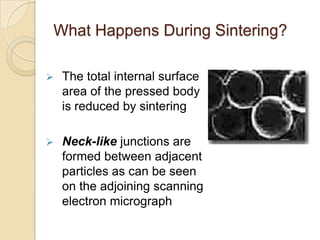
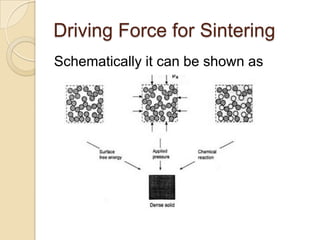
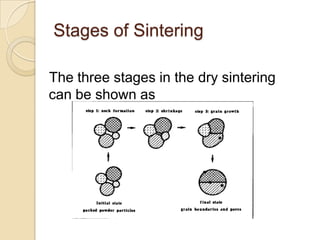
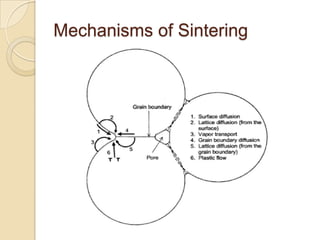
Sintering is a process that uses heat to consolidate powder materials into a solid form without melting them. There are three main stages of sintering: initial bonding and neck formation between particles, densification and pore shrinkage, and final grain growth. The driving forces for sintering include reducing surface curvature, applied pressure, and chemical reactions. Key parameters that affect sintering include powder properties, consolidation method, firing temperature and atmosphere. The main mechanisms are surface, lattice, and grain boundary diffusion which allow atoms to migrate and bonds to form between powder particles over time.