Embed presentation
Download to read offline

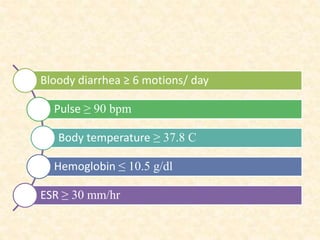






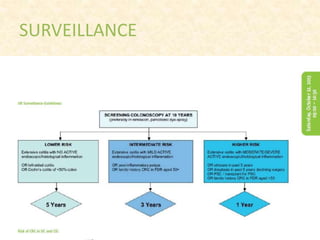


This document provides guidelines for the management of severe ulcerative colitis. It recommends initial treatment with IV methylprednisolone and high dose oral 5-ASA. If the patient does not achieve remission within 3 days, azathioprine or infliximab should be considered. Hospital admission is necessary for IV fluids and antibiotics may be used if there is fever or leukocytosis. Colonoscopy should be avoided due to risk of perforation. Total colectomy is advised if the patient has ≥8 bowel movements or a CRP of ≥45 mg/L.









