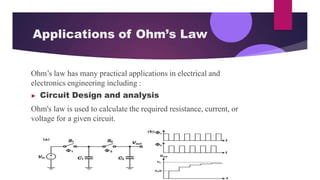
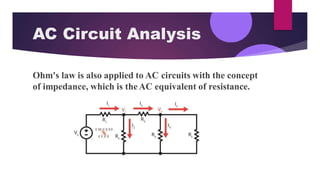
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied, with the constant of proportionality being the resistance of the conductor. Mathematically, this is expressed as I = V/R, where I is current, V is voltage, and R is resistance. Resistance is defined as the opposition to current flow and is measured in Ohms. Ohm's law has many applications in circuit design, electrical safety analysis, AC circuit analysis, and electrical heating devices.