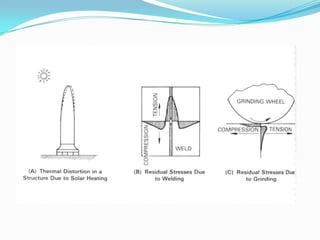
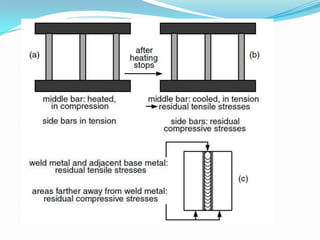
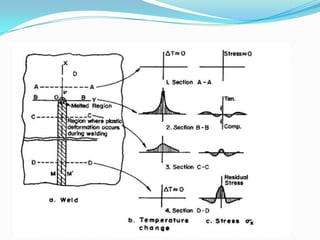
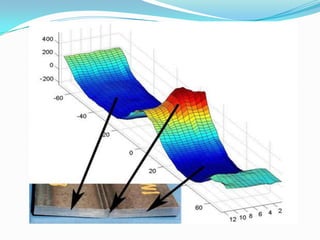
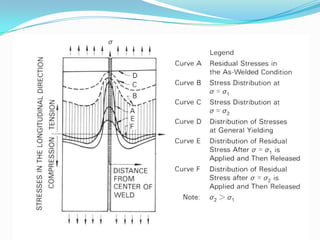
Residual stresses are stresses that exist in a material after external loads have been removed. They are caused by non-uniform temperatures during welding which lead to uneven strain. Residual stresses form from mismatches in thermal expansion and contraction between the weld metal and base metal. Higher heat input welds and greater restraint during welding generally result in higher residual stresses, with tensile stresses in the weld metal and compressive stresses farther away. Residual stresses can decrease strength and increase susceptibility to cracking if not properly addressed.