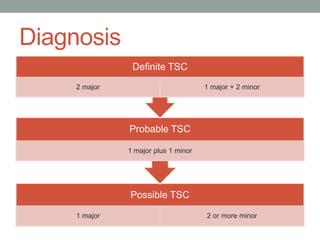
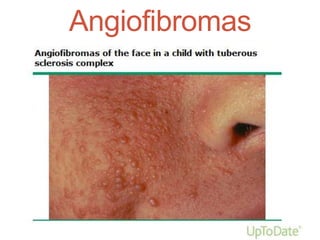
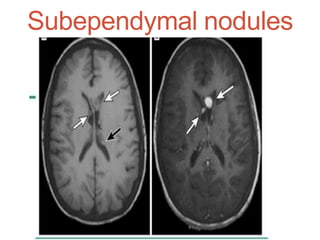
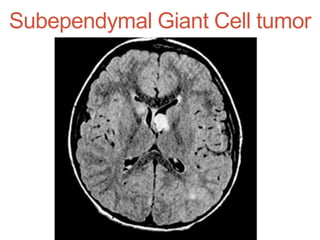
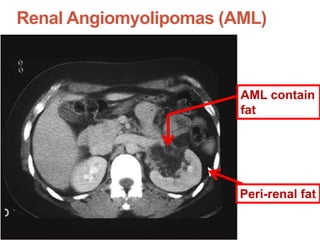
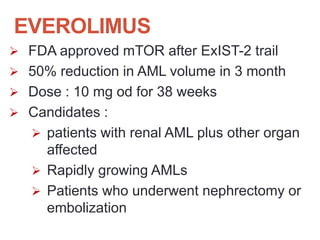
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is an inherited neurocutaneous disorder caused by mutations in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene, resulting in the growth of benign tumors (hamartomas) in multiple organs. Major features include facial angiofibromas, hypomelanotic macules, shagreen patches, retinal nodular hamartomas, cortical tubers, subependymal nodules, and cardiac rhabdomyomas. Common manifestations are seizures (80-90%), cognitive deficits (44-65%), renal angiomyolipomas (40-70%), and retinal hamartomas. Everolimus has been approved to treat renal angiomyolipomas and subependymal