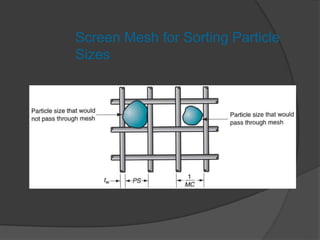
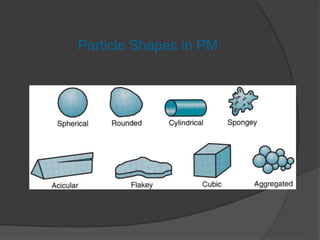
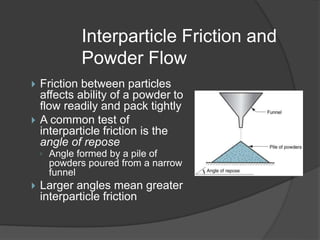
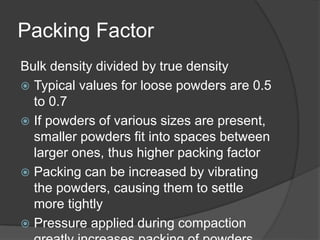
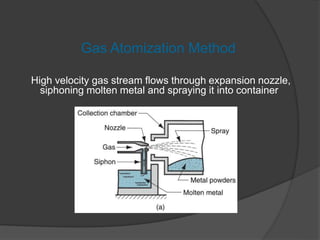
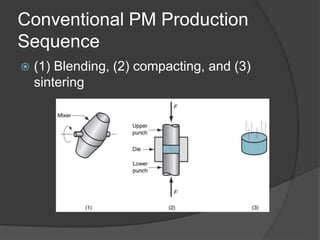
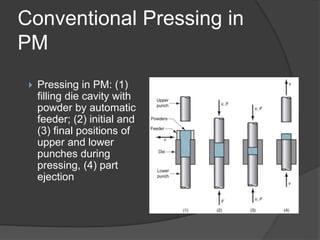
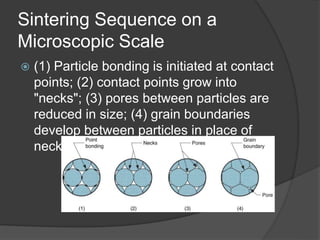
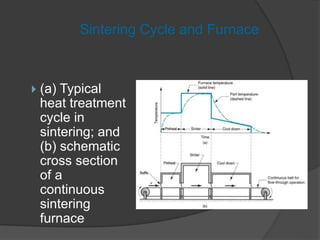
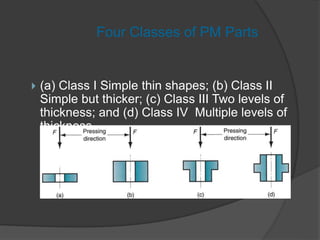
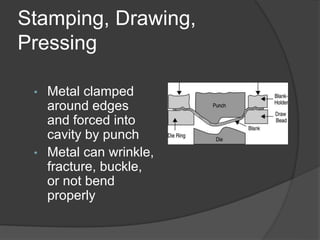
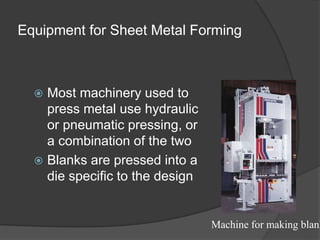
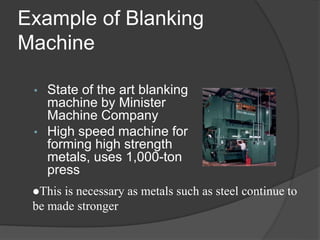
This document provides an overview of powder metallurgy, including the production of metallic powders, conventional pressing and sintering techniques, and alternative pressing methods. The key steps in conventional powder metallurgy are (1) blending and mixing powders, (2) compacting the powders using pressing, and (3) sintering the compacted parts at temperatures below the melting point to bond the particles. Common powder metallurgy materials include iron, steel, aluminum and their alloys. Powder metallurgy is well-suited for producing net-shape or near-net-shape parts like gears, bearings, and fasteners in large quantities.