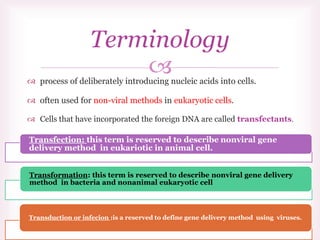
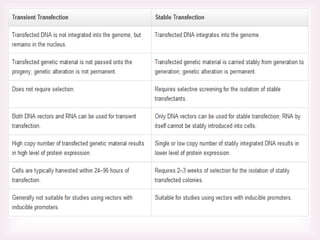
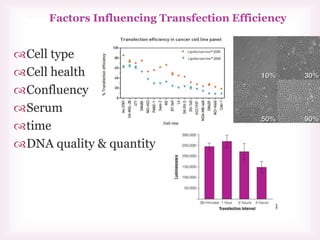
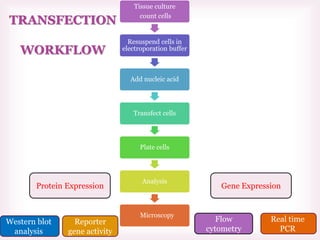
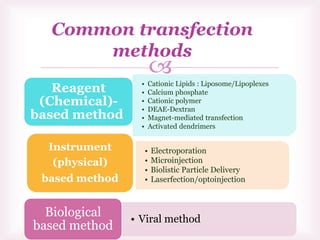
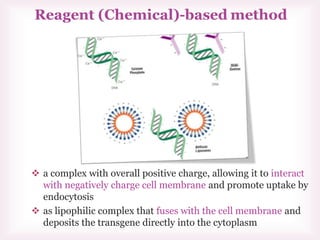
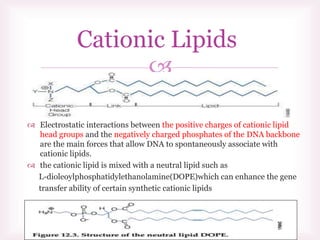
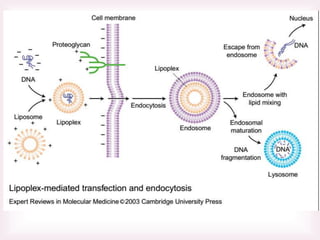
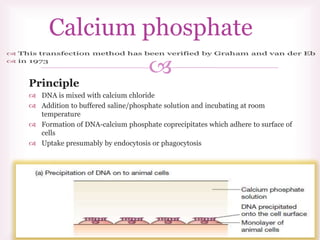
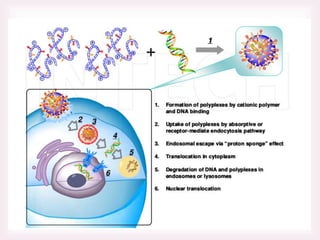
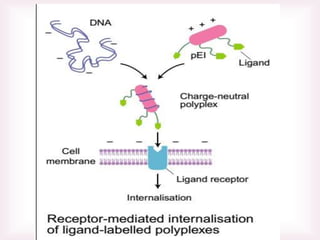
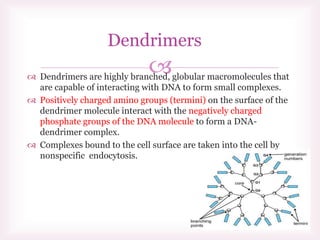
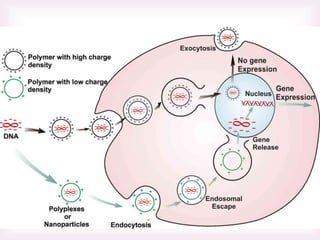
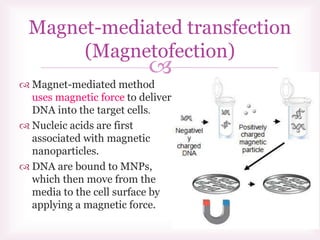
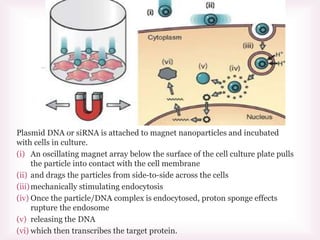
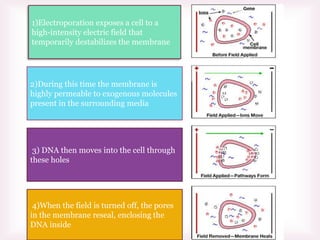
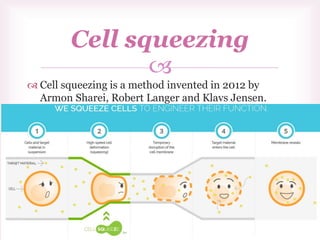
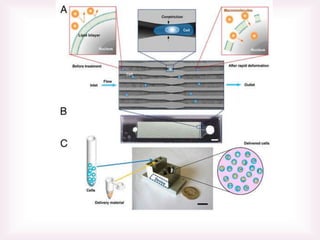
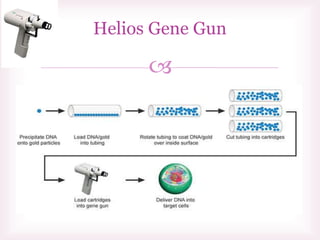
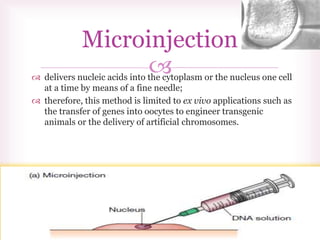
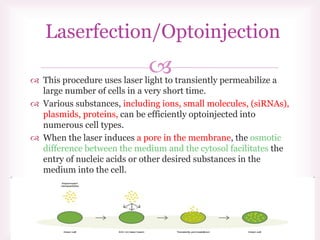
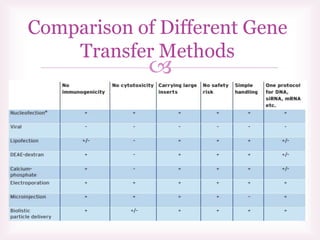
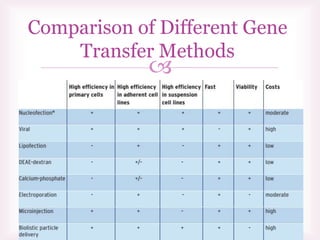
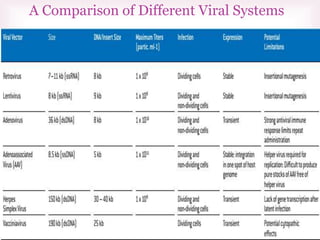
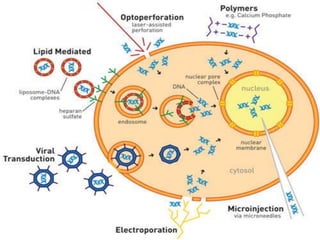
This document discusses various methods of transfection, which is the process of introducing nucleic acids into cells. It describes both physical and chemical transfection methods. Physical methods include electroporation, microinjection, and cell squeezing, which introduce DNA directly into cells using physical forces. Chemical methods involve using reagents like cationic lipids, calcium phosphate, and cationic polymers to form complexes with DNA that are then taken up by cells. The document discusses the principles, advantages, and disadvantages of many common transfection methods.