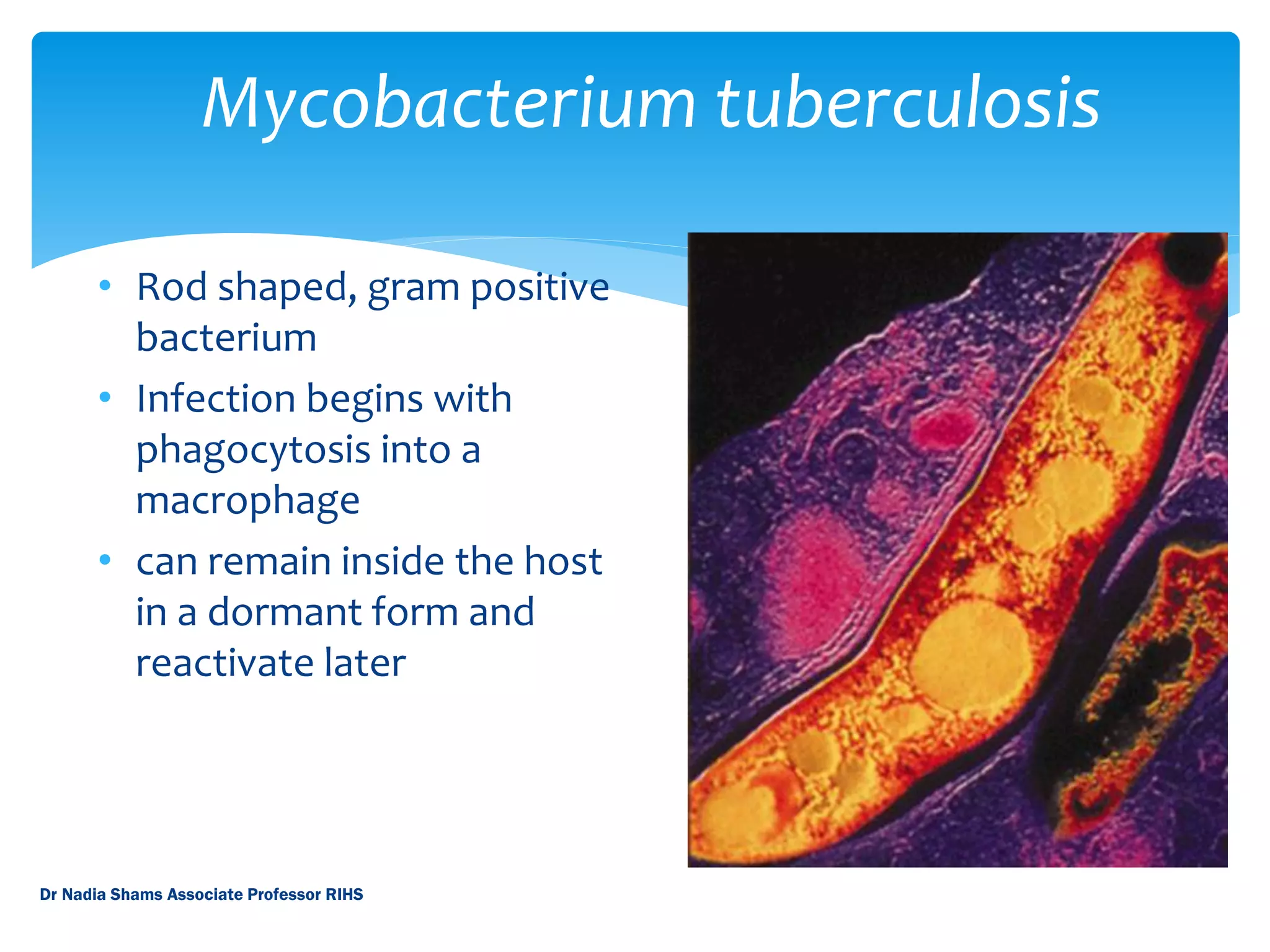
Tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is one of the top infectious killers worldwide, with around 2 million deaths per year. The disease is spread through the air when people who are sick with TB cough, sneeze or spit. Common symptoms include coughing, chest pain, fever, night sweats and weight loss. Diagnosis involves tests of sputum, blood, or other fluids and tissues from the body. While treatable with antibiotics, drug-resistant strains have emerged as a serious public health threat, especially in developing countries which account for the vast majority of TB cases globally.