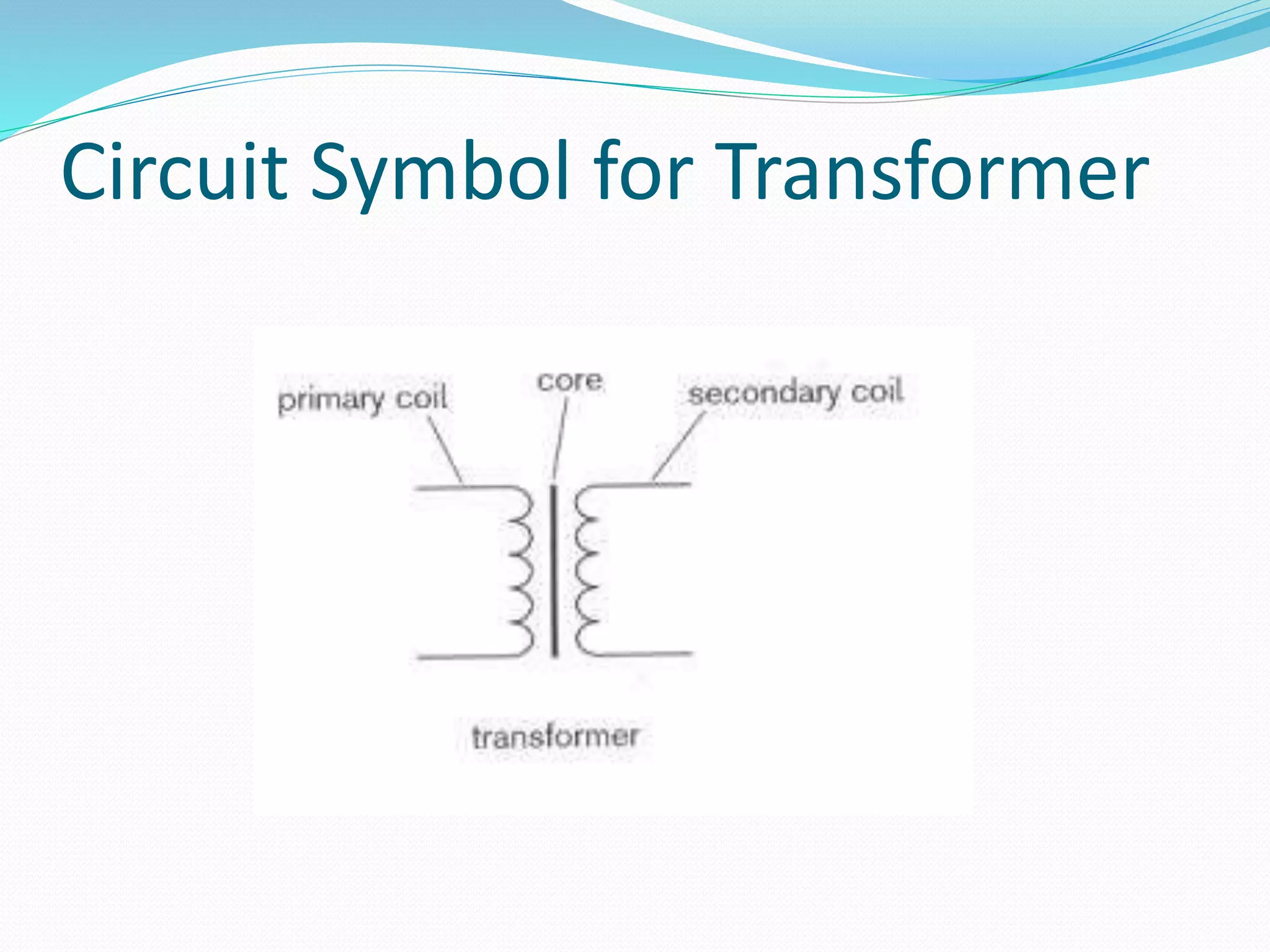
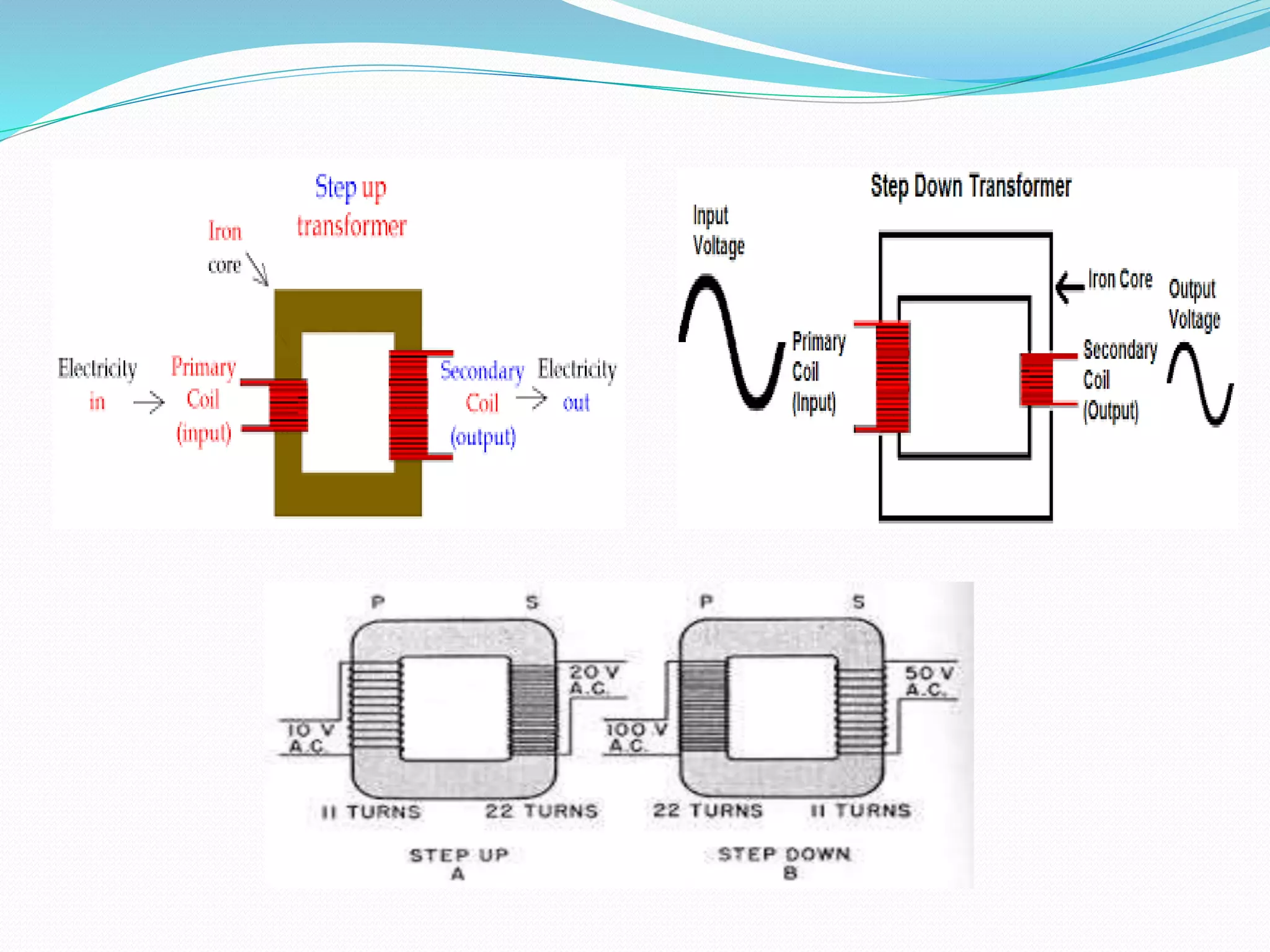
A transformer is an electric device that uses mutual induction to change alternating current voltages. It consists of two coils - a primary coil and secondary coil - wound around an iron core. Transformers can either step up or step down voltages. A step up transformer has fewer turns in the primary coil than the secondary coil, while a step down transformer has more turns in the primary coil. The alternating current passing through the primary coil induces an alternating current in the secondary coil through electromagnetic induction. Transformers are used to render current earth-free and alter voltages for different applications.