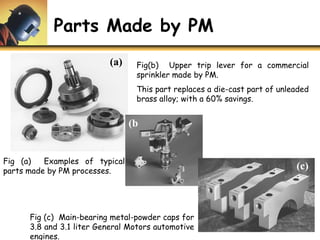
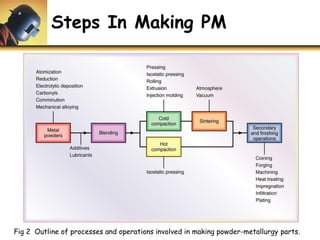
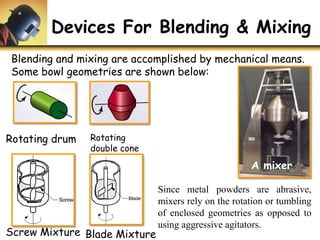
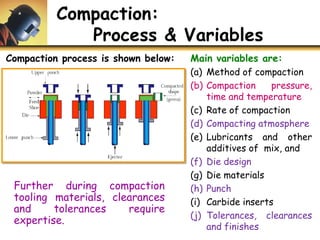
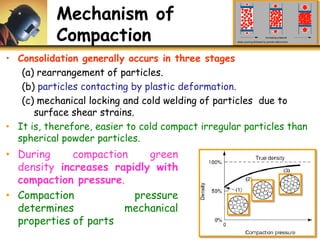
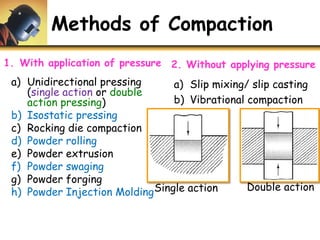
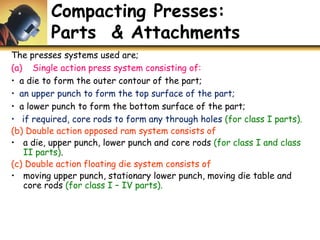
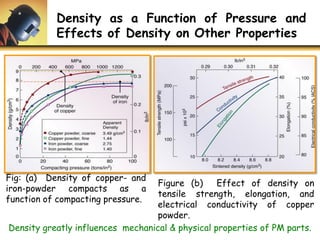
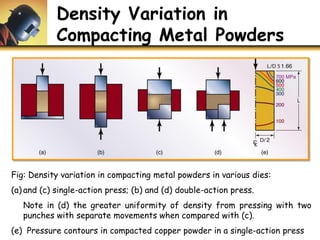
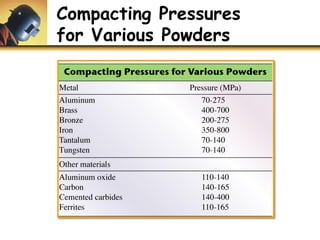
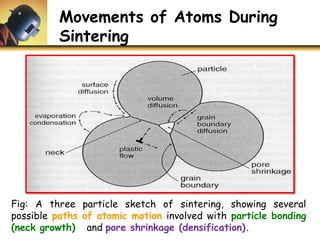
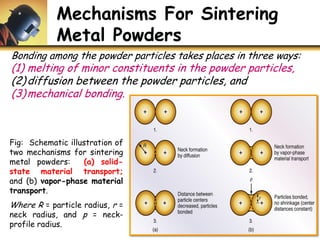
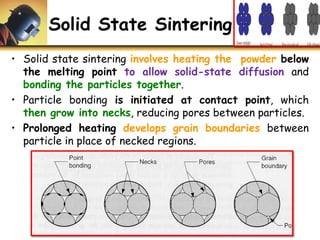
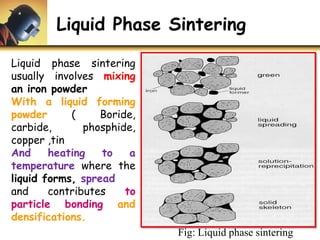
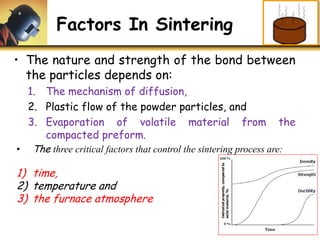
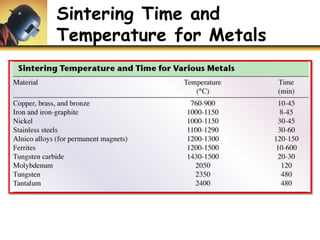
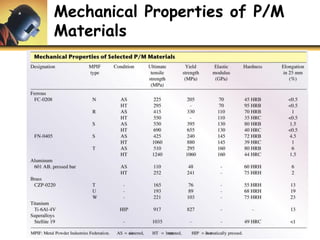
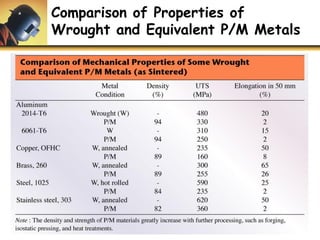
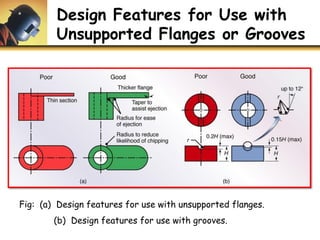
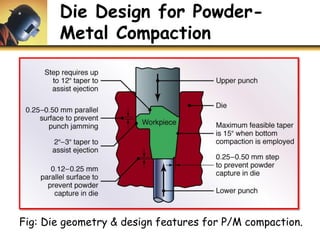
This document discusses powder metallurgy, including its definition, advantages, limitations, applications, and basic production steps. Powder metallurgy involves blending metal powders, compacting them into a desired shape, and sintering the compact to bond the particles. It allows for net-shape production, close tolerances without machining, and complex alloy compositions. Common applications include gears, bearings, and electrical contacts. The basic steps are powder production, blending, compaction in a die, and sintering to densify and strengthen the part. Design considerations for powder metallurgy parts include simple shapes, adequate wall thickness, and avoiding undercuts.