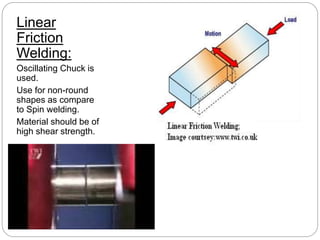
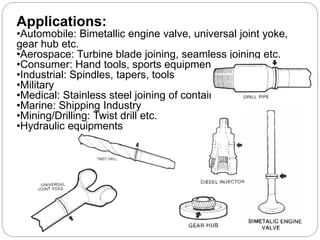
Friction welding is a solid state joining process that uses mechanical friction to fuse materials together without melting. There are several types of friction welding including spin welding, linear friction welding, friction surfacing, and friction stir welding. The process involves rotating or oscillating one material against another under pressure to generate heat and plasticize the surfaces. Friction welding produces high quality welds with small heat affected zones and without the need for filler metals. It has advantages over other welding methods like lower heat input and cost. However, it is generally limited to flat geometries and small parts.