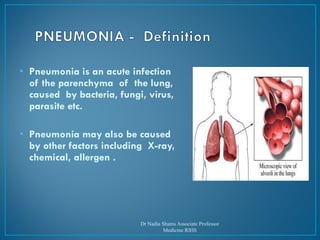
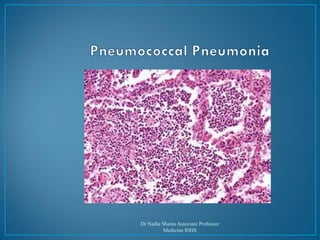
This document discusses pneumonia, including different types such as community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), and pneumonia in immunocompromised patients (ICAP). It covers topics like causes, clinical features, investigations, treatment, and prevention of pneumonia. Key points include that Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common pathogen in CAP, enteric gram-negative organisms and Staphylococcus aureus are common causes of HAP, and treatment depends on suspected pathogen and includes antibiotics with gram-negative and staphylococcal coverage for HAP.