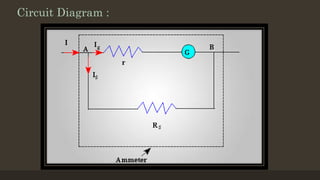
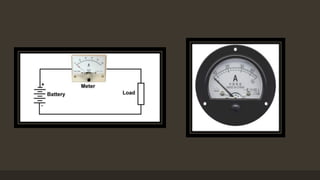
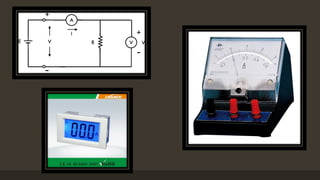
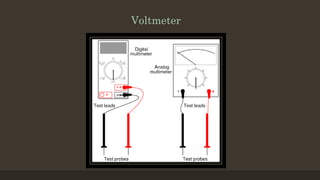
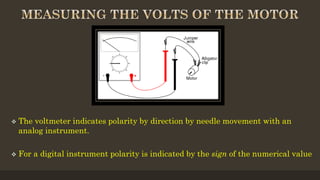
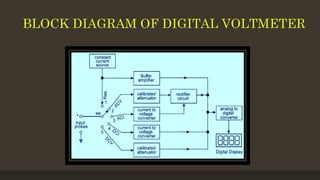
The document provides an overview of ammeters and voltmeters, explaining their functions in measuring electric current and voltage, respectively. Ammeter is described as a low-resistance device used in series to measure current, while a voltmeter measures potential difference across points in a circuit in parallel. Additionally, it covers the principles, types of measurements (analog and digital), and components essential for their operation.