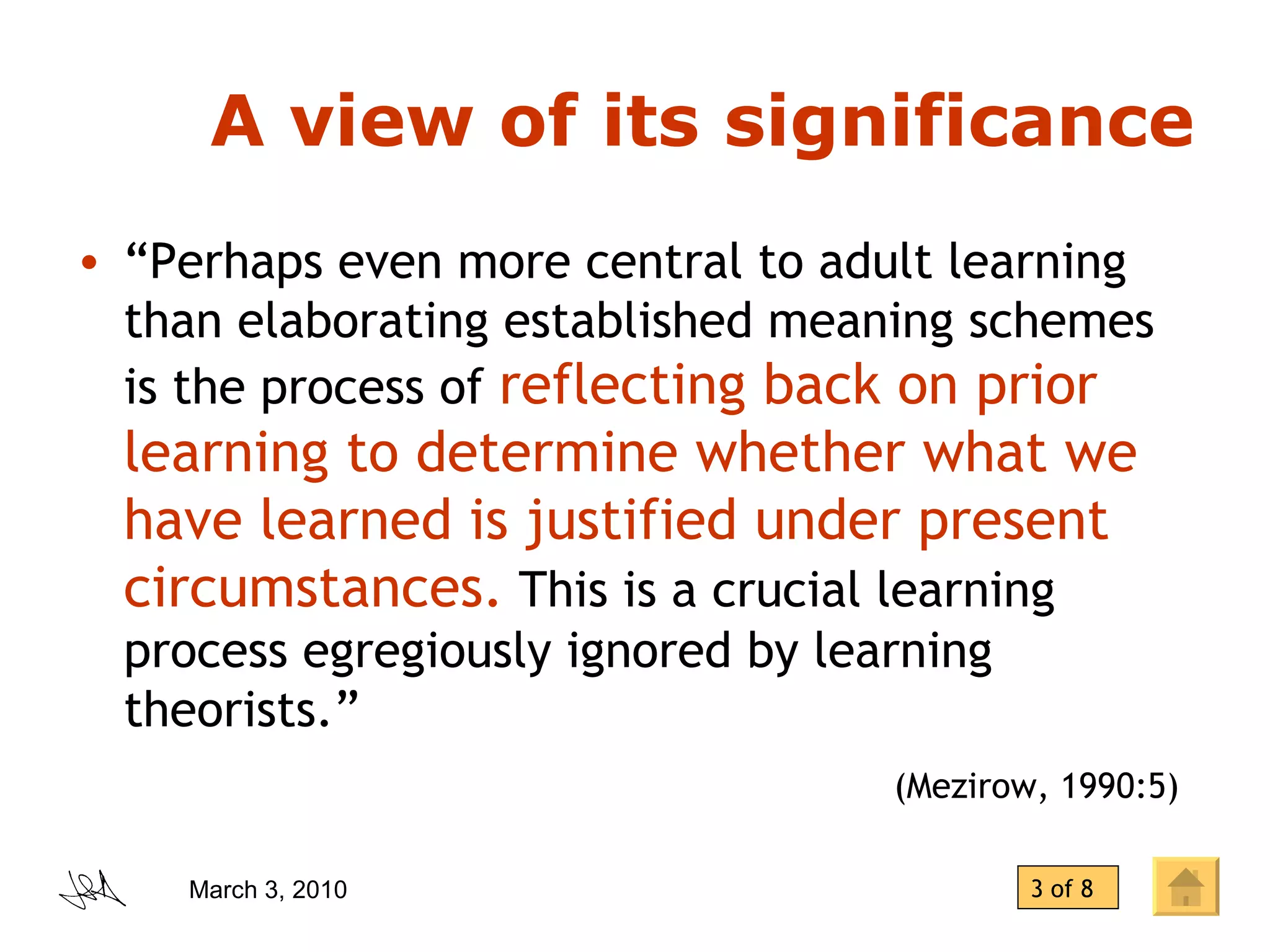
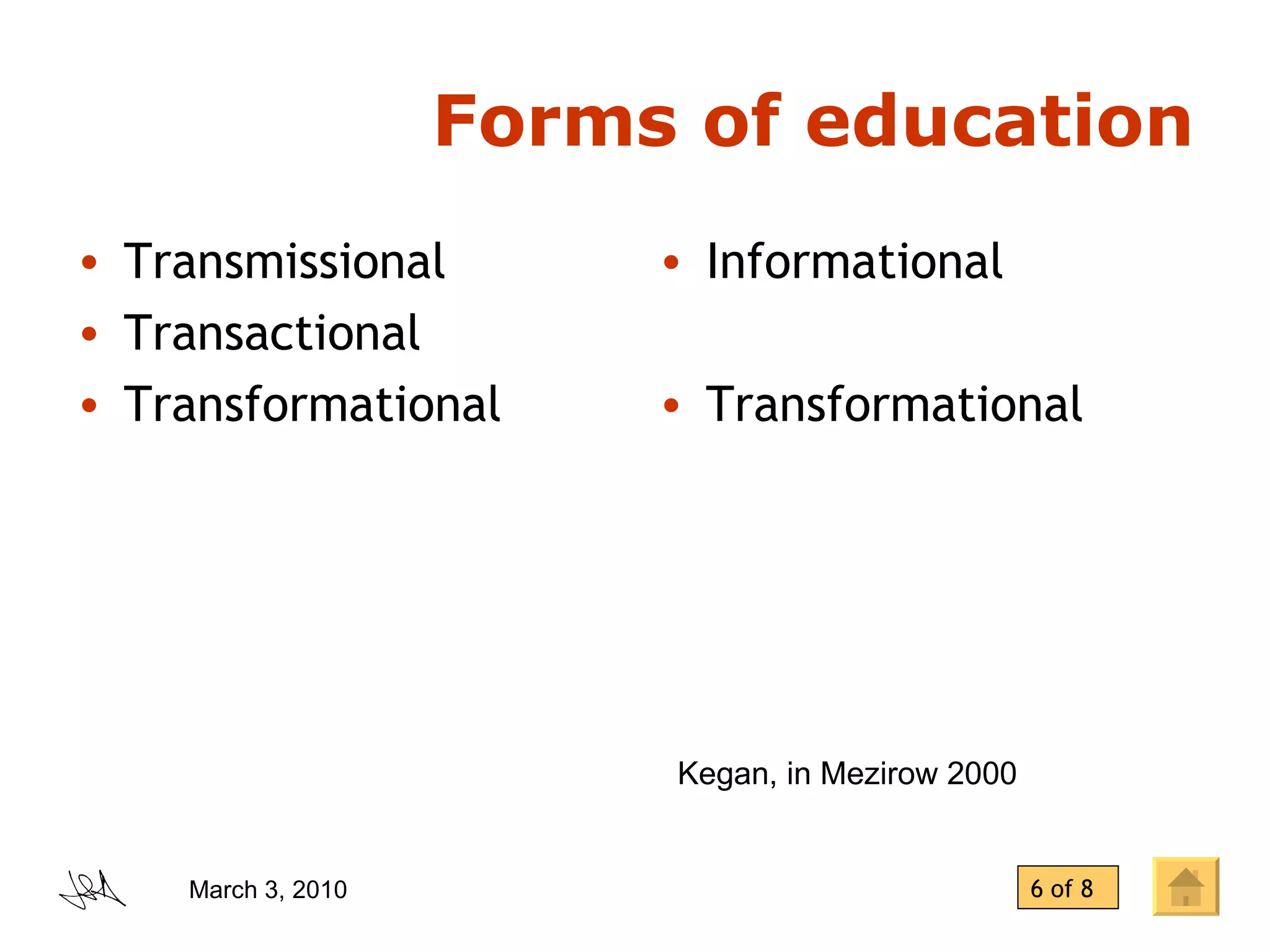
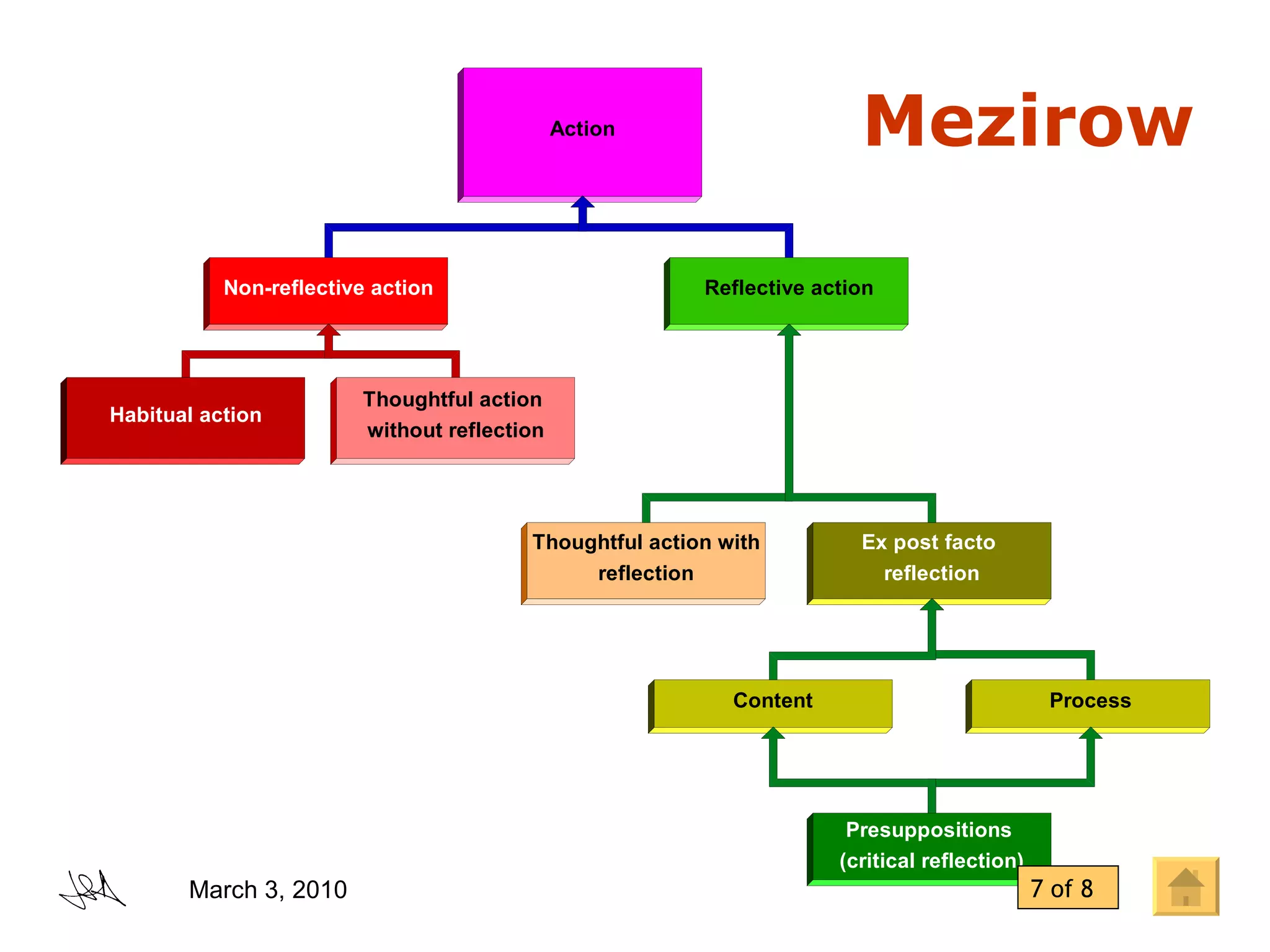
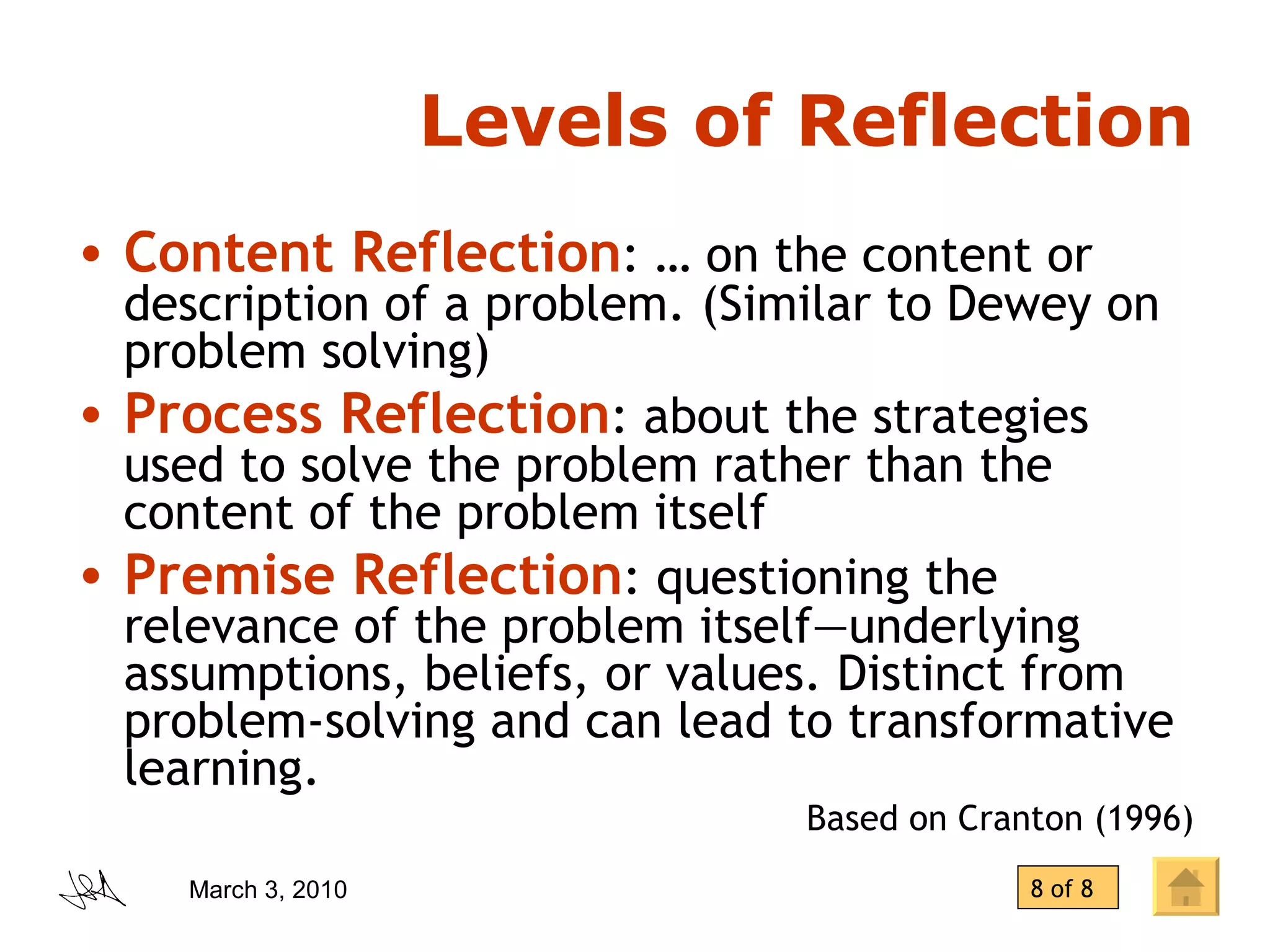
The document discusses the concept of "transformative learning" which involves experiencing a deep shift in one's basic premises, thoughts, feelings, and actions that changes one's perspective and way of being in the world. It provides definitions and perspectives from scholars including that transformative learning involves critically reflecting on prior learning and assumptions to determine if they are still valid. It also outlines Mezirow's stages of perspective transformation and different forms and levels of reflection that can lead to transformative learning experiences.