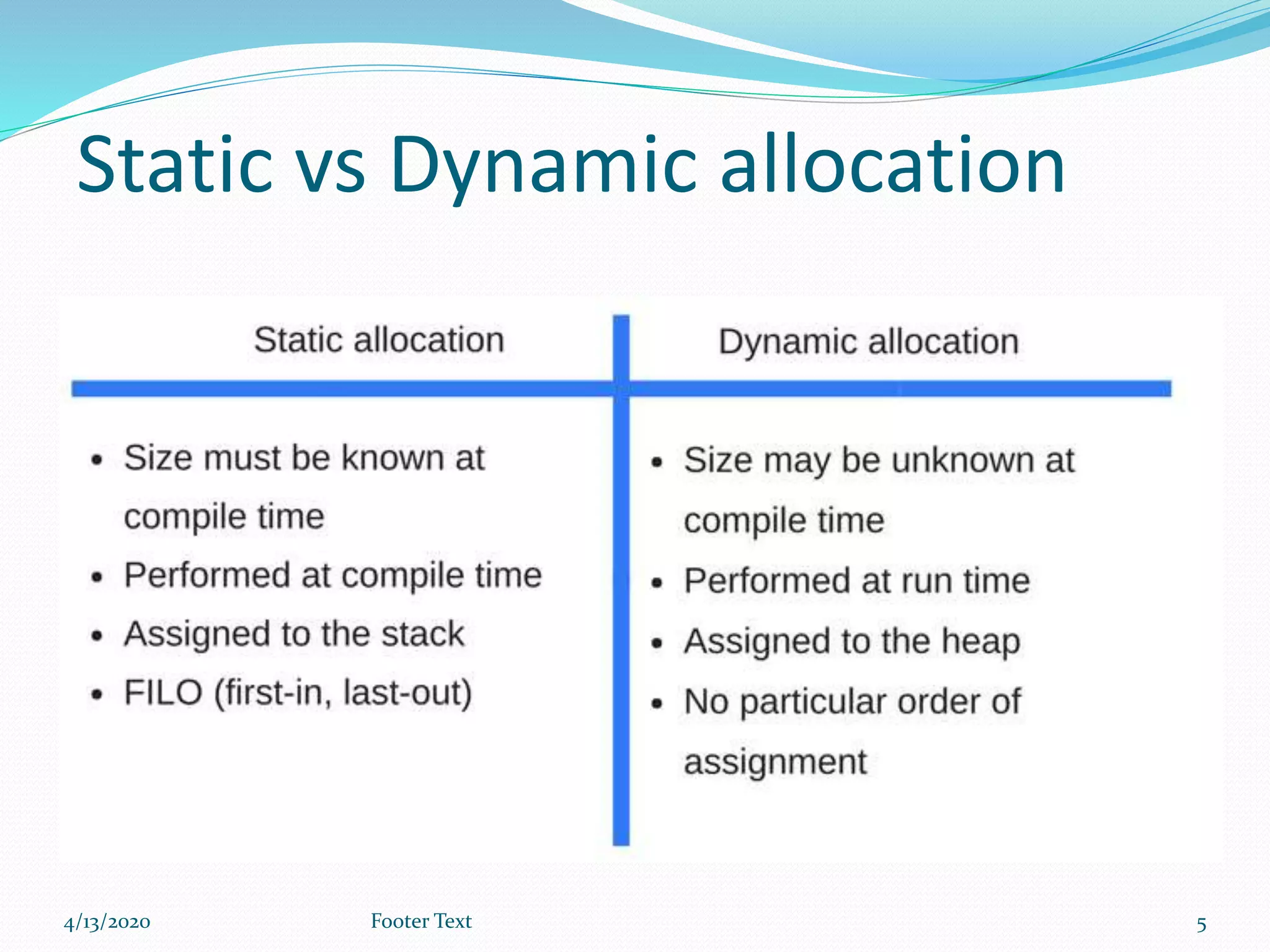
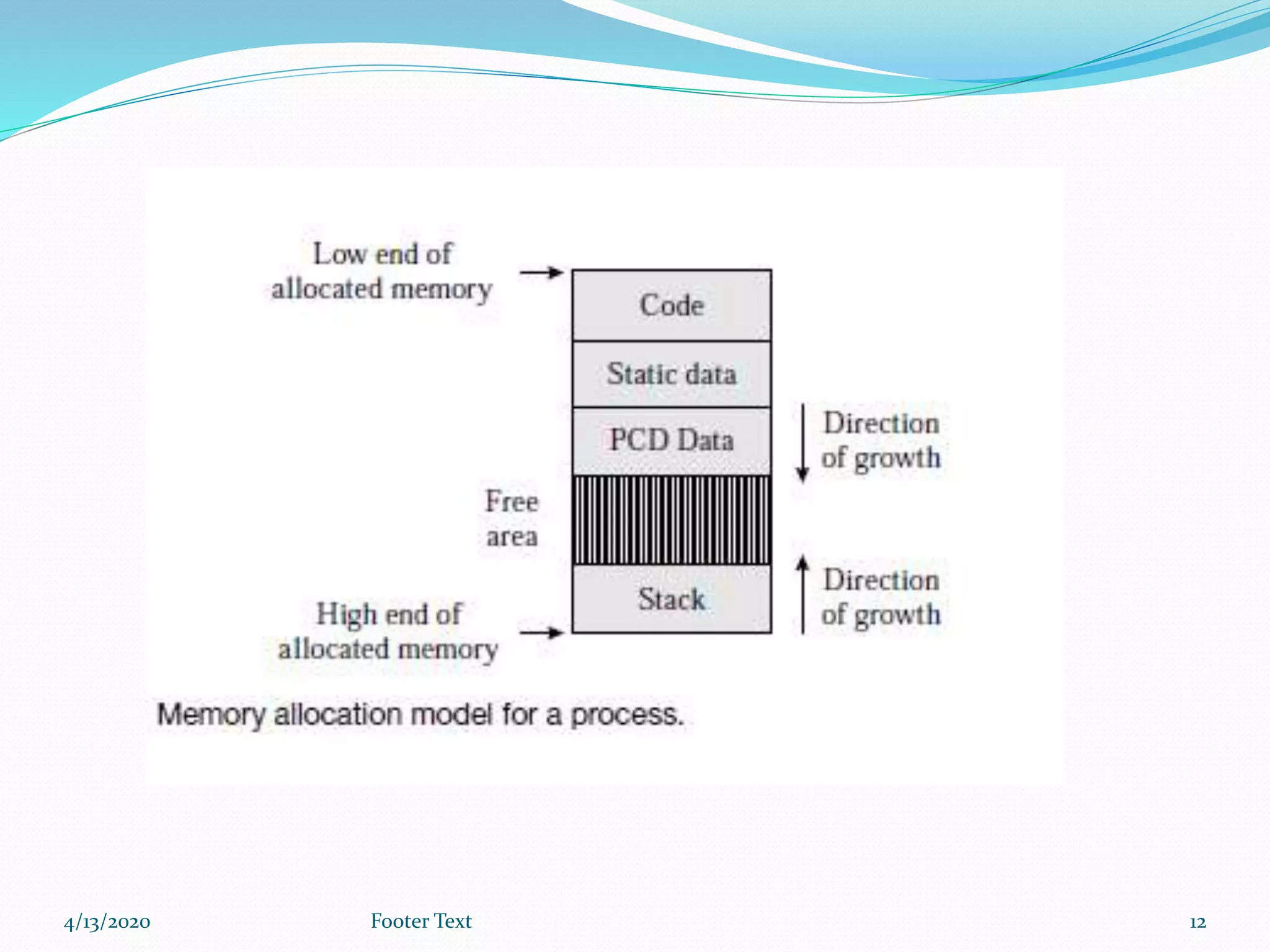
The document provides an overview of memory allocation in programming, outlining its two main types: static and dynamic memory allocation. It explains how memory is assigned during runtime and details stack-based and heap-based memory allocation methods, including the behaviors and structures associated with each. Finally, it describes how the operating system manages memory allocation when creating processes for executing programs.