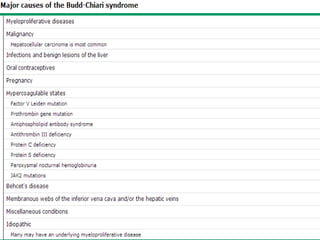
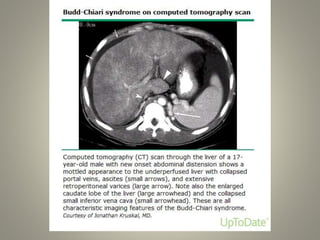
Budd-Chiari syndrome is a condition where there is obstruction of the hepatic veins or inferior vena cava, preventing normal blood flow out of the liver. It can be caused by multiple underlying disorders or risk factors for thrombosis in over 80% of patients. Common clinical manifestations include ascites in 84% of patients, hepatomegaly in 76%, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis involves Doppler ultrasound, CT, MRI, or venography. Treatment depends on whether the disease is acute, subacute, or chronic, and may involve medical management with anticoagulation or thrombolytic therapy, or surgical options like angioplasty, TIPS, shunts, or liver transplantation.