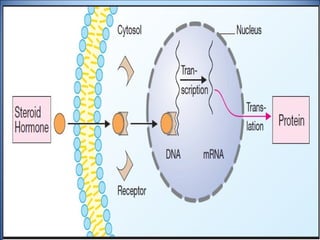
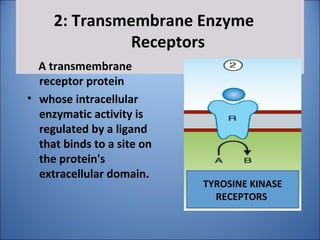
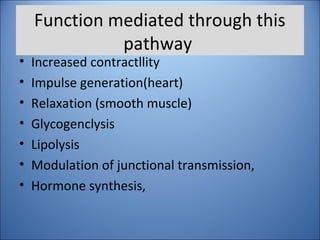
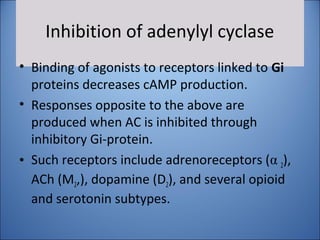
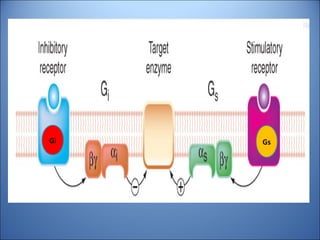
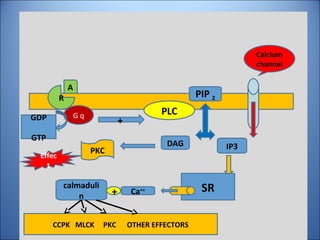
This document discusses pharmacodynamics, which is the study of how drugs act on the body and produce their effects. It describes several key concepts:
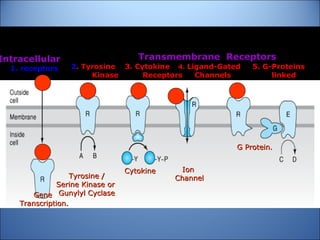
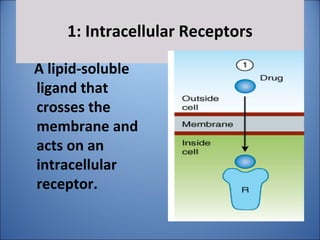
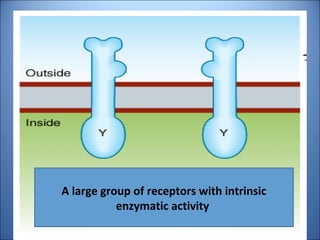
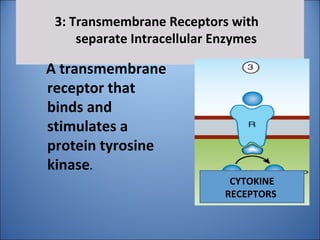
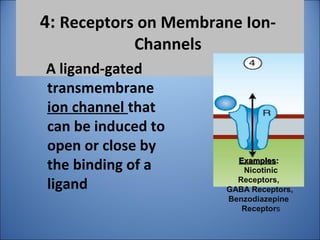
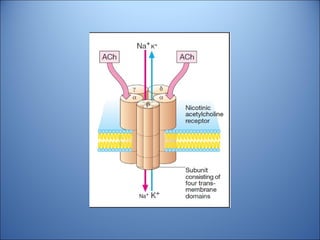
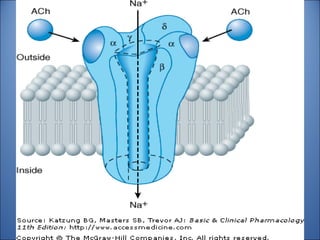
1. Drugs act by interacting with receptors or enzymes in tissues. Common sites of action include receptors, ion channels, and enzymes.
2. The mechanism of action describes how a drug modifies physiological or biochemical functions at the molecular level, such as by activating or inhibiting receptors.
3. Pharmacological effects refer to the physiological or biochemical changes caused by drugs, including their therapeutic and toxic effects. Drugs can stimulate or depress functions and may have agonistic, antagonistic, or other complex effects.
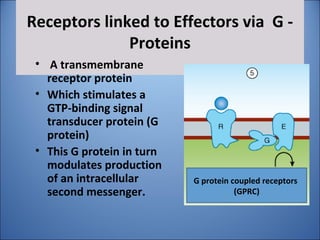
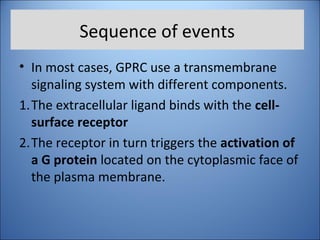
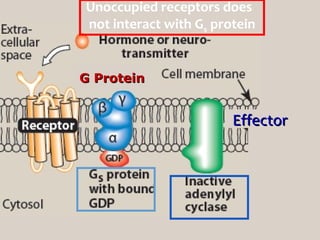
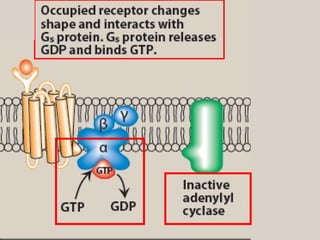
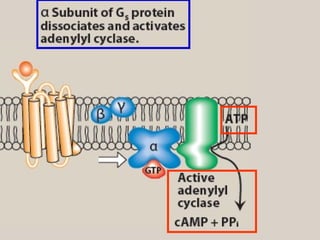
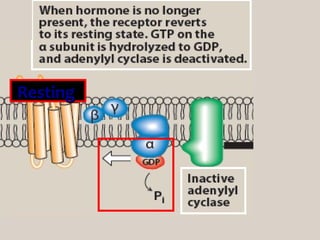
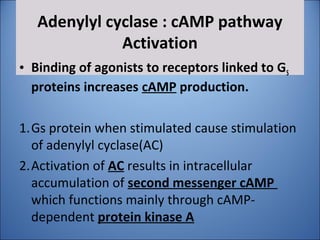
4. Several signaling pathways are involved in how receptors