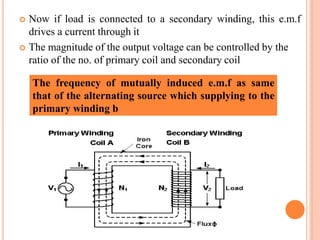
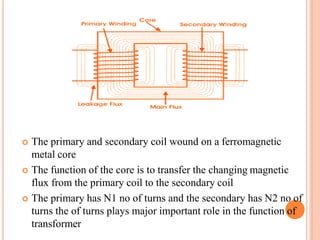
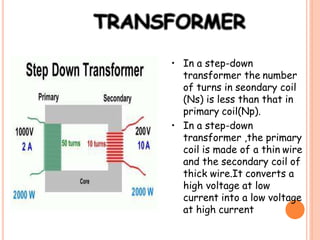
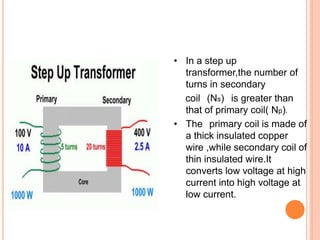
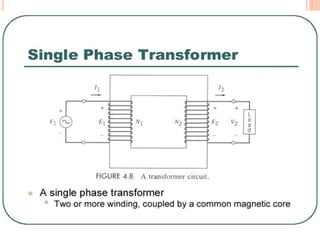
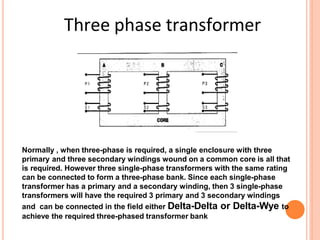
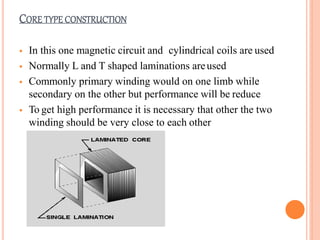
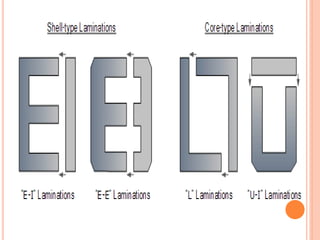
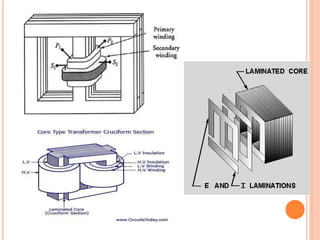
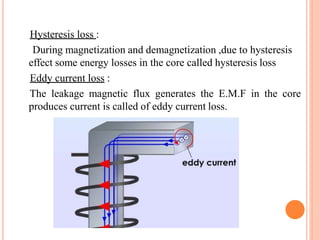
The document discusses the construction and working of transformers. It explains that a transformer transfers electrical power from one alternating current circuit to another through mutual induction without direct electrical contact. It has a primary winding that receives input power and a secondary winding that delivers output power. The transformer works by inducing voltage in the secondary winding through a changing magnetic field generated by the primary winding around a shared ferromagnetic core. The document further describes step-up and step-down transformers, classifications, losses, and applications of transformers.