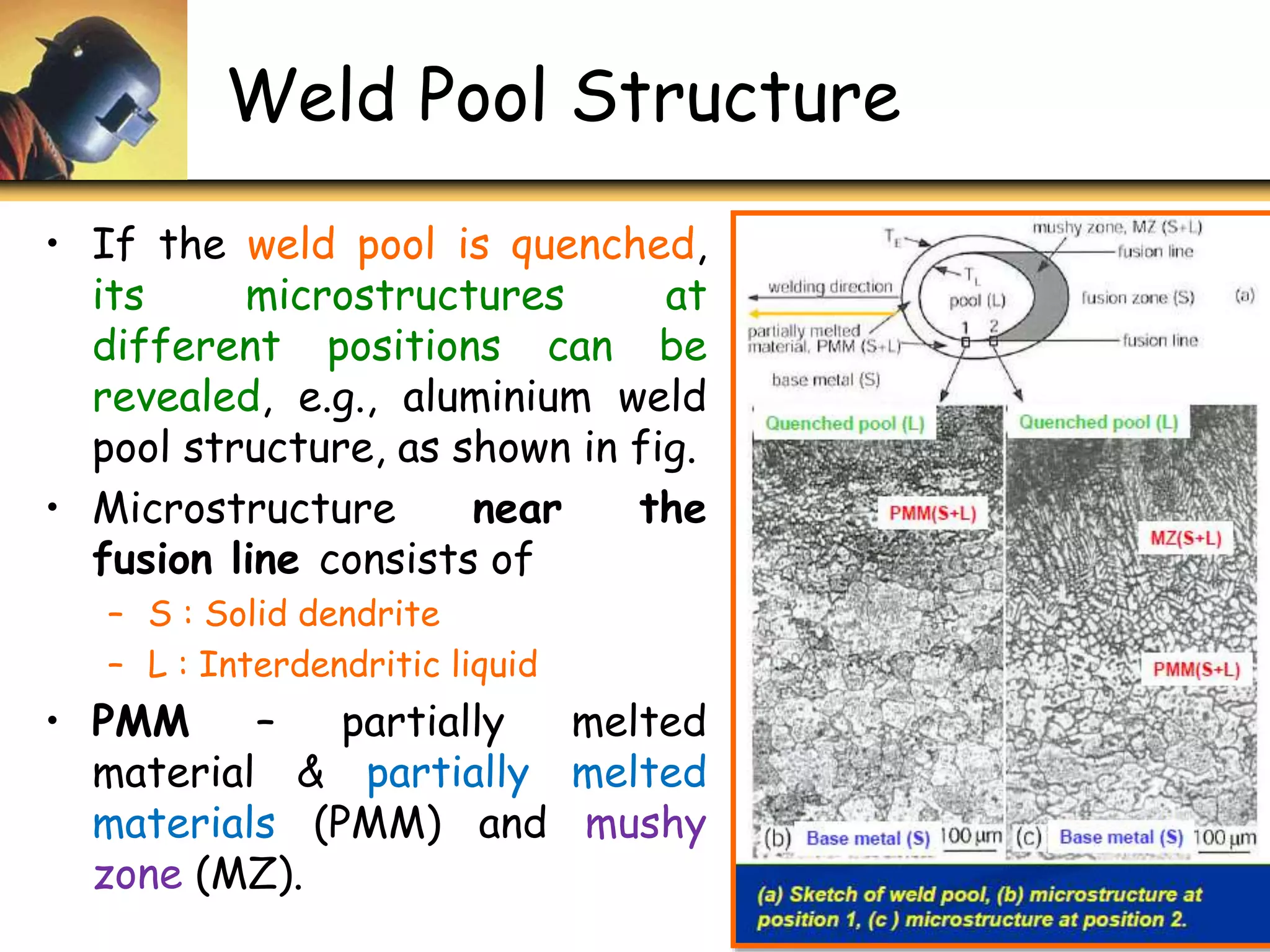
This document discusses welding metallurgy and the structure of fusion welds. It describes the different zones that make up a typical fusion welded joint, including the fusion zone, weld interface, heat affected zone, and base material. It explains how the microstructure varies across these zones due to melting and solidification processes during welding. Factors like welding parameters, heat input, and joint geometry are described as influencing weld pool shape and grain structure. The concept of thermal severity number is introduced as a way to assess cracking susceptibility based on total plate thickness.