According to the document:
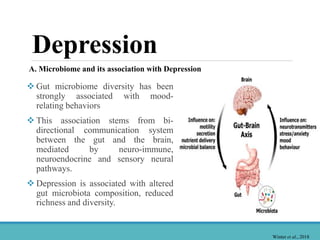
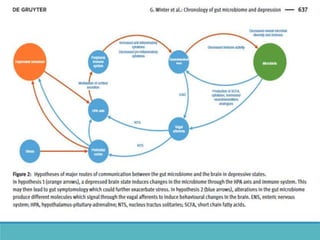
1. Microbiome dysbiosis is associated with depression, as certain genera like Proteobacteria increase due to depression-induced inflammation while genera like Coprococcus decrease.
2. Depression and stress can disrupt the gut microbiome composition, reducing diversity.
3. Microbiome restoration through probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal transplants shows promise in improving depression symptoms by regulating the microbiome-gut-brain axis.