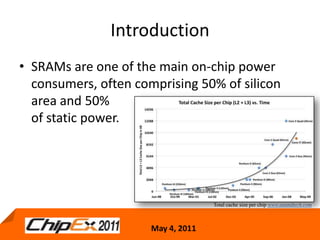
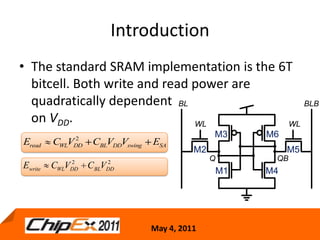
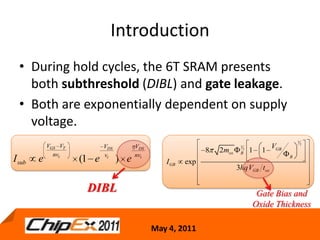
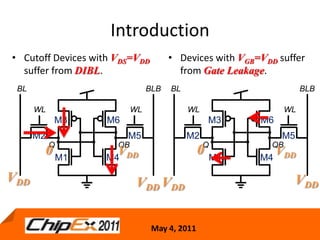
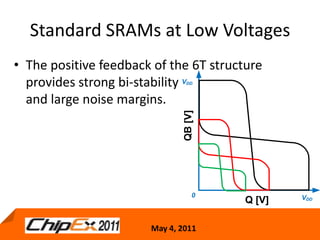
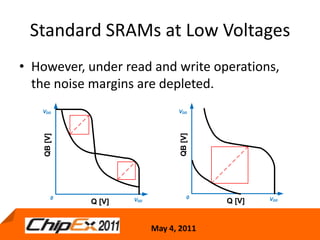
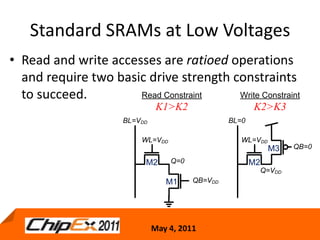
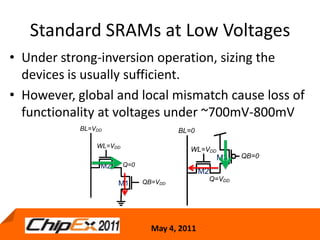
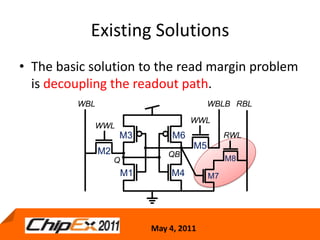
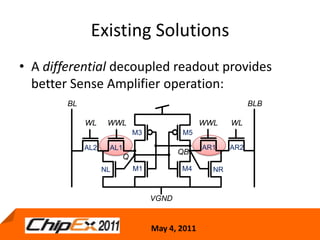
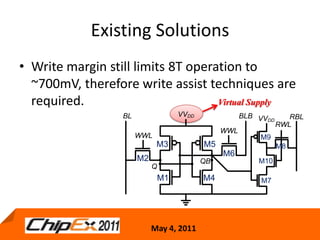
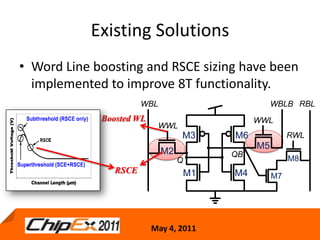
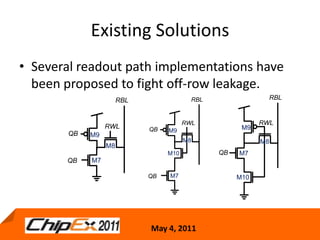
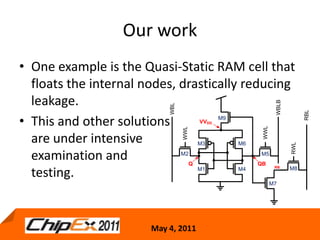
This document discusses challenges in designing low voltage SRAM and existing solutions. Standard 6T SRAM cells experience issues at voltages under 700-800mV due to loss of read and write margins from mismatch. Existing solutions to improve read margins include differential readout and write assist techniques like word line boosting. However, write margins still limit operation to around 700mV. The document introduces work by the Low Power Circuits and Systems Lab to modify the internal SRAM cell structure, such as a quasi-static RAM cell that floats internal nodes to drastically reduce leakage. This and other innovative solutions are being examined and tested.