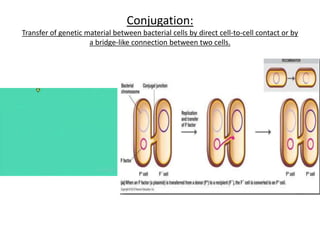
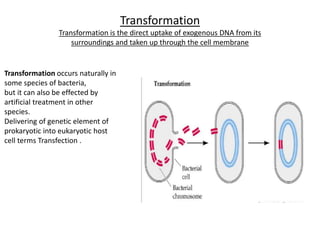
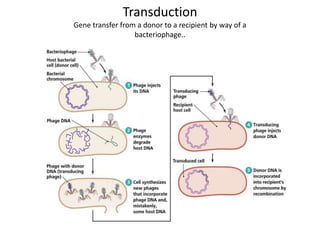
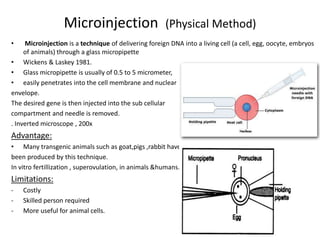
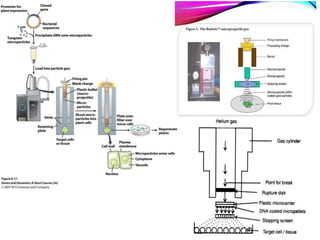
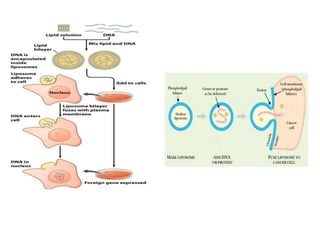
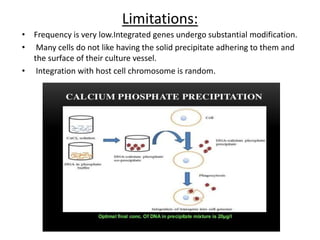
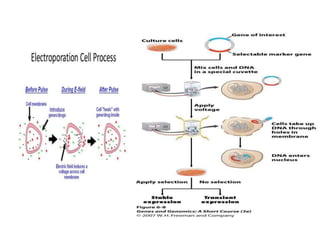
Gene transfer methods in animals can be natural or artificial. Natural methods include conjugation, transformation, and transduction which transfer genes between bacteria. Artificial methods like microinjection, biolistics, liposome mediated transfer, calcium phosphate mediated transfer, and electroporation are used to directly insert genes into cells. These techniques transfer genes into organisms for genetic engineering applications such as producing transgenic animals, developing vaccines, and gene therapy to treat diseases.