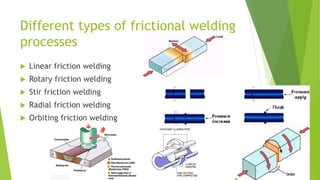
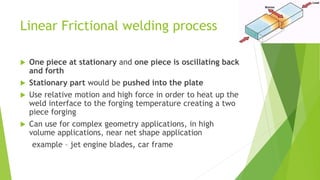
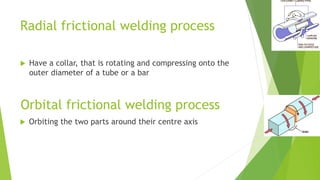
Frictional welding is a solid-state welding process that uses relative motion and high force between two contacting workpieces to generate heat through friction and form a joint. There are different types of frictional welding processes defined by the motion used - linear, rotary, stir, radial, and orbital friction welding. Frictional welding produces joints with low surface impurities and narrow heat-affected zones. It can join similar and dissimilar metals for applications in automotive, aerospace, consumer products, medical, and other industries.