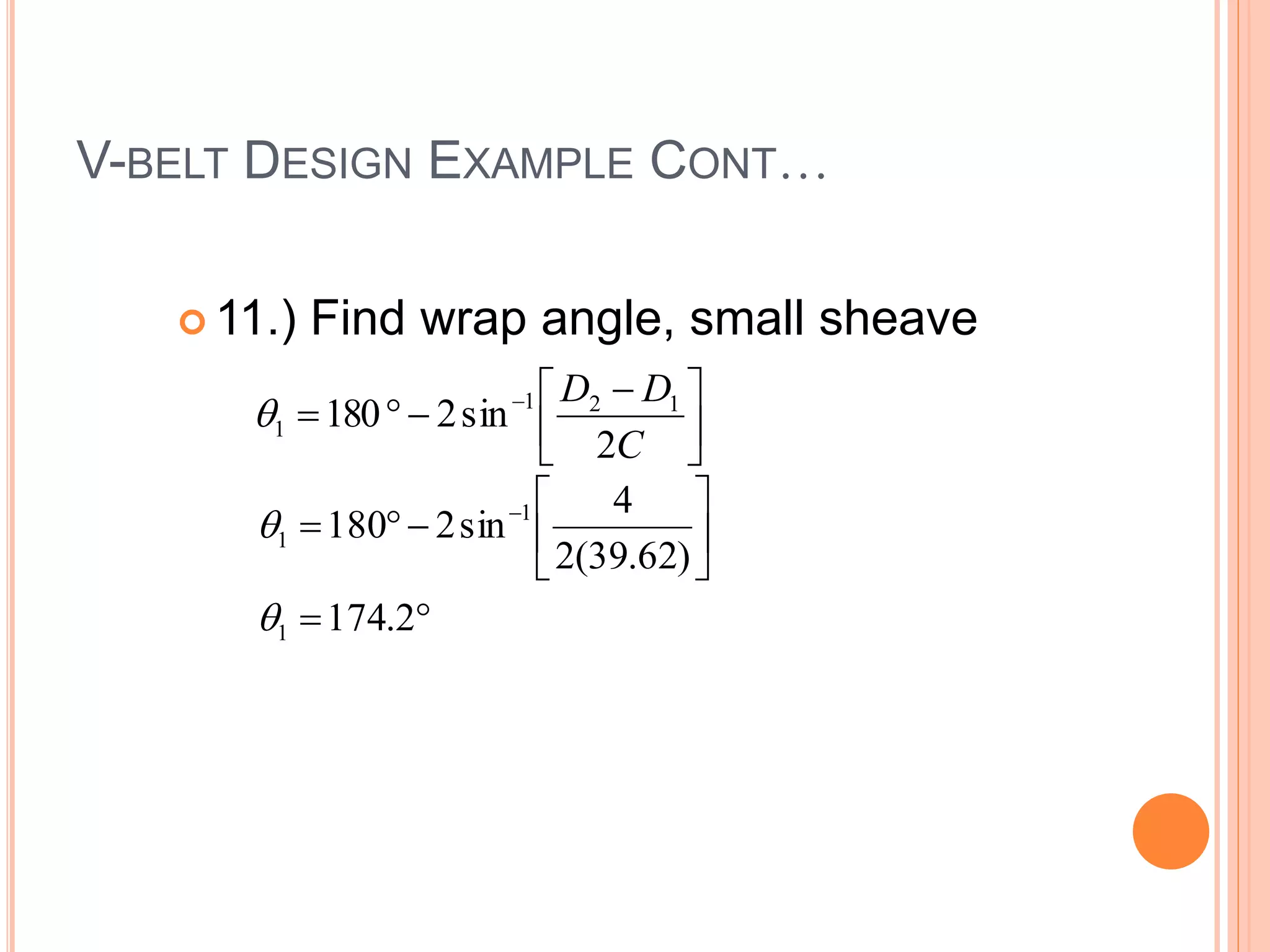
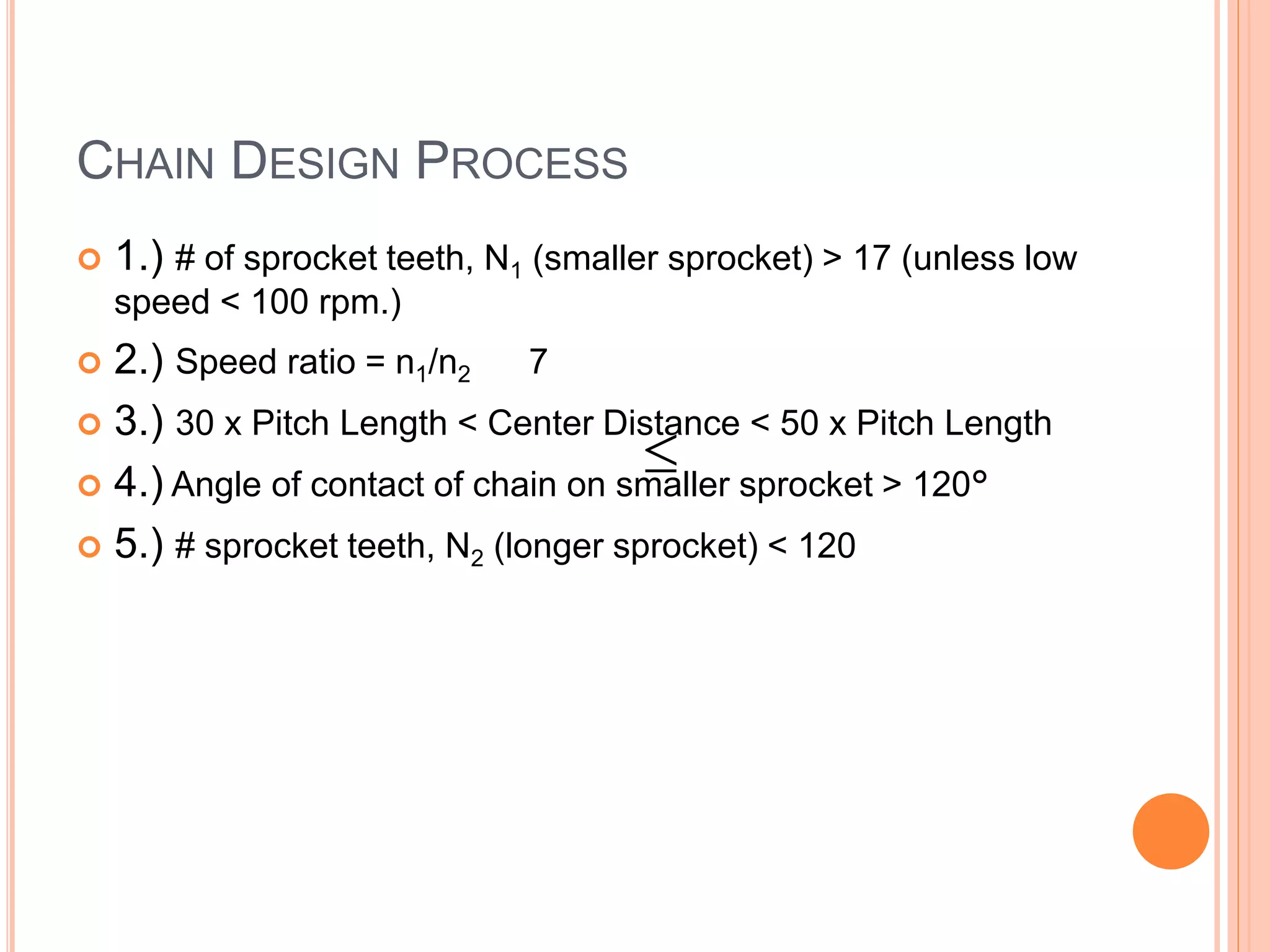
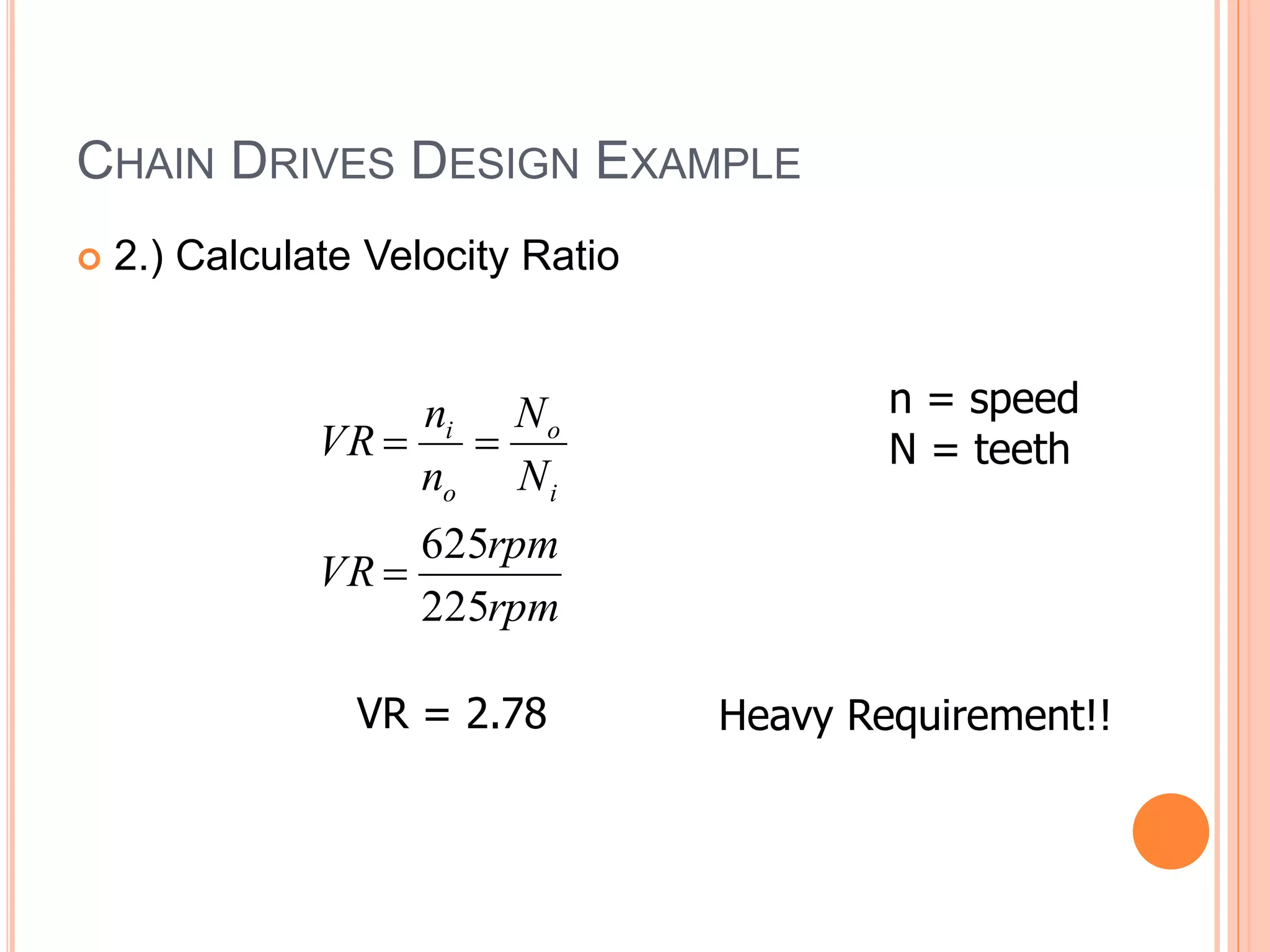
This document provides an overview of belt drives and chain drives. It discusses their applications and differences. Belt drives are used for high speed, low torque applications, while chain drives are used for low speed, high torque applications. The document then provides details on the design process for V-belt drives, including selecting belt type, calculating speed ratio, sizing sheaves, determining power rating, and selecting belt length. An example design problem is worked through step-by-step to illustrate the full V-belt drive design process. Finally, the document discusses chain drive design, including types of chains, construction, and provides an example design problem for sizing a chain drive.