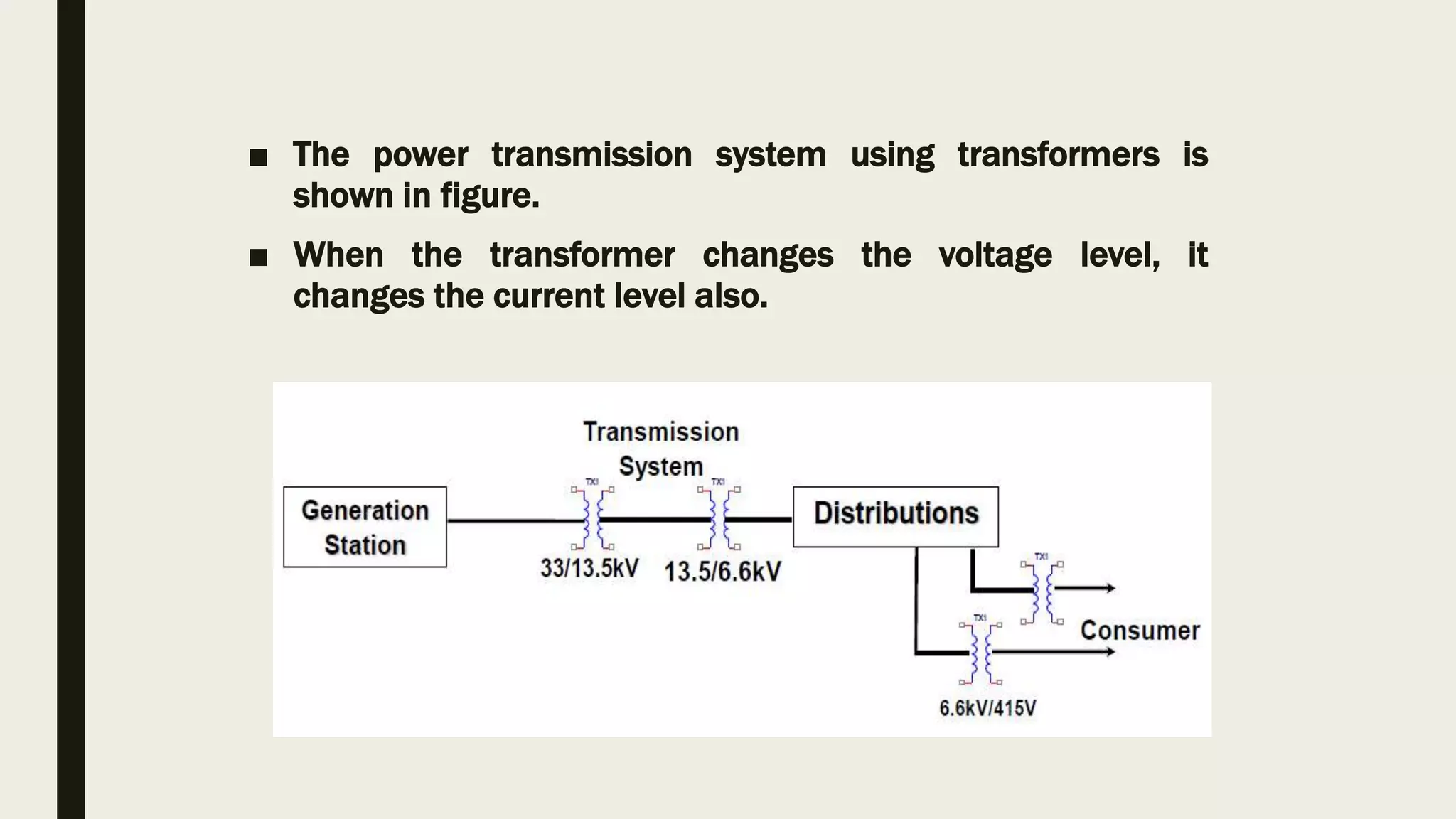
The document discusses the transformer, including its basic principles, construction, and types. A transformer transfers electrical energy from one AC circuit to another by means of a changing magnetic field produced by an input current in its primary winding. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in a secondary winding. The voltage can be increased or decreased depending on the relative number of turns in the primary and secondary windings. Transformers allow efficient transmission of power over long distances and stepping voltages up or down for use in homes and industry.