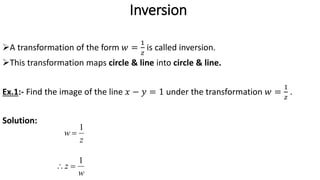
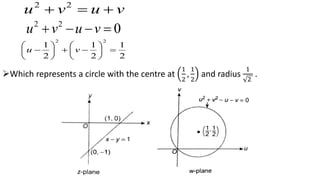
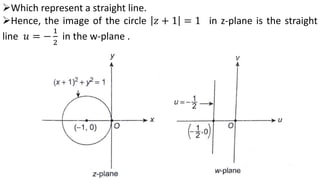
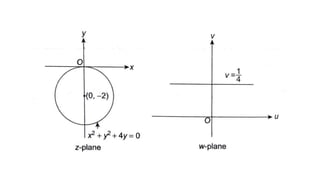
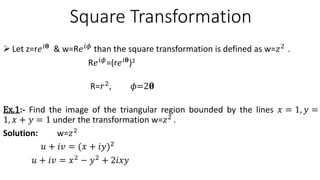
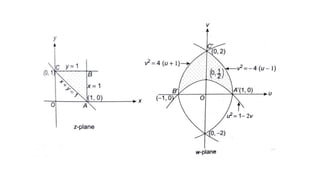
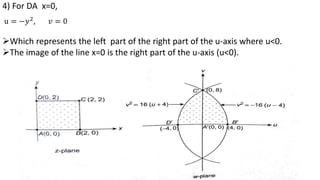
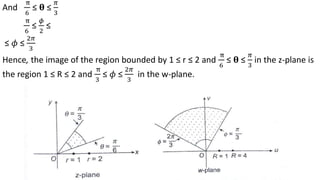
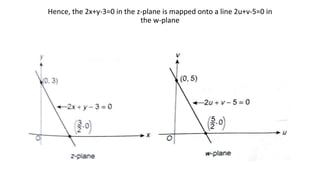
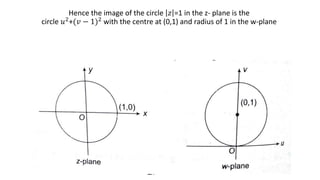
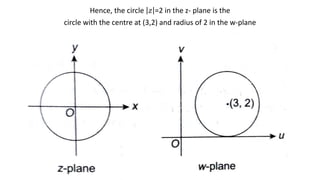
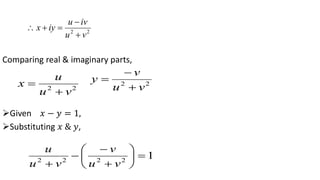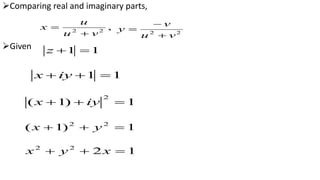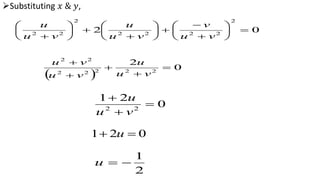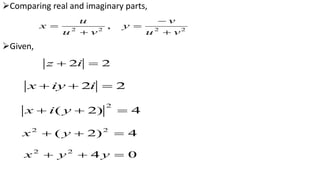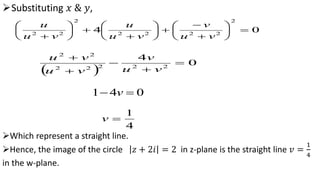This document provides examples of transformations involving complex variables and their applications. It contains 3 examples of inversion transformations where a line or circle in the z-plane is transformed to a circle or line in the w-plane. It also contains 2 examples of square transformations where a region in the z-plane is transformed to parabolic regions in the w-plane. Additionally, it discusses finding the image of a line or circle under translations in the complex plane.