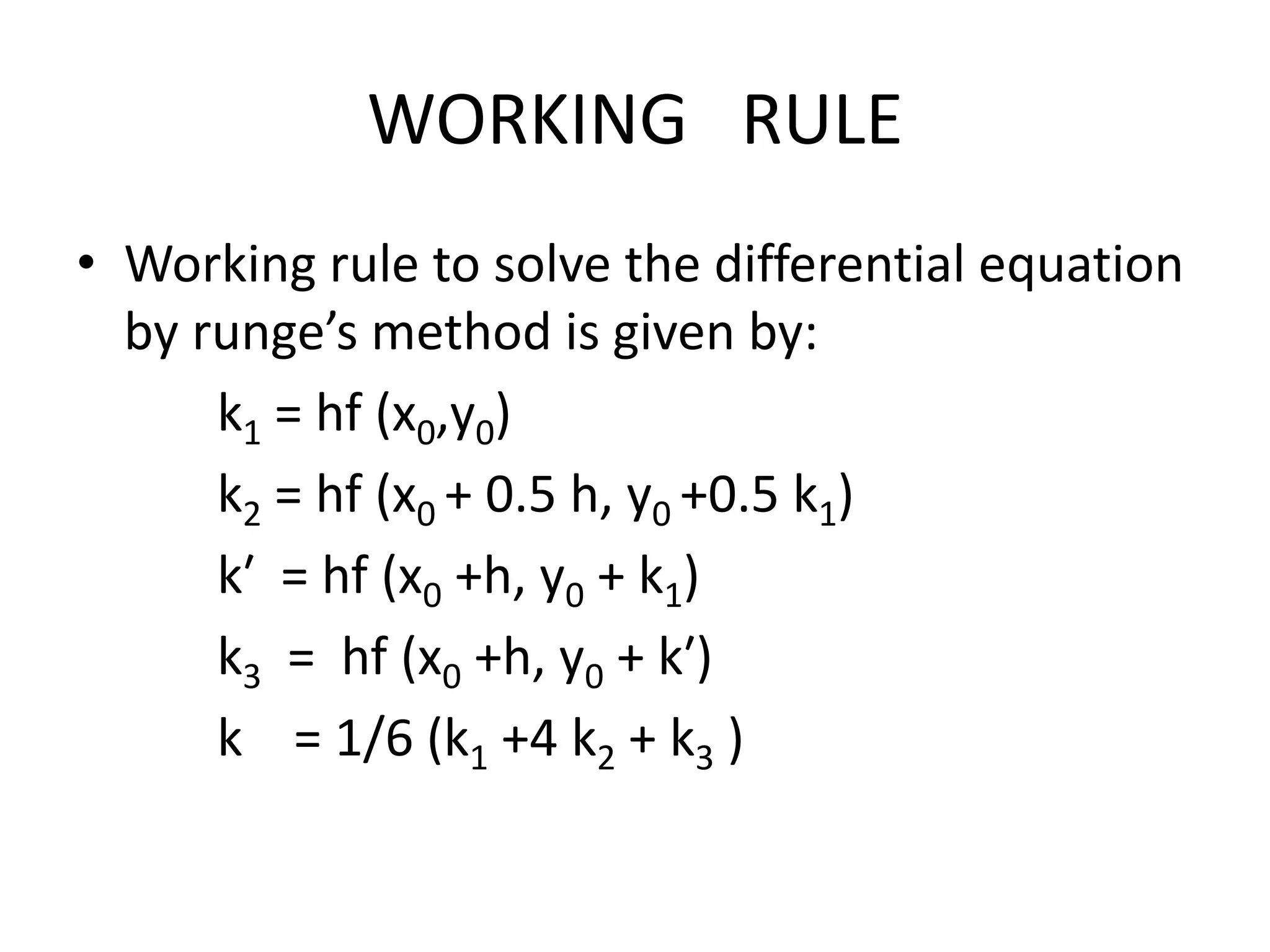
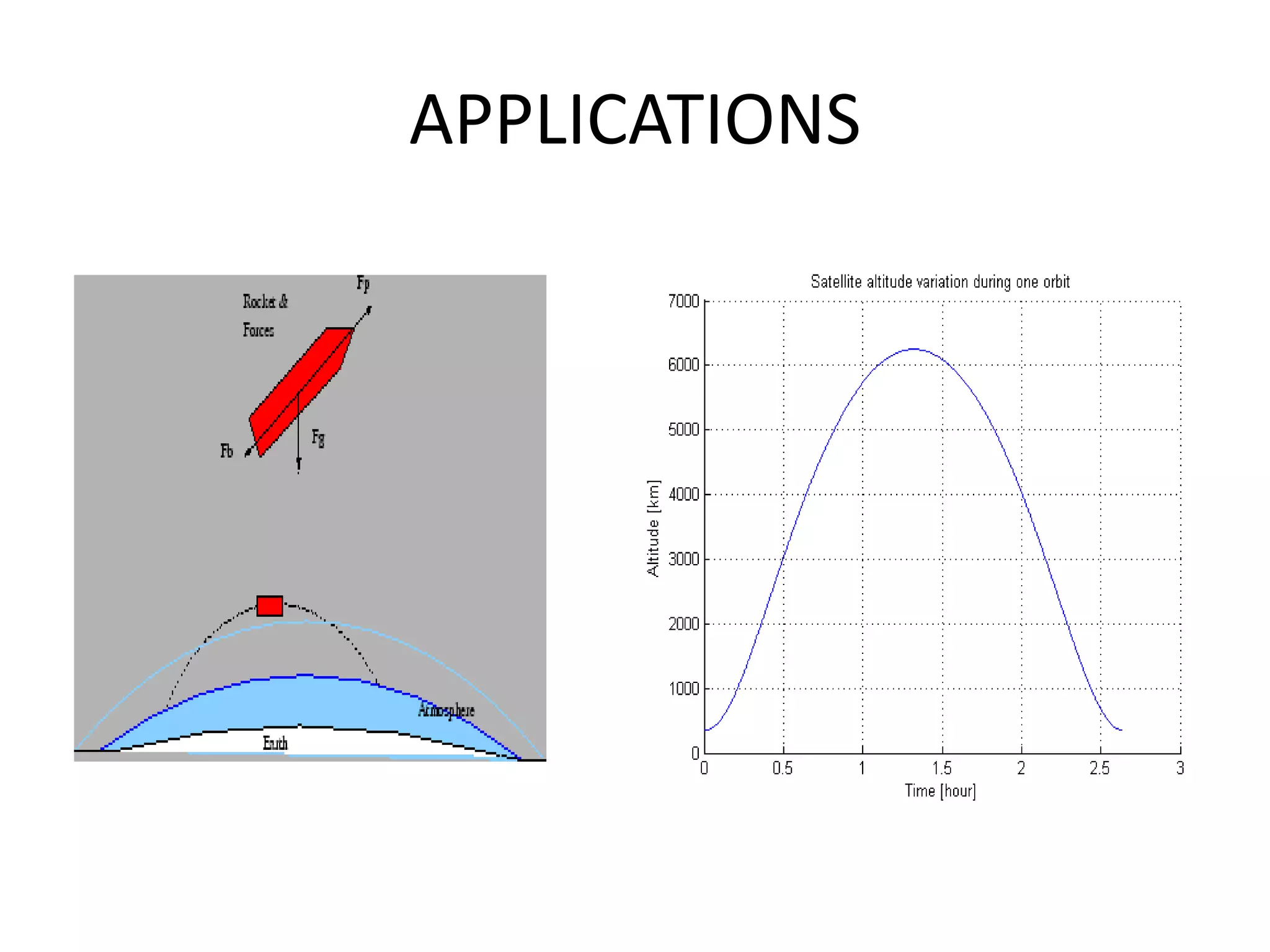
The document discusses numerical methods for solving first-order ordinary differential equations, particularly focusing on the Runge-Kutta methods introduced by mathematicians Runge and Kutta. These methods are noted for their accuracy and efficiency in calculating solutions for applications such as rocket trajectories. The conclusion emphasizes the superiority of the Runge-Kutta method in optimizing rocket paths, despite a longer computation time compared to other methods.