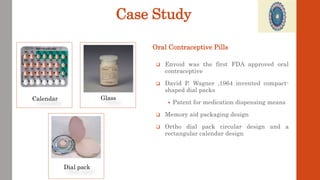
This document discusses pharmaceutical packaging technology. It describes the different types of primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging used to surround pharmaceutical products from production to use. The functions of packaging include product identification, protection, facilitating usage, and promotion. The document also discusses various packaging materials, case studies on innovative drug packaging designs, regulatory requirements, and recent advancements in packaging technology.