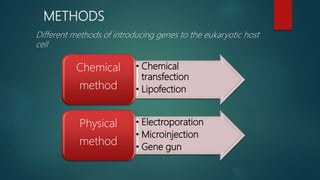
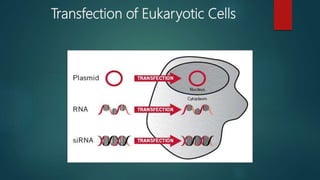
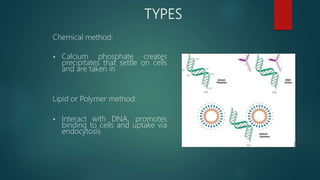
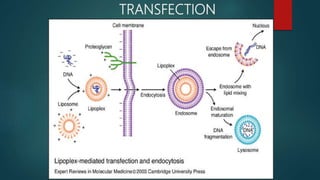
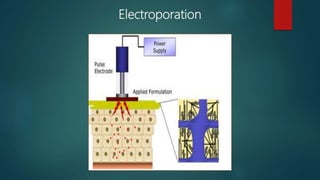
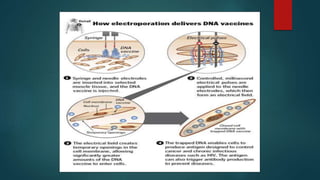
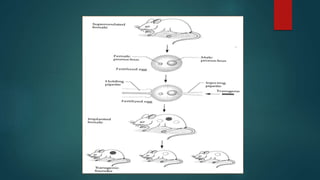
The document outlines various methods for transferring DNA into eukaryotic host cells, including chemical transfection, electroporation, microinjection, and gene gun techniques. Each method has its specific applications and advantages, such as the efficiency of liposome-mediated transport and the direct targeting of cells with microinjection. However, challenges like efficiency dependency on cell health and high costs of certain methods are also noted.