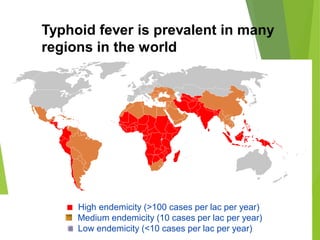
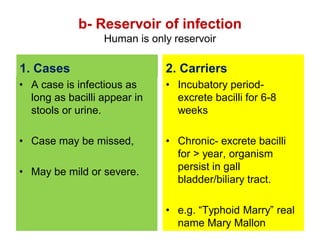
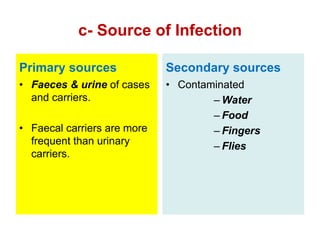
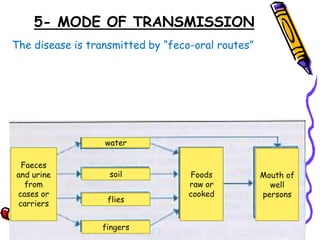
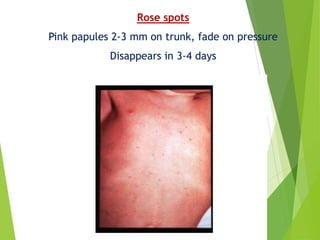
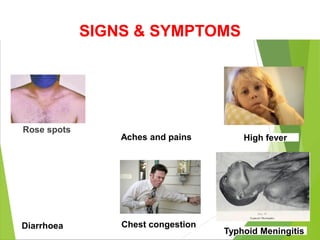
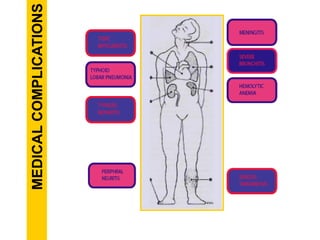
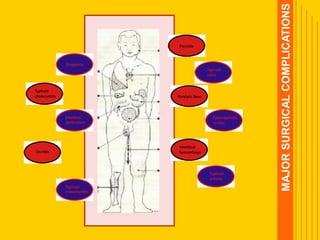
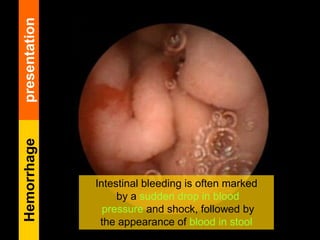
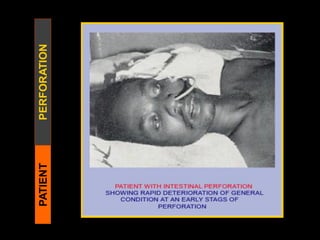
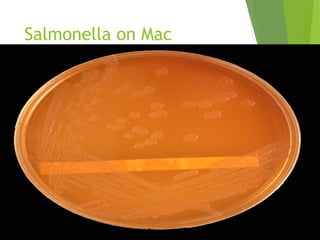
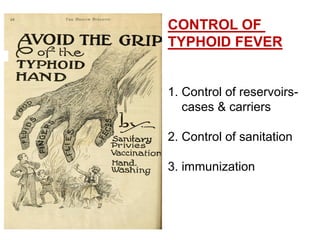
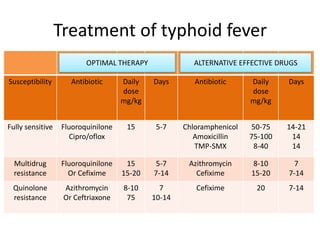
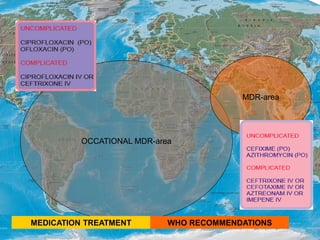
Typhoid fever is a systemic bacterial infection caused by Salmonella typhi. It is characterized by a continuous fever that follows a step-ladder pattern over 3-4 weeks. Major transmission routes are through contaminated food, water, or contact with the feces or urine of infected individuals. The disease is most prevalent in areas with poor sanitation and is considered an indicator of general sanitation levels. Diagnosis involves blood and stool cultures early in infection or serological tests detecting antibodies. Treatment consists of antibiotics like fluoroquinolones or third generation cephalosporins. Control relies on identification and treatment of cases and carriers, improved sanitation and access to clean water, and immunization with oral or injectable vaccines