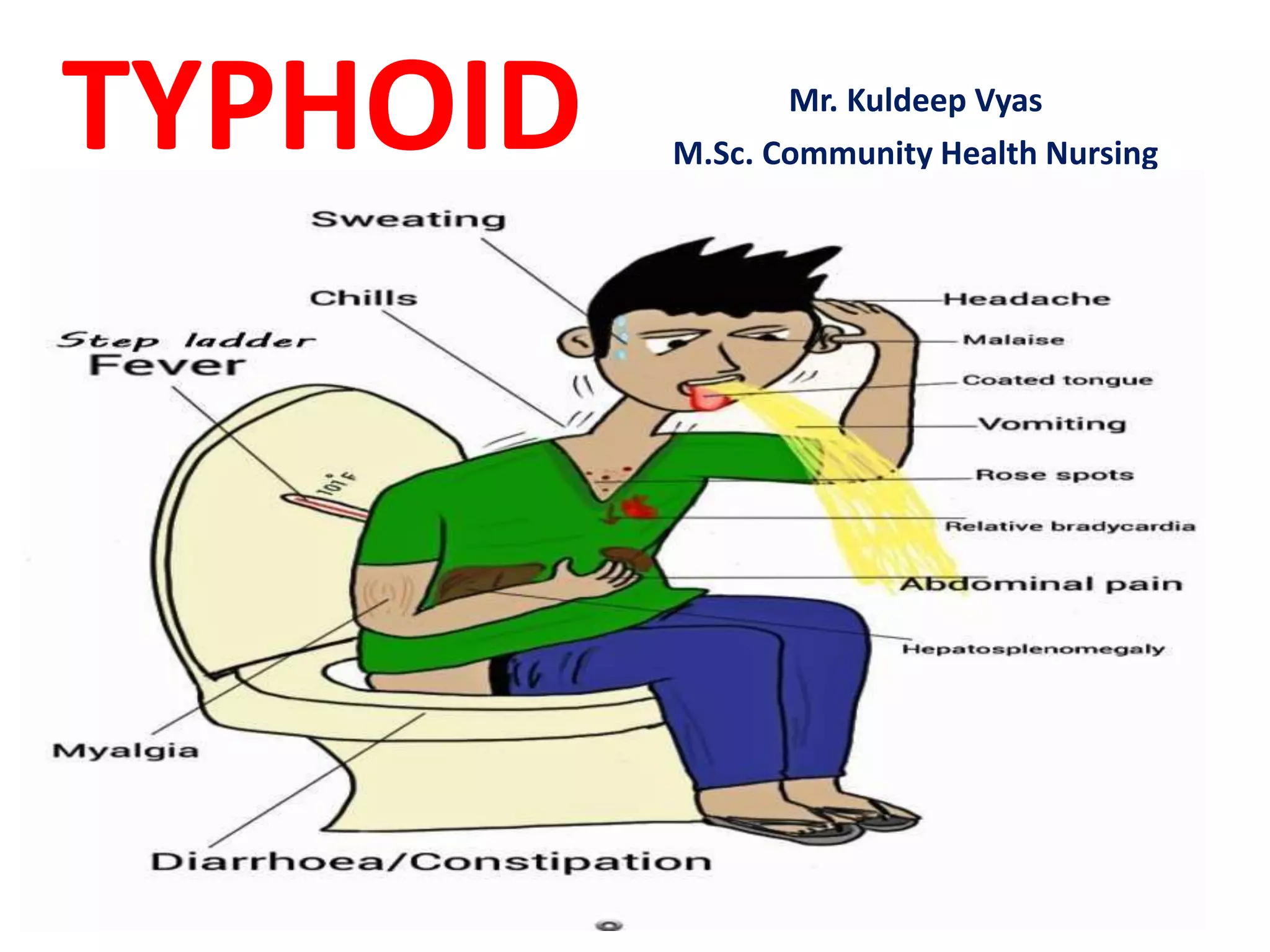
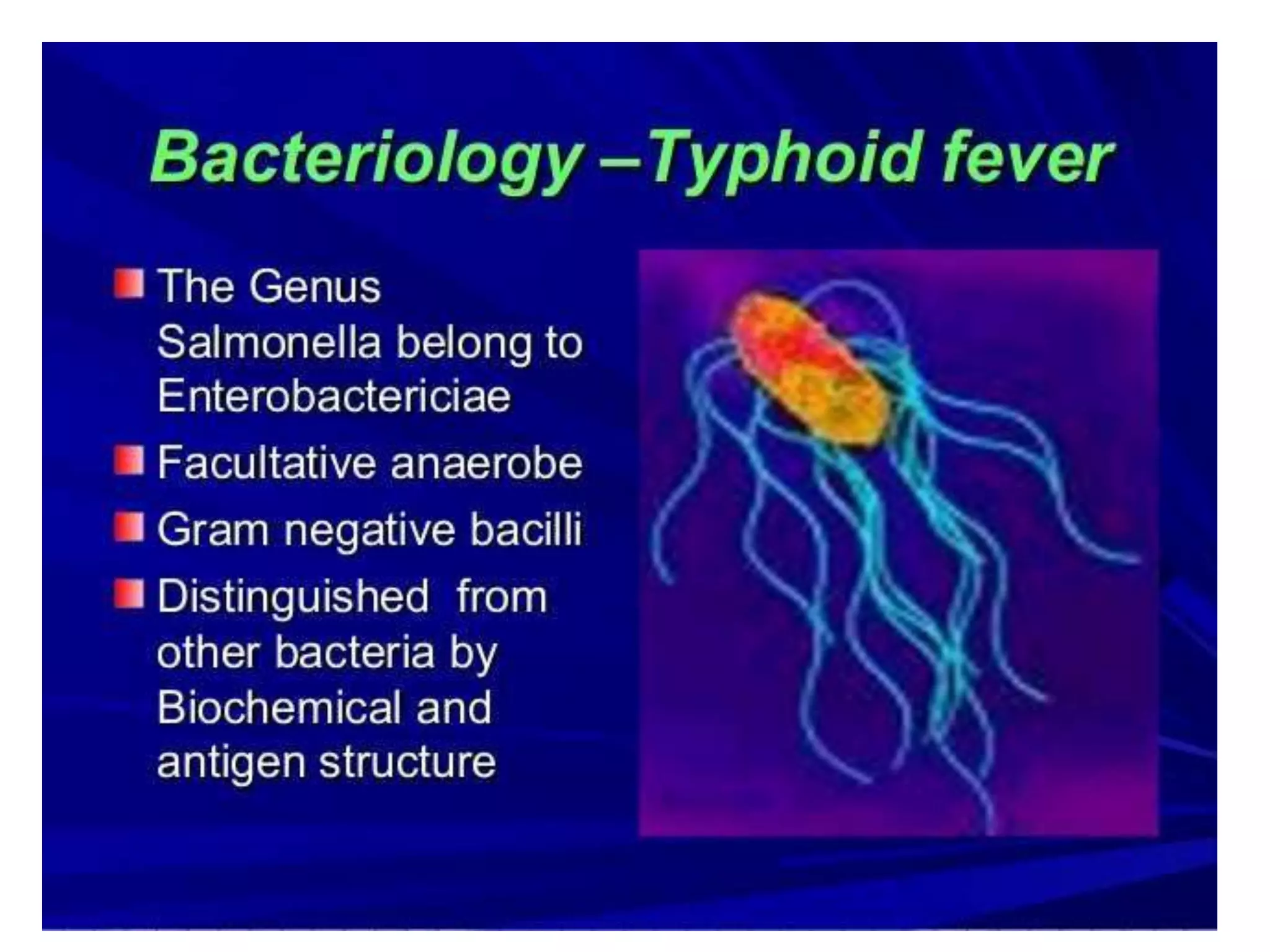
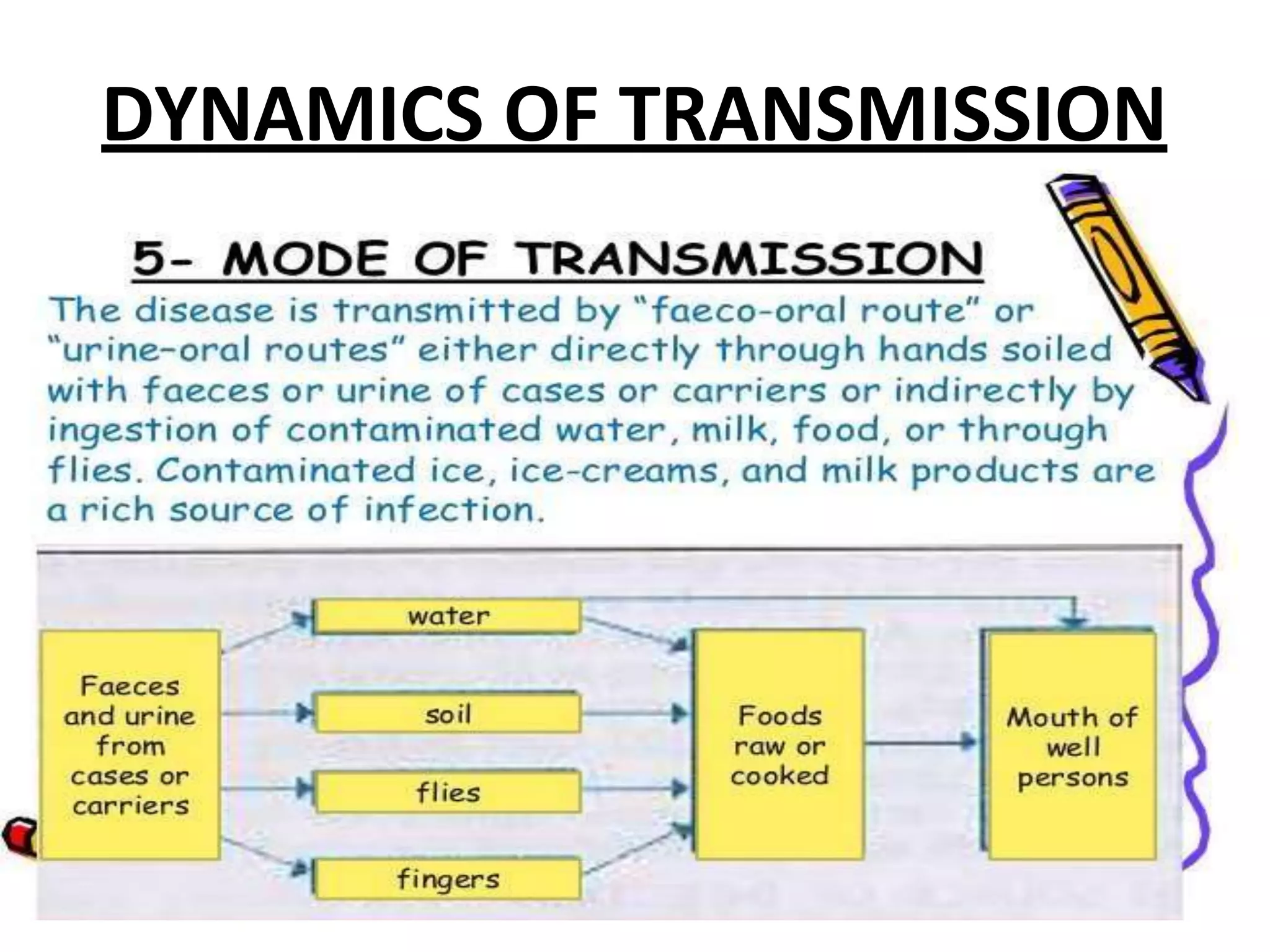
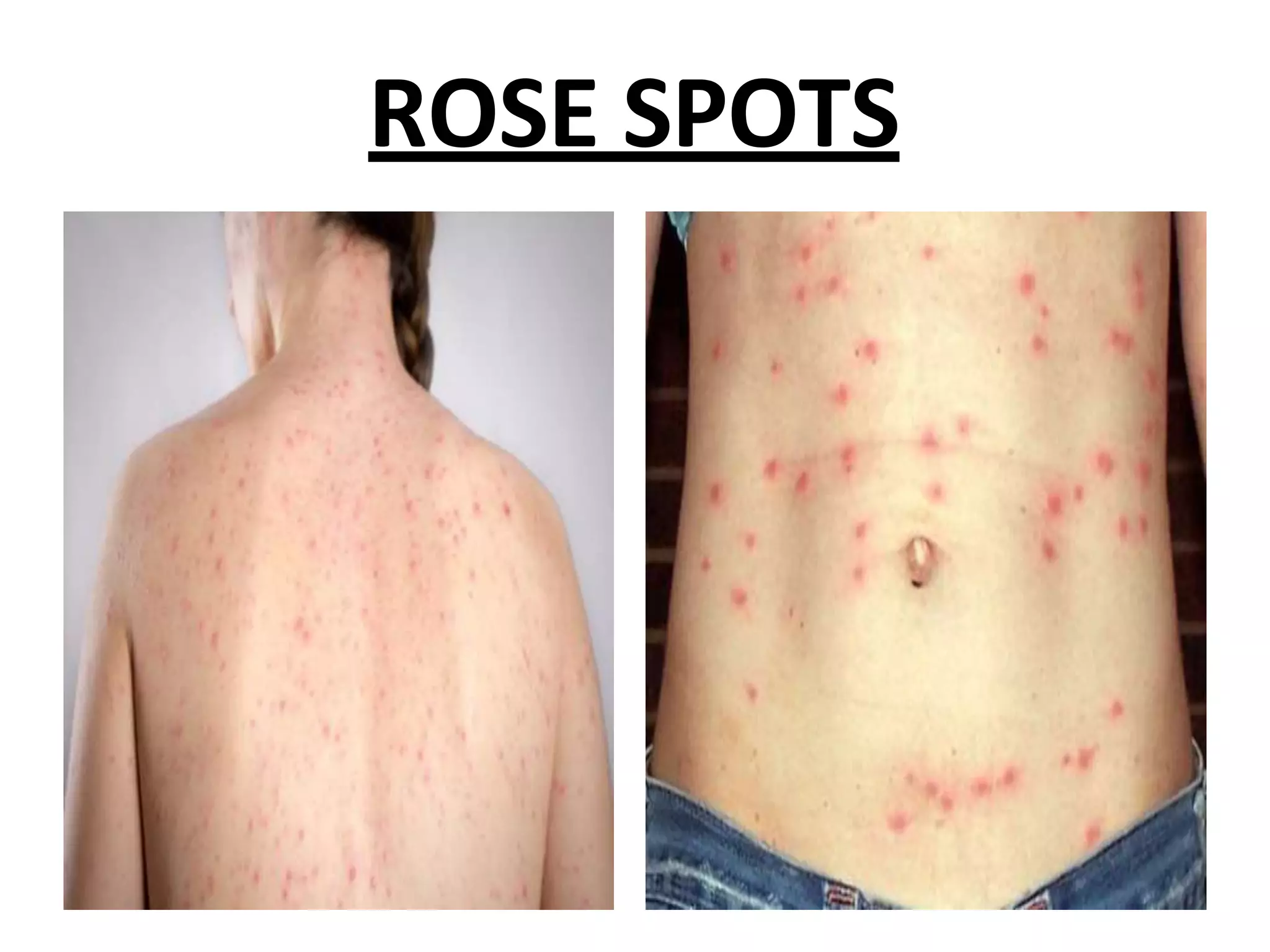
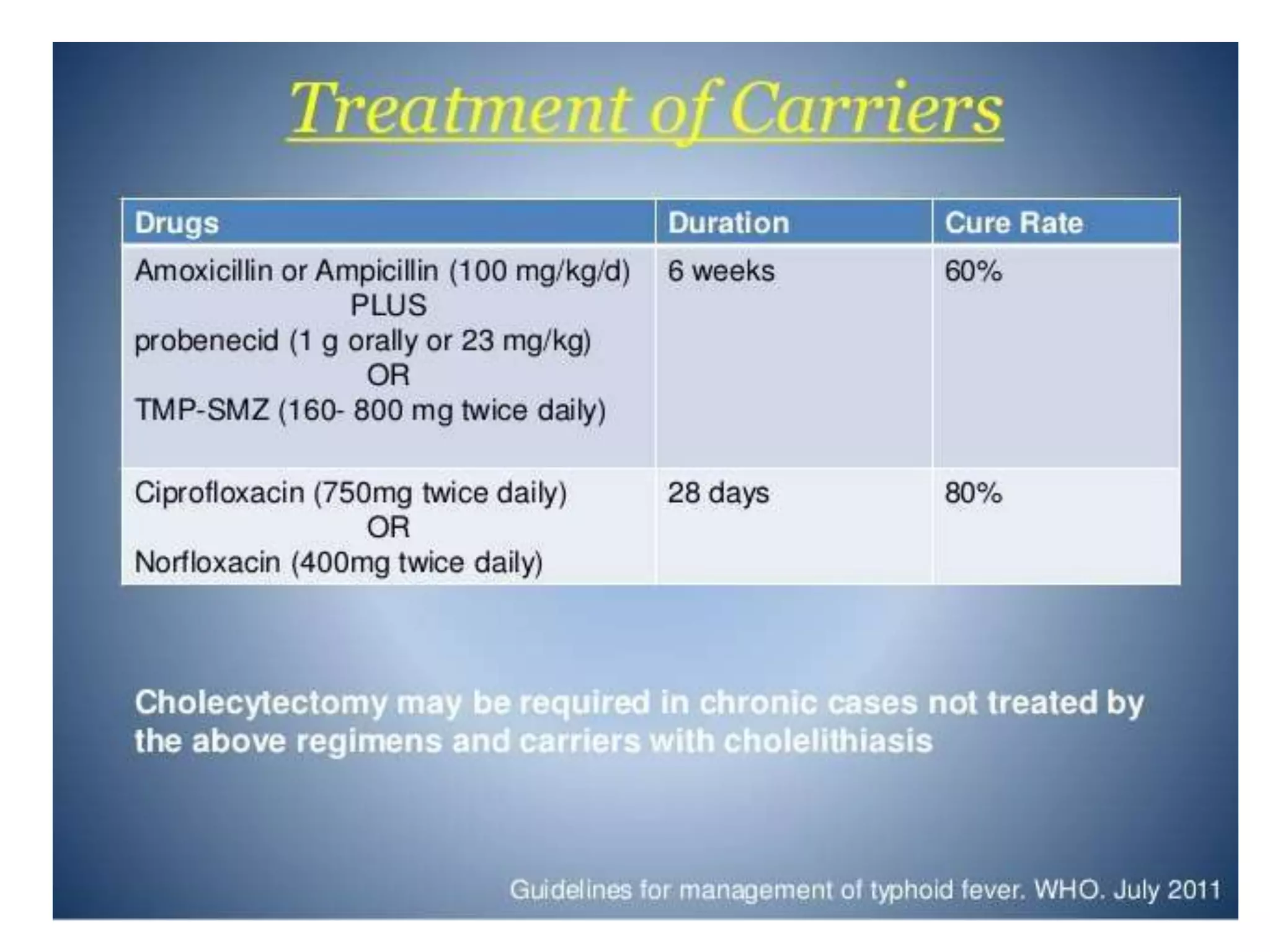
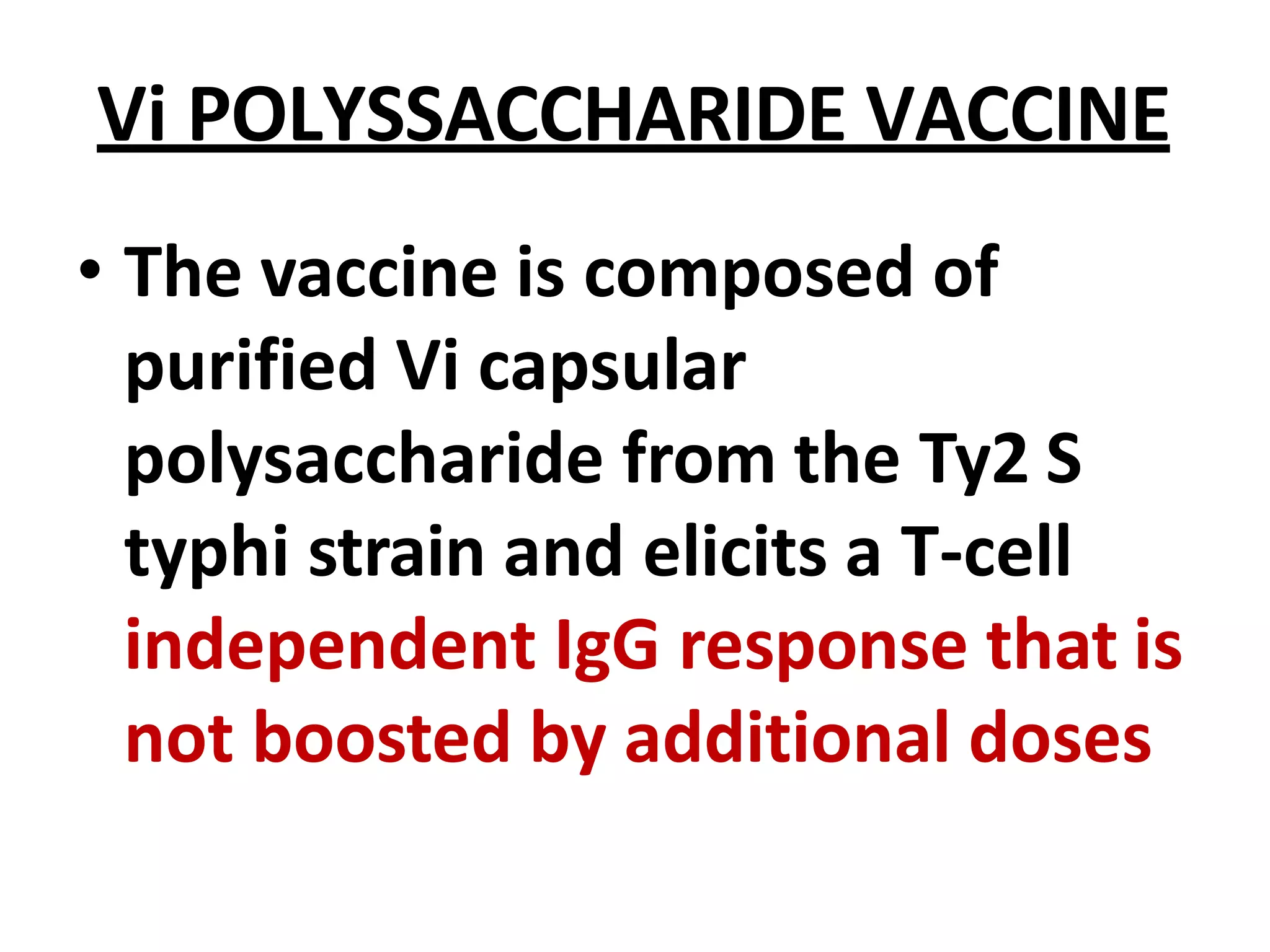
Typhoid fever is caused by Salmonella typhi bacteria. It presents with a sustained fever for 2-3 weeks and can lead to serious complications involving the intestines or other organs if left untreated. Humans are the only reservoir, transmitting the bacteria through feces and urine. Controlling transmission requires identifying infected individuals and carriers, providing proper treatment, ensuring sanitary conditions for food and water, and implementing vaccination programs. Identifying and managing chronic carriers who can shed bacteria for many years remains a challenge to fully eliminating typhoid.