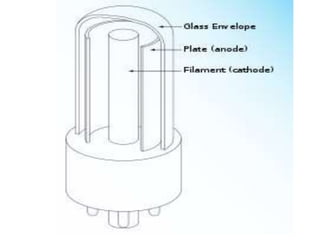
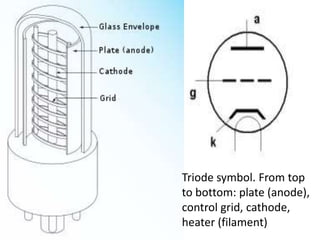
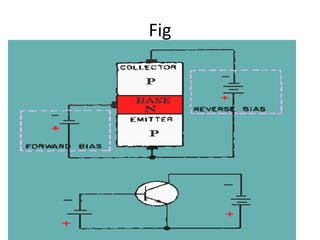
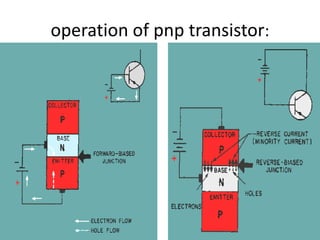
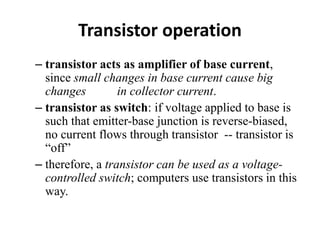
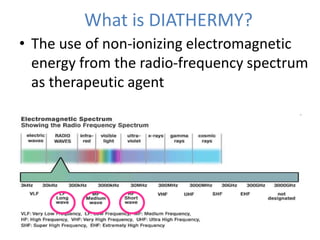
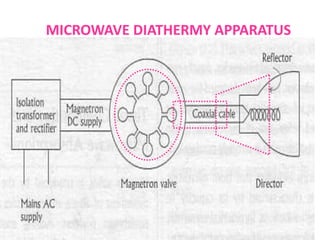
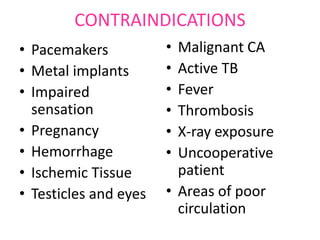
This document discusses high frequency currents and their production and use in diathermy. It describes how high frequency currents are produced using thermionic valves like diodes and triodes to generate oscillations above 500,000 cycles per second. It then discusses how different types of diathermy, like shortwave and microwave, are produced using oscillators, resonator circuits, and for microwaves, a magnetron. The therapeutic effects of diathermy include increased blood flow and tissue heating, as well as its indications for pain relief and soft tissue injuries and contraindications.